Updated June 9, 2023
Introduction to HBase Commands
HBase Command is an Open-source Framework. It runs on the Hadoop file-distributed System (HDFS) used to store sparse data sets. The key components of HBase are Zookeeper, Region, and HBase Master. Hbase consists of an active HBase Master server and one Region Server. Hmaster is responsible for monitoring the all-region server in a cluster. Hbase automatically partitions regions. Regions are stored in a file in a distributed manner. They provide random read and write operations on large datasets. They are horizontally scalable (any no. of columns can be added), and two critical structures of HBase are row and column keys, respectively.
Basic HBase Commands (Operational Commands) are
After base Installation, interactive shell to execute commands:
Data Definition Language / Data Manipulation Commands
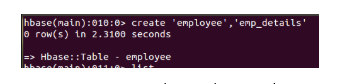
- Create: It creates a new table.
- Put: Inserts a new tuple into the record.
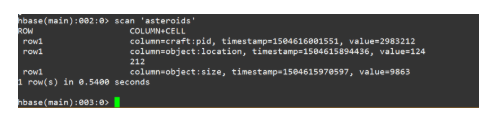
- Scan: It returns the data stored in the table.
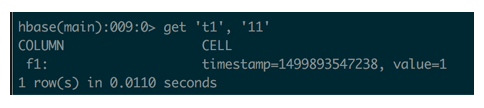
- Get: It returns the record.
- Help: List all the commands.
base(main): 020:0> list’ namespace name: mydb’
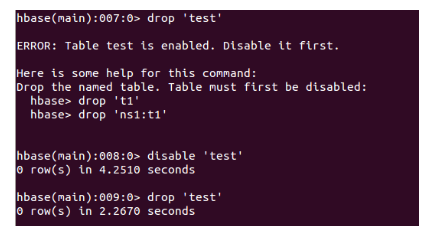
- Drop: To delete a specific cell in a table.
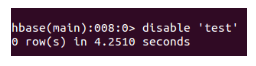
- To disable the table:
Syntax: disable ‘dataTable.’
- Updating data: A new column value set for the same row key is created to update the column. No Update keyword is used here.
Example: Update dataTable(row key 112) to change the rating to ‘8’:
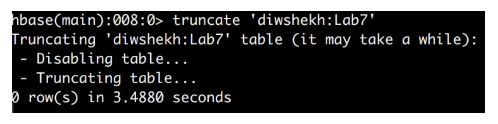
- Truncate: This command keeps the schema but not the records.
Syntax: hbase> truncate <tablename>
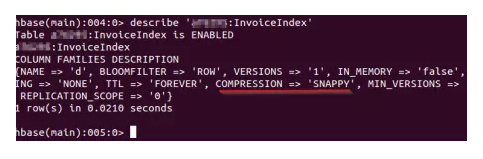
- Describe: Used to describe the Existing namespace.
The above output screenshot gives the following explanations:
Scanning table ‘invoice’ with attributes RAW=>true, VERSIONS=>0.
Displaying rows with column families and values in the table.
It displays random output not in the same order as the values inserted in the table
Intermediate Hbase Commands
- Create: They are used to create a table in HBase.
example: create ‘table name,’ <column family>’
- disable: It is used to disable a created table.
example: Hbase> disable ‘table name’
- is_disabled: This command verifies whether a table has been disabled.
example: hbase> is disabled ‘table name.’
1. Security Commands
Users utilize the following Hbase commands to ensure the security of the database by preventing unauthorized access.
- Grant: This command gives the right permission access to read, write, and execute.
example: hbase>grant< username> <permissions>[<tablename> [col name]
- Revoke: This command is used to revoke user access to a table.
example:hbase> revoke<user>
- User_permissions: This command list all the access given to the table
example: hbase> user_permission’ table name.’
2. Cluster Replication Commands
Cluster setup in HBase involves executing commands to add or stop the replication of clusters.
- Add peer: to add peer to clusters to replicate the data
example: hbase>add_peer ‘4’, zk4, zk5, zk6, zk7:/hbase-prod
- Start_replication: deletes all the metadata information on the peer.
example:hbase>start_replication
- Stop replication: Stops all the replication process
example:hbase>stop_replication
3. Configuring Table commands
- pme_config: This command is used to get a table’s deployment status and configuration. They write the configuration to HBase/HDFS.
- pme_dump: This command helps with debugging and troubleshooting. They output the information on the table.
- pme_set_autocompare: This command temporarily sets the autocomparerecords configuration property for the PME table.
- pme_set_autoderive: This command temporarily sets the autoderiverecords configuration property for the PME table.
- pme_set_autolink: This command sets the autolinkrecordsconfiguration property temporarily for the identified PME table.
- pme_disable_all: This command Disables all tables in HBase that are pme_enabled.
Advanced HBase commands
Let’s go over some of the commands listed below:-
Hbase Namespace Commands
A namespace is a logical grouping of tables; users share access to the table but with different privileges.
There are six namespace commands they are:
- Create_namespace: They are used to create a new namespace.
base(main): 019:0> create ‘namespace name:mydb,’ ‘cf’
0 row(s) in 2.3760 seconds=>
Hbase:: Table – ‘namespacename:mydb
- List namespace: They list the no.of rows in the namespace.
- Load Test Tool: They test the cluster by performing read/write.
Example: Hbase: ltt -h
- wal: To get a list of Wal files.
Example: hbase wal
wal <filename> [-h] [-j] [-p] [-r]
where -h output help message
-j output Json
-p Print values
-r region to filter
- Clean: This command removes all hbase-related information from HDFS.
- Alter Namespace: They alter the created namespace in HBase.
Example: base clean hbase(main): 046:0> alter_namespace ‘name2’, {METHOD => ‘set’, ‘PROERTY_NAME’ => ‘PROPERTY_VALUE’}
- Describe Namespace: They describe the existing namespace in Hbase.
Example: hbase(main):047:0> describe_namespace ‘name3’
DESCRIPTION
{NAME => ' namespace name ', PROERTY_NAME => 'PROPERTY_VALUE'}
- Hbase Snapshot:
They allow us to take a copy of a table and export it to another cluster. IBM Cloud Object Storage is a suitable option for storing it.
Example: base org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.Export test cos://mysql.my
- Delete a snapshot
example: hbase shell>> delete _snapshot ‘ snapshot name’
- View Snapshot info
example: hbase shell>> snapshot_info snapshot name
Tips and Tricks To use HBase commands
Online analytical experts favor HBase because of its robust capabilities for accessing data through random reads and write. Representing the logical arrangements of a row in a base table is very important. Rows are stored as row keys. The row key can directly access any row. We can use HBase Shell (Command-line interface) to create an Hbase table, add rows, scan the complete table, and apply filters that filter rows based on specific constraints. Consider significant factors while creating a table design. They are Column families, rows, versions, and read/write schemas. When creating a table design in HBase, the base uses no data types and stores everything as a byte array.
Additionally, HBase does not support transactions. We can interact with HBase in two ways: either using Java API or HBase Shell. Increasing the request handler thread count can instantly sustain the capacity of the HBase cluster.
Conclusion
HBase shell and general commands give appropriate information about different data manipulation types, table management, and cluster replication commands. These commands allow you to perform multiple functions on tables in HBase. Hive combines with HBase to execute SQL queries, but their schemas lack adaptability. HBase clusters are backed up by full cluster shutdown; on a live cluster, they have automatic failover support.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to HBase Commands. Here we have discussed basic, advanced, and some immediate HBase commands. You may also look at the following article to learn more –