Updated April 26, 2023
Difference Between Apache Storm vs Kafka
Apache Kafka handles a large amount of data in a fraction of a second. It is a distributed message broker which relies on topics and partitions. Apache Storm is a fault-tolerant, distributed framework for real-time computation and processing of data streams. It takes the data from various data sources such as HBase, Kafka, Cassandra, and many other applications and processes the data in real time. It has been written in Clojure and Java.
Let us study more about Apache Storm vs Apache Kafka in detail:
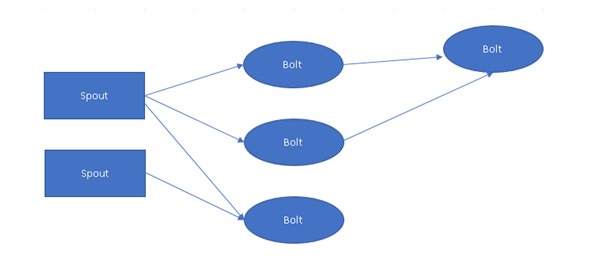
Figure 1, Basic Stream Processing Diagram of Apache Storm
In Figure 1, Basic stream processing is carried out. Spout and Bolt are two main components of Apache Storm, and both are part of Storm Topology, which takes the data stream from data sources to process it.
Topology: Storm topology is the combination of Spout and Bolt. It is the same as the Map and Reduces in Hadoop.
Stream: Stream can be considered as Data Pipeline. It is the actual data that we received from a data source.
Spout: Spout receive data from different-different data sources such as APIs. It continuously receives data from data sources and sends it to Bolt for processing.
Bolt: It is a logical processing unit that takes data from Spout and performs logical operations such as aggregation, filtering, joining & interacting with data sources and databases.
Apache Kafka: Provides real-time data streaming. It takes the data from different websites such as Facebook, Twitter, and APIs and passes the data to any different processing application (Apache Storm) in a Hadoop environment.
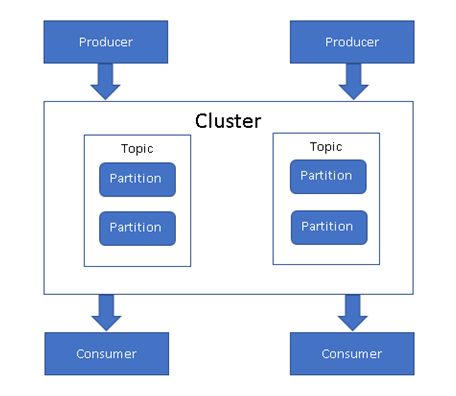
Figure 2, Architecture and components of Apache Kafka.
Kafka stores messages/data which it receives from different data sources called “Producer.” Once it gets the data, it partitions the messages through “Partition” within different “Topic.”
Kafka Cluster is a combination of Topics and Partitions. The Partitions index and stores the messages. The consumer takes the messages from partitions and queries the messages. Apache Kafka can be used with Apache HBase, Apache Spark, and Apache Storm.
The following APIs handle all the Messaging (Publishing and Subscribing) data within Kafka Cluster.
- Producer API: It permits the application to publish the stream of records.
- Consumer API: This API is being used to subscribe to the topics.
- Stream API: This Stream provides the result after converting the input into the output stream.
- Connector API: This links the topics with existing applications.
The main use of Apache Kafka is for Website Activity Tracking, Metrics, Log Aggregation, Event Sourcing, and other live data stream capturing. It is good for streaming and reliably gets data between applications or systems.
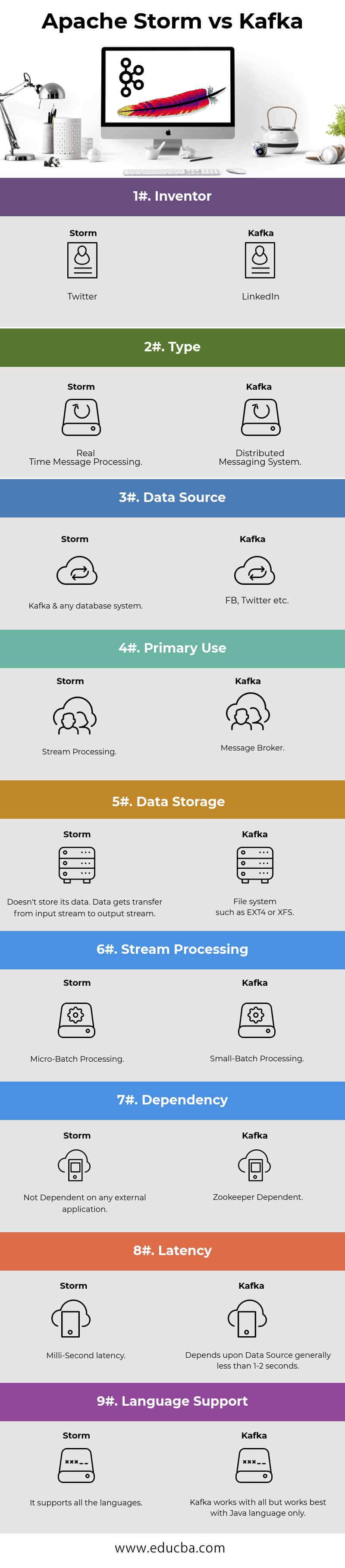
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Apache Storm vs Kafka (Infographics)
Below are the Top 9 Differences between Apache Storm vs Kafka:
Key Differences Between Apache Storm vs Kafka
Following is the key difference between Apache Storm vs Kafka:
- Apache Storm ensures complete data security, while in Kafka, data loss is not guaranteed, but it’s very low, like Netflix achieved 0.01% of data loss for 7 Million message transactions per day.
- Kafka can store its data on a local filesystem, while Apache Storm is just a data processing framework.
- Storm works on a Real-time messaging system, while Kafka used to store incoming messages before processing.
- Apache Kafka is used for processing real-time data, while Storm is used for transforming the data.
- Kafka gets its data from the actual data source, while Storm pulls it from Kafka itself for further processes.
- Kafka is an application to transfer real-time application data from one source application to another, while Storm is an aggregation & computation unit.
- Kafka is a real-time streaming unit, while Storm works on the stream pulled from Kafka.
- It’s mandatory to have Apache Zookeeper while setting up the Kafka another side; Storm is not Zookeeper dependent.
- Kafka works as a water pipeline that stores and forwards the data, while Storm takes the data from such pipelines and processes it further.
- Kafka is a great data source for Storm, while Storm can process data stored in Kafka.
- Apache Storm has an inbuilt feature to auto-restart its daemons, while Kafka is fault-tolerant due to Zookeeper.
Apache Storm vs Kafka Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Apache Storm vs Kafka.
| Comparison Points | Storm | Kafka |
| Inventor | ||
| Type | Real-Time Message Processing | Distributed Messaging System |
| Data Source | Kafka & any database system | FB, Twitter, etc. |
| Primary Use | Stream Processing | Message Broker |
| Data Storage | Doesn’t store its data. Data gets transferred from the input stream to the output stream. | File systems such as EXT4 or XFS. |
| Stream Processing | Micro-Batch Processing. | Small-Batch Processing. |
| Dependency | Not Dependent on any external application. | Zookeeper Dependent. |
| Latency | Milli-Second latency. | Depending upon Data Source, it generally takes less than 1-2 seconds. |
| Language Support | It supports all languages. | Kafka works with all but works best with Java language only. |
Conclusion
Apache Storm vs Kafka are independent and have different purposes in the Hadoop cluster environment. Apache Storm vs Kafka are both independent of each other. However, it is recommended to use Storm with Kafka as Kafka can replicate the data to Storm in case of packet drop. Also, it authenticates before sending it to Storm. Kafka’s role is to work as middleware. It takes data from various sources, and Storms processes the messages quickly. Counting and segregating online votes is the real-time example for Apache Storm. Apache Storm vs Kafka both have excellent capability in real-time data streaming and are very capable systems for real-time analytics.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Apache Storm vs Kafka. Here we have discussed Apache Storm vs Kafka head-to-head comparison, key differences, and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –