Updated March 8, 2023

Introduction to C++ Commands
C++ is an object-oriented language which was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup. It is a middle level; language which supports both high level and low-level language features. It is considered to be a superset of C and which supports all features of C language. It provides all object-oriented programming features like encapsulation, data hiding, inheritance, and polymorphism. It also has all standard libraries which act as the building block. Let us have a look at the basics and slowly move towards the advanced functions that C++ Command provides.
Basic C++ Commands
The basic commands are as follows.
1. #define
This C++ Command can be used to substitute a particular value throughout the file in which it is located. This helps the compiler to go through the entire file and replaces the name of that macro which was created with the value which was defined. The replacement of this string stops at the end of the line.

2. #error
This Command helps in displaying the error message which is defined and indicates the compiler to stop when this command is encountered. When the compiler comes across this command then the compiler displays the line number and message which is mentioned. This helps the programmer in debugging easily.
![]()
3. #include
This includes Command helps in including the mentioned files in the code and making use of those. It can be used in two ways:
- #include <filename>
- #include “filename”
When angular brackets are used when a file needs to search or include through the standard library directories. When there are quotes specified then it indicates that this filename needs to be searched in the current directory.

4. #pragma
By making use of this C++ command the programmer has the capability to let the compiler know of what different things are to be done. #pragma is usually implementation specific and its use can vary from one compiler to another. There are different options which can be used and one can be to trace the program execution.

5. #line
This C++ Command is used to change the value of __LINE__ and __FILE__ variables. These variables display the current file and also the line from which it is being read.
![]()
6. #if
This Command helps in specifying conditions that are to be followed. It enables the user to simply apply logic control and if the condition is true then the code will immediately follow the command that will be compiled.
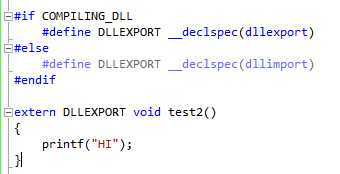
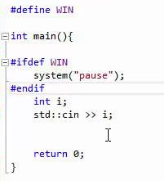
7. #ifdef
This C++ Command is useful to check if a macro has been defined by #define statement or not. If it is already defined hen it executes the next statement that follows.
8. Cout
When a user wants to print some text or value of any variable that was defined previously then cout is used. It displays all values on the screen.

9. Cin
In order to accept the value from the user and assign it to a particular variable, the developer must make use of cin variable. Any value can be accepted from the user and assigned to the variable of any data type that is created.

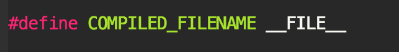
10. __FILE__
This variable helps in representing the current file that is being processed. It can be defined and use in the entire code and used.
Intermediate C++ Commands
Following are the C++ commands which should be understood on an intermediate level.
1. Variable definition
A variable can be defined and lets the compiler know about where to create a variable. It also lets the compiler know how much storage is required. This definition needs a specific data type and also can contain a list of one or more variables which can follow the data type. The data type can be char, int, float, double, bool, etc.
2. Lvalue and Rvalue
The value expressions can be referred to any memory location which is called ‘lvalue’. It can appear on either left hand or right-hand side of the assignment. Rvalue is used when the data value stored at an address in the memory. It cannot have a value which can be assigned to it and it will appear on the right-hand side of the assignment.
3. Scope of Variables
The scope of variables can be either local or global. If the scope is local then it is accessible only in the function or block where the variables are defined. If the variables are defined outside all functions then they are global and can be accessed anywhere in the code.
4. Literals
Literals can be defined as the values which a program cannot alter. These can be constants which can be divided into Integer Numerals, Floating-Point Numerals, Characters, Strings, and Boolean Values.
5. Modifiers
A modifier can be used to change the meaning of the base data type and use it more precisely in different situations. The data modifiers are: signed, unsigned, long and short. These can be applied to integer base types.
6. Qualifiers
Qualifiers provide extra information regarding the variables which they precede. C++ provides three of these. Namely, these are const, volatile and restrict.
7. Storage class
This defines the scope and lifetime of variables that are present within a function. The storage classes that are provided by C++ are auto, register, static, extern and mutable.
8. Operators
This C++ Command provides all operators which are supported by C. to name a few, it supports Arithmetic Operators, Relational Operators, Logical Operators, Bitwise Operators, Assignment Operators, and Misc Operators.
9. Loops
In order to perform tasks that are performed repeatedly C++ has provided looping functions. These help in performing a set of instructions repeatedly until a specific condition is met. These loops are while, for, do..while and nested loops.
10. Arrays
An array is a data structure which is used to store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements which belong to the same type. An array stores a collection of data and is used as variables of the same type.
Advanced C++ Commands
Following is the advanced commands mentioned below.
1. C++ Files
To work with files, C++ provides the fstream library. It has three new data types – of stream, stream, and fstream. Using these it can be specified in the data type is output file stream, input file stream or any file stream respectively
2. Exception Handling
In order to handle the errors that occur at run time, C++ provides exception handling mechanism. It has tried, catch and throw blocks. Using these all exceptions that occurred can be handled.
Tips and Tricks
- Do not get confused between the assignment operator (=) and for equality operator (==).
- Make use of ‘using’ statement when you are working with smaller programs.
- Do not make use of global variables except for communication between functions
- Make use of Local variables with for statement
- Make as much use of classes and objects as possible.
Conclusion
Hence using C++ Command is very beneficial as it is an object-oriented language. It helps in inheritance and as a result, reusing of code. C++ provides all functions of C along with these functionalities. It is very important to learn C++ Command as a base for learning other object-oriented languages.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to C++ Commands. Here we have discussed concept, basic, intermediate as well as advanced C++ Commands along with tips and tricks. You may also look at the following article to learn more –


