Difference Between Small Data vs Big Data
Small Data is nothing but data that are small enough comprehensive for humans in a volume and also for formatting, which makes it accessible, informative, and actionable. Traditional data processing cannot deal with large or complex data; these data are called Big Data. When Data volume grows beyond a specific limit, traditional systems and methodologies are insufficient to process data or transform data into a valid format. This is why data is generally categorized into small data vs big data.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Small Data vs Big Data (Infographics)
Below is the top 10 difference between Small Data vs Big Data:
Key Differences Between Small Data vs Big Data
The differences between Small Data vs Big Data are explained in the points presented below:
- Data Collection – Usually, Small Data is part of OLTP systems and collected in a more controlled manner and then inserted into the caching layer or database. Databases will have read replicas to support immediate analytics queries if needed. The Big Data collection pipeline will have queues like AWS Kinesis or Google Pub/Sub to balance high-velocity data. Downstream will have streaming pipelines for real-time analytics and batch jobs for cold data processing.
- Data Processing – Since the transaction system generates the majority of Small Data, analytics on top of it will generally be batch-oriented. In some rare cases, analytics queries run directly on top of transaction systems. Big Data environments will have both batch and stream processing pipelines. A stream is used for real-time analytics like credit card fraud detection or stock price prediction. Batch processing implements complex business logic with data and advanced algorithms.
- Scalability – Small Data systems typically scale vertically. Vertical scaling increases system capacity by adding more resources to the same machine. Vertical scaling is costly but lesser complex to manage. Big Data systems mainly depend on a horizontally scalable architecture, which gives more agility at a lesser cost. Pre-emptive virtual machines in the cloud make horizontally scalable systems even more affordable.
- Data modeling – Transaction systems typically generate Small Data that is normalized. ETL(Extract Transform Load) data pipelines convert it into star or snowflake schema in a data warehouse. Here schema is consistently enforced while writing data which is relatively easy as data is more structured. As mentioned above, tabular data is only a fraction of Big Data. Here data is replicated much more for various reasons like failure handover or due to some limitation of the underlying database engine(For example, some databases only support one secondary index per dataset). A schema is not enforced when writing. Instead, a schema is validated while reading data.
- Storage & Computation Coupling – In traditional databases that mainly handle Small Data, storage and computing are tightly coupled. Inserting and retrieving data to and from the database is only possible through the given interface. You cannot put data directly into the database filesystem or query existing data using other DB engines. This architecture greatly helps to ensure data integrity. Big Data systems have a very loose coupling between storage and computing. Typically, organizations store data in a distributed data storage system like HDFS, AWS S3, or Google GCS, then select a compute engine to query the data or perform ETL later. For example, interactive queries might be executed using Presto(Link) and ETL using Apache Hive on the same data.
- Data Science – Machine learning algorithms require input data in a well-structured and adequately encoded format. Most of the time, input data will be from transactional systems like a data warehouse and Big Data storage like a data lake. Machine learning algorithms running solely on Small Data will be easy as the data preparation stage is narrow. Preparing and enriching data in the Big Data environment takes much more time. Big Data gives many options for data science experimentation due to the high volume and variety of data.
- Data Security – Security practices for Small Data reside on enterprise data warehouses or transaction systems provided by corresponding database providers that might include user privileges, data encryption, hashing, etc. Securing Big Data systems are much more complicated and challenging. Security best practices include encrypting data at rest and transit, isolating cluster networks, strong access control rules, etc.
Small Data vs Big Data Comparison Table
Below are the points describing the comparisons between Small Data vs Big Data.
| Basis of Comparison | Small Data | Big Data |
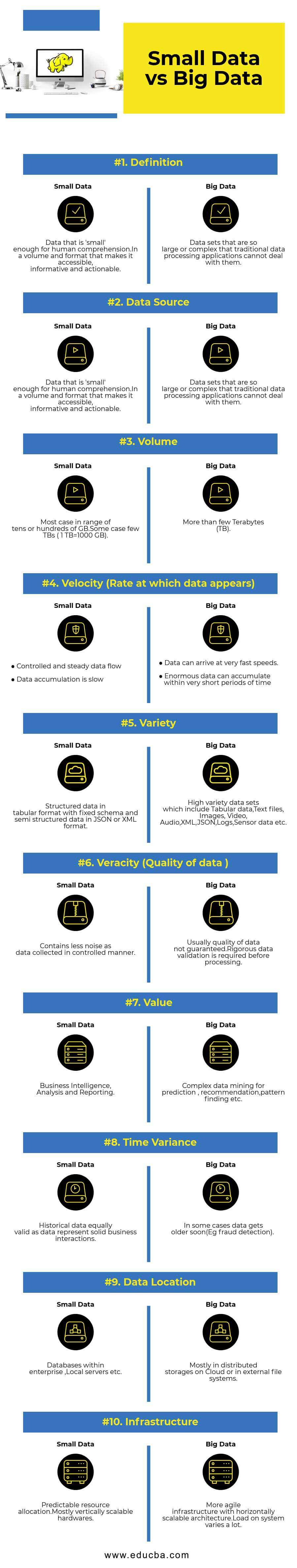
| Definition | Data that is ‘small’ enough for human comprehension.In a volume and format that makes it accessible, informative, and actionable. | Data sets that are so large or complex that traditional data processing applications cannot deal with them. |
| Data Source |
|
|
| Volume | Most cases are in a range of tens or hundreds of GB.In some cases, few TBs ( 1 TB=1000 GB). | More than a few Terabytes (TB). |
| Velocity (Rate at which data appears) |
|
|
| Variety | Structured data in tabular format with fixed schema and semi-structured data in JSON or XML format. | A high variety of data sets includes Tabular data, Text files, Images, Video, Audio, XML, JSON, Logs, Sensor data, etc. |
| Veracity (Quality of data ) | Collecting data in a controlled manner results in less noise in the data. | One cannot guarantee data quality and thus requires rigorous data validation before processing. |
| Value | Business Intelligence, Analysis, and Reporting | Complex data mining for prediction, recommendation, pattern finding, etc. |
| Time Variance | Historical data is equally valid as data represent solid business interactions. | Sometimes, data gets older soon(Eg, fraud detection). |
| Data Location | Databases within an enterprise, Local servers, etc. | Mostly in distributed storage on cloud or external file systems. |
| Infrastructure | Predictable resource allocation.Mostly vertically scalable hardware. | More agile infrastructure with a horizontally scalable architecture. The load on the system varies a lot. |
Conclusion
The ultimate goal of data analysis is to get timely insights to support decision-making. They are categorizing data into Small and Big to help tackle challenges in analyzing data of each world separately with proper tools. The line between the two categories varies with emerging advanced data processing systems, which makes even big data querying much faster and less complex.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Small Data vs Big Data. Here we have discussed Small Data vs Big Data head-to-head comparison, key differences, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


