Difference Between Big Data vs Data Science
The big data approach cannot be easily achieved using traditional data analysis methods. Instead, unstructured data requires specialized data modeling techniques, tools, and systems to extract insights and information as needed by organizations. Data science is a scientific approach that applies mathematical and statistical ideas and computer tools for processing big data. Data science is a specialized field that combines multiple areas such as statistics, mathematics, intelligent data capture techniques, data cleansing, mining, and programming to prepare and align big data for smart analysis to extract insights and information.
Currently, all of us are witnessing an unprecedented growth of information generated worldwide and on the internet resulting in the concept of big data. Data science is quite challenging due to the complexities of combining and applying different methods, algorithms, and complex programming techniques to perform intelligent analysis in large volumes of data. Hence, data science has evolved from big data, and data science is inseparable.
This concept refers to the extensive collection of heterogeneous data from different sources and is not usually available in standard database formats we are generally aware of. Big data encompasses all types of data, namely structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information that can be easily found online.
Big data includes:
- Unstructured data – Social networks, emails, blogs, tweets, digital images, digital audio/video feeds, online data sources, mobile data, sensor data, web pages, etc.
- Semi-structured – XML files, system log files, text files, etc.
- Structured data – RDBMS (databases), OLTP, transaction data, and other structured data formats.
Therefore, all data and information, irrespective of its type or format, can be understood as big data. Big data processing usually begins with aggregating data from multiple sources.
Figure: An example of data sources for big data.
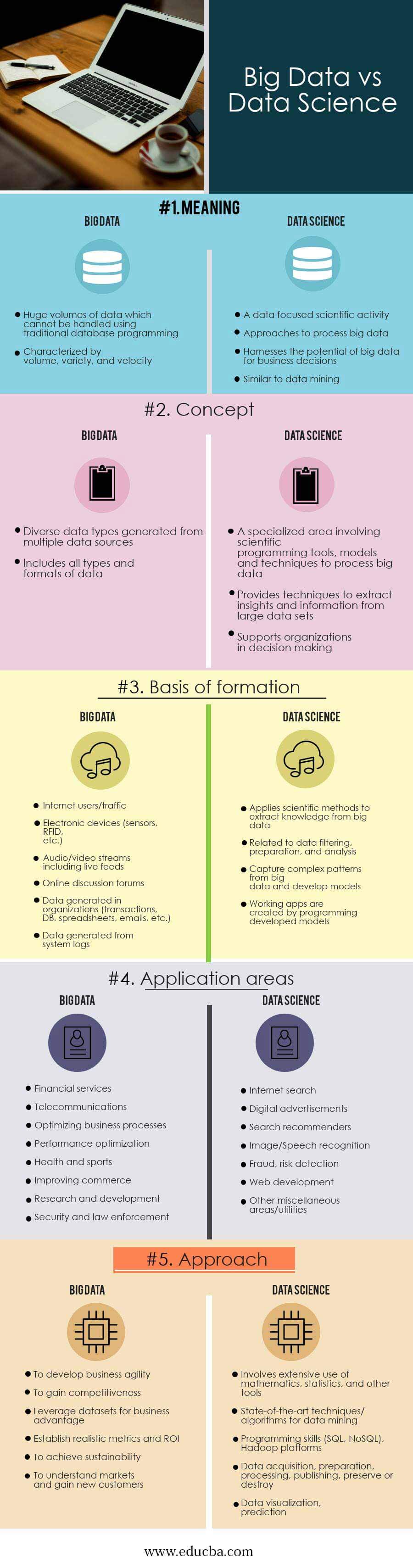
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Big Data vs Data Science (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 comparisons between Big Data vs Data Science:
Key Differences Between Big Data vs Data Science
Provided below are some of the main differences between big data vs data science concepts:
- Organizations need big data to improve efficiencies, understand new markets, and enhance competitiveness. In contrast, data science provides the methods or mechanisms to understand and utilize big data’s potential promptly.
- Currently, for organizations, there is no limit to the amount of valuable data that can be collected. Still, to use all this data to extract meaningful information for organizational decisions, data science is needed.
- Big data is characterized by its velocity variety and volume (3Vs), while data science provides the methods or techniques to analyze data characterized by 3Vs.
- Big data provides performance potential. However, it is a significant challenge to dig out insight information from big data to utilize its potential for enhancing performance. Data science uses theoretical and experimental approaches in addition to deductive and inductive reasoning. It takes responsibility to uncover all hidden insightful information from a complex mesh of unstructured data, thus supporting organizations to realize the potential of big data.
- Big data analysis performs the mining of useful information from large datasets. Contrary to analysis, data science uses machine learning algorithms and statistical methods to train the computer to learn without much programming to make predictions from big data. Hence data science must not be confused with big data analytics.
- Big data relates more to technology (Hadoop, Java, Hive, etc.), distributed computing, and analytics tools and software. This is opposed to data science which focuses on strategies for business decisions and data dissemination using mathematics, statistics, and data structures and methods mentioned earlier.
From the above differences between big data and data science, it may be noted that data science is included in the concept of big data. Data science plays a vital role in many application areas. Data science works on big data to derive valuable insights through predictive analysis, using results to make intelligent decisions. Therefore, data science is included in big data rather than the other way around.
Big Data vs Data Science Comparison Table
The table below provides the fundamental differences between big data vs data science:
| Basis for Comparison | Big Data | Data Science |
|
Meaning |
|
|
| Concept |
|
|
| Basis of formation |
|
|
| Application areas |
|
|
| Approach |
|
|
Conclusion
The emerging field of big data and data science is explored in this post. Big data is here to stay in the coming years because, according to current data growth trends, new data will be generated at 1.7 million MB per second by 2020, according to estimates by Forbes Magazine. This growth of big data will have immense potential and must be managed effectively by organizations. The area of data science is explored here for its role in realizing the potential of big data. Data science is evolving rapidly, with new techniques developed continuously, which can support data science professionals into the future.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Big Data vs Data Science. Here we discuss the head-to-head comparison, key differences, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –