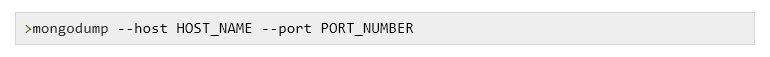Introduction to MongoDB Commands
MongoDB is a cross-platform, document-oriented, open-source database management system with high availability, performance, and scalability. MongoDB, a NoSQL database, finds extensive use in big data applications and other complex data processing tasks that do not align well with the relational database model. Instead of using the relational database notion of storing data in tables, MongoDB architecture is built on collections and documents. Here we discuss the MongoDB commands.
Why MongoDB Commands?
- It can easily control global data, ensuring fast performance and compliance.
- It provides a flexible data model. This goes with the case where the app needs to be built from scratch or the case of updating a single record.
- Scaling the application ensures that there is no downtime.
Features
- MongoDB command uses a master-slave replication concept. To prevent database downtime, this replica feature is essential.
- This database can run over multiple servers; various servers duplicate the data. The result of which it’s a significant advantage in case of hardware failure.
- MongoDB command comes with the auto-sharding feature, which distributes data across multiple physical partitions known as shards. The result of which automatic load balancing happens.
- It’s schema-less. Hence more efficient.
Basic of MongoDB Commands
1. Create database
In MongoDB use, DATABASE_NAME is used to create a database. If this name database doesn’t exist, it will get created, and else it will return the existing one.
To check the current database now:
By default, the MongoDB command comes with the database name “test.” Suppose you inserted a document without specifying the database; MongoDB will automatically store it in a “test” database.
2. Drop Database
If the database is not specified, it will delete the default database, “test.”
3. Create Collection
To create a collection, the MongoDB command used is: db.createCollection(name, options)
Here, the name is the Collection’s name & options are a document used to specify the Collection’s configuration. Though the “Options” parameter is optional, it’s good to provide it.
4. Drop Collection
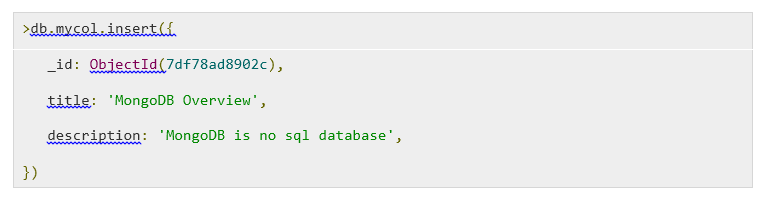
5. Insert Document
To insert data into a database collection in MongoDB, you can use the “insert()” or “save()” method.
Here “mycol” is the collection name. If the Collection doesn’t exist, then the MongoDB command will create the database collection, which will be inserted.
6. Query Document
Querying Collection is done by the find() method.
As the find() method will show the findings in a non-structured way, a structured pretty() method is used to get the results.
Intermediate MongoDB Commands
1. Limit()
This MongoDB command limits the no. of records need to use in MongoDB. The argument of this function accepts only number types. The argument is the number of the Document that needs to be displayed.
2. Sort()
This is to the records of MongoDB. 1 & -1 are used to sort the documents. 1 is for ascending, whereas -1 is for descending.
3. Indexing is the concept that helps MongoDB to scan documents in an inefficient way
Advanced Commands of MongoDB
1. Aggregate ()
This MongoDB command helps process the data, which returns the calculated result. This can group values from multiple documents together.
2. Replication
Replication in MongoDB is achieved using a replication set. A replica set is a group of MongoDB processes with the same dataset. Replica set provides:
- High availability
- Redundancy hence faults tolerant/disaster recovery.
In replica, one node is the primary node, and the rest are the secondary node. All write operations remain with the primary node.
Let’s see; you can convert a standalone MongoDB instance into a replica set.
Here are the steps for that:
Close is already running the MongoDB server.
Now Start the MongoDB server by specifying — replSet option.
Syntax:
3. Create & restore Backup
To create the Backup, the mongodump command is used. The server’s data will be dumped into a dump directory(/bin/dump/). Options are there to limit the data.
To restore a backup in MongoDB, you would use the “mongorestore” command.
4. Monitor Deployment
To check the status of all your running processes/instances, a mongostat command is helpful. It tracks and returns the counter of database operations. These counters include inserts, updates, queries, deletes, and cursors. This MongoDB command is beneficial as it shows your status about low running memory, some performance issues, etc.
You must go to your MongoDB installation bin directory and run mongostat.
Tips and Tricks to Use MongoDB Commands
- Pre-allocate space: When you know your Document will grow to a certain size. This is an optimization technique in MongoDB. Insert a document and add a garbage field.
- Try fetching data in a single query.
- As MongoDB is, by default, case sensitive.
Example:
db.people.find({name: ‘Russell’}) &
db.people.find({name: ‘russell’}) are different.
While performing a search, it’s a good habit to use regex. Like:
db.people.find({name: /russell/i})
- Prefer Odd No. of Replica Sets: Using replica sets is an easy way to add redundancy and enhance read performance. All nodes replicate the data, and it can be retrieved in case of a primary node failure. They vote amongst themselves and elect a primary node. Using the odd number of the replica will make voting more accessible in case of failure.
- Secure MongoDB using a firewall: As MongoDB itself doesn’t provide any authentication, it’s better to secure it with a firewall and mapping it to the correct interface.
- No joins: MongoDB, a NoSQL database, does not support joins. One must write multiple queries to retrieve data from more than two collections. Writing queries can become hectic if the schema is not well organized. This may result in the re-designing of the schema. It’s always better to spend some extra time to design a schema.
Conclusion
MongoDB commands are the best practice solution to maintain high availability, efficient and scalable operations, which is today’s business demand.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to MongoDB commands. Here we have discussed basic, intermediate, and advanced MongoDB commands and tips and tricks to use those commands. You may also look at the following article to learn more –