Difference Between Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence is a technology used to gather, store, access, and analyze data to help business users make better decisions; on the other hand, Artificial Intelligence is a way to make a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or software that thinks intelligently like humans. Artificial Intelligence is based on the study of how human thinks, learn, decide, and work to resolve an issue and then use the outcome of this study as a basis for developing intelligent software and systems.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence (Infographics)
Below are the Top 6 Comparision Between Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence:
Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence Comparison Table
Following is the comparison table between Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence.
| Basis of Comparison | Artificial Intelligence | Business Intelligence |
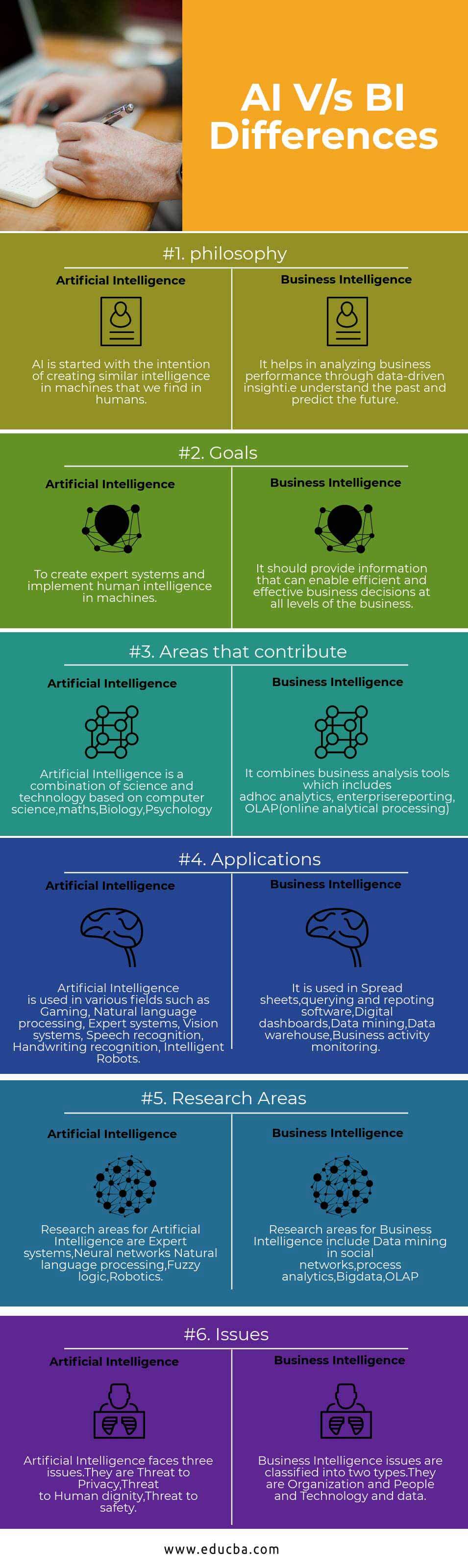
| Philosophy | AI started with the intention of creating similar intelligence in machines that we find in humans. | It helps analyze business performance through data-driven insight i.e. understanding the past and predicting the future. |
| Goals | To create expert systems and implement human intelligence in machines. | It should provide information that can enable efficient and effective business decisions at all levels of the business. |
| Areas that Contribute | Artificial intelligence combines science and technology based on computer science, maths, Biology, and Psychology. | It combines business analysis tools, including ad-hoc analytics, enterprise reporting, and OLAP(online analytical processing). |
| Applications | Artificial Intelligence is used in various fields, such as Gaming, Natural language processing, Expert systems, Vision systems, Speech recognition, Handwriting recognition, and Intelligent Robots. | It is used in Spreadsheets, querying and reporting software, Digital dashboards, Data mining, Data warehouse, and Business activity monitoring. |
| Research Areas | Research areas for Artificial Intelligence are Expert systems, Neural networks, Natural language processing, Fuzzy logic, and Robotics. | Research areas for Business Intelligence include Data mining in social networks, process analytics, Bigdata, and OLAP. |
| Issues | Artificial intelligence faces three issues. They are Threats to Privacy, Threat to Human dignity, and Threat to safety. | Business Intelligence issues are classified into two types. They are Organization and People and Technology and data. |
Algorithms in Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence
The Algorithms in Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence are explained below:
| Artificial Intelligence Algorithms | Business Intelligence Algorithms |
| Breadth-first search algorithm
It starts from the root node, explores neighbor nodes first, and moves to the next-level neighbor nodes. It provides the shortest path to the solution and can be implemented using FIFO. |
Decision Tree Algorithm
This extracts the predictive information as human-understandable rules, which can be if-then-else, leading to the predictive information. |
| Depth First Search Algorithm
This algorithm uses LIFO(Last in, first out)data structure. It creates nodes the same as breadth-first search but differs in only order. In each iteration, it stores the nodes from root to leaf and cannot check duplicate nodes. |
Naive Bayes
It makes predictions using the Bayes algorithm, which derives probability prediction from the underlying evidence, as observed in data. |
| Uniform Cost Search Algorithm
In this algorithm, sorting is done by increasing the path’s cost to a node. It continuously expands the least-cost node. This search is identical to the Breadth-first search if each transition has the same cost. It explores the path in the increasing order of cost. |
Generalized Linear Models
It implements logistic regression for the classification of binary targets and linear regression for continuous targets. It supports confidence bounds for prediction probabilities and confidence bounds for prediction. |
| Iterative Deepening Depth-first Search
It performs the depth-first search at level-1, starts over, then executes a complete depth-first search to level 2 and continues until it gets the solution. |
Minimum Description Length
It is an information-theoretic model selection principle. It assumes that the most simple, compact data representation is the best way to explain it. |
| Pure Heuristic Search
It expands nodes in the order of their Heuristic values. It creates two lists, a closed list for the already developed nodes and an open list for the created but unexpanded nodes. The shorter paths are saved, and longer paths are disposed of. |
K-Means Algorithm
A distance-based clustering algorithm partitions the data into a pre-determined number of clusters. Each cluster has a centroid. |
| Travelling Salesman Problem
In this algorithm, the main aim is to find a low-cost tour that starts from a city, visits all cities en route exactly once, and ends at the same city starting. |
Apriori Algorithm
It performs market-based analysis by discovering co-occurring items within a set. This algorithm finds rules with support greater than a specified minimum support and confidence greater than a specified minimum confidence. |
| Hill-Climbing Search
An iterative algorithm starts with an arbitrary solution to a problem and attempts to find a better solution by incrementally changing a single solution element. If that change produces a better solution, an incremental change is taken as a new solution. This process is repeated until there are no further improvements. |
Support Vector Machine
Distinct versions of SVM use different kernel functions to handle different types of data sets. Linear and Gaussian(non-linear) kernels are supported.SVM classification attempts to separate the target classes with the widest possible margin.SVM regression tries to find a continuous function such that the maximum number of data points lie within an epsilon-wide tube around it. |
| Other algorithms include Simulated annealing, Local beam search, A* Search, and Bidirectional search. | BI supports/uses Non-negative Matrix Factorization, class Support vector machine, Orthogonal Partitioning clustering, and Maximum Entropy. |
Integration of Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence and Business Intelligence are a perfect match. Artificial Intelligence and Business Intelligence are witnessed through AI-powered alerts, from basic threshold to advanced neural network alerts. They help a business stay in full control of key success factors by alarming them as soon as something occurs. Combined with innovative business dashboards, these AI advances will continue revolutionizing the business intelligence landscape. These businesses step away from the time-intensive process of digging through data to unearth trends and reacting to costly issues.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is at the center of a new enterprise to build a computational model of intelligence. The main assumption is that the intelligence of humans can be represented in terms of symbol structures and symbolic operations, which can be programmed in a digital computer. Business Intelligence allows groups within an organization to gain actionable insight from business data and leverage these insights to meet criteria. Business Intelligence solutions offer business focussed analysis at a scale, complexity, and speed i.e., not achievable with basic operational systems reporting or spreadsheet analysis, thereby delivering significant value.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence. Here we have discussed Artificial Intelligence vs Business Intelligence head-to-head comparison, key differences, and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –