Updated October 10, 2023
Introduction to Raspberry Pi
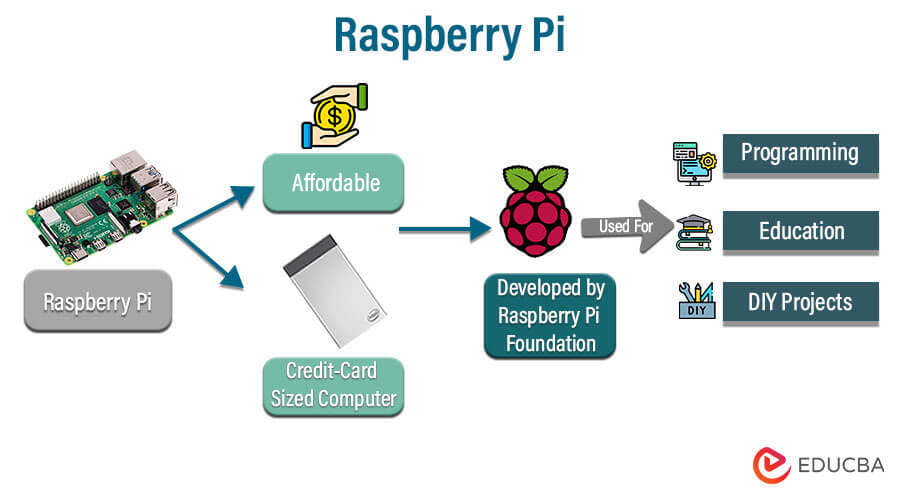
Raspberry Pi is a series of SBCs (Single Board Computer) founded by the Raspberry Pi Foundation in 2008. It aimed initially at teaching coding to children. Hence, we developed a solution with a low-cost, credit-card-sized computer to inspire children and make it more accessible. It is a computer that plugs into a computer monitor or TV and uses a standard keyboard and mouse. Learning programming languages like Scratch and Python is beneficial. It can do everything and anything similar to a desktop computer or laptop, right from browsing the internet, playing high-definition videos, making word-processing, spreadsheets, and playing games.
It can communicate with the outside world and has been helpful in a broad array of digital projects, right from parent detectors and music machines to weather-tweeting birdhouses and stations with infrared cameras. So, as a whole, Rpi is to learn to do home automation, programming skills, build hardware projects, and even use them in industrial applications.
Table of Contents
Generations of Raspberry Pi
| Generation | Models | Release Year | RAM | GPU | USB Ports | Ethernet | Wi-Fi & Bluetooth | Display Outputs | GPIO Pins |
| First Generation | Raspberry Pi 1 Model A | 2012 | 256 MB | VideoCore IV | 1 x USB 2 | No | No | HDMI, Composite | 26 |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B | 2012 | 512 MB | VideoCore IV | 2 x USB 2 | 10/100 Mbps | No | HDMI, Composite | 26 | |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+ | 2014 | 256 MB | VideoCore IV | 1 x USB 2 | No | No | HDMI, Composite | 40 | |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+ | 2014 | 512 MB | VideoCore IV | 4 x USB 2 | 10/100 Mbps | No | HDMI, Composite | 40 | |
| Second Generation | Raspberry Pi 2 Model B | 2015 | 1 GB | VideoCore IV | 4 x USB 2 | 10/100 Mbps | No | HDMI, Composite | 40 |
| Third Generation | Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | 2016 | 1 GB | VideoCore IV | 4 x USB 2 | 10/100 Mbps | 802.11n, Bluetooth 4.2 | HDMI, Composite | 40 |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ | 2018 | 1 GB | VideoCore IV | 4 x USB 2 | Gigabit | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 4.2 | HDMI, Composite | 40 | |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ | 2018 | 512 MB | VideoCore IV | 1 x USB 2 | No | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 4.2 | HDMI, Composite | 40 | |
| Fourth Generation | Raspberry Pi 4 Model B | 2019 | 2GB, 4GB, 8GB | VideoCore VI | 2 x USB 3 | Gigabit | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.0 | 2 x micro HDMI, Composite | 40 |
| Other Notable Models | Raspberry Pi Zero | 2015 | 512 MB | VideoCore IV | 1 x Micro | No | No | Mini HDMI, GPIO Header | 40 |
| Raspberry Pi Zero W | 2017 | 512 MB | VideoCore IV | 1 x Micro | No | 802.11n, Bluetooth 4.1 | Mini HDMI, GPIO Header | 40 | |
| Raspberry Pi Compute | 2017 | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | |
| Raspberry Pi 400 | 2020 | 4 GB | VideoCore VI | 2 x USB 3 | No | 802.11ac, Bluetooth 5.0 | 2 x micro HDMI | 40 | |
| Raspberry Pi Pico | 2021 | 2 MB Flash | No | 1 x USB 2 | No | No | No | 26 |
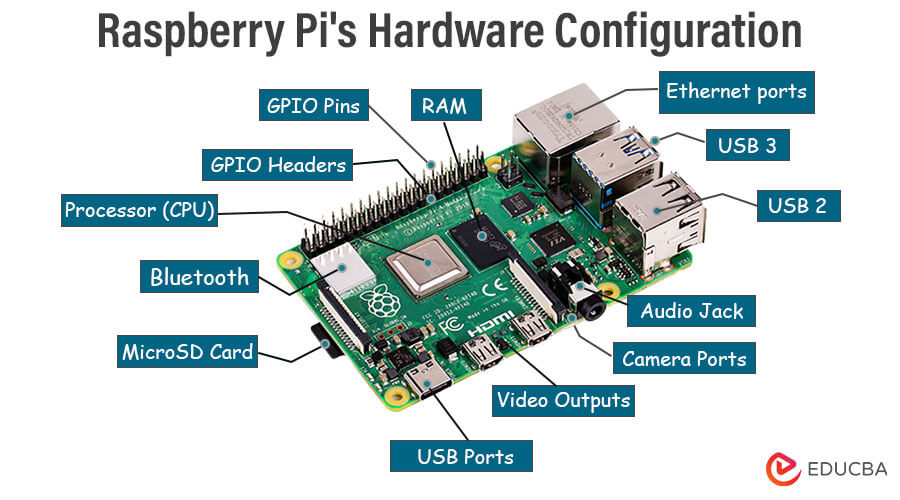
Raspberry Pi’s Hardware Configuration
The following is a list of the essential components that make up the hardware configuration of a typical Raspberry Pi board:
- Processor (CPU): An ARM-based CPU powers the Raspberry Pi, handling computing operations. The CPU’s performance and architecture vary between Raspberry Pi models, with computing power increasing from generation to generation.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): A Raspberry Pi’s GPU controls graphics rendering, video playback, and other multimedia functions. It helps offload graphical processing from the CPU, improving the board’s overall performance and multimedia capabilities.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM stores data that the CPU requires quick access to. The Raspberry Pi’s model-dependent RAM quantity directly impacts multitasking and overall system responsiveness.
- Input/Output (I/O) Ports and GPIO Pins: Raspberry Pi boards have several I/O ports, including the USB port for connecting peripherals like a mouse, keyboard, and storage devices. The Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins enable users to interact with external components, making it suited for hardware projects.
- Storage Options: Users often employ a microSD card as the primary storage medium for the operating system and user data on the Raspberry Pi. Specific models might incorporate onboard eMMC storage; external storage devices can connect via USB ports.
- Connectivity: Raspberry Pi boards include connectivity choices such as Ethernet ports, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. These features enable internet connection, networking, communication with other devices, and remote control.
- Video and Audio Output: Raspberry Pi boards have HDMI or composite video outputs connecting to displays and monitors. Audio output options, such as a 3.5mm audio jack or HDMI audio, permit sound playing for multimedia applications.
- Power Supply: A power source, typically via a micro USB or USB-C connection, is required to deliver the energy necessary for the Raspberry Pi to operate.
- Cooling Solutions: Additional cooling solutions, such as heat sinks or fans, may be required to regulate heat generated during operation, depending on the model and intended use, especially for intensive tasks.
- Camera and Display Interfaces: Some Raspberry Pi models provide specialized ports for connecting cameras and displays, allowing for image capturing and visual output applications.
- Operating System (OS): The Raspberry Pi can run various operating systems, especially Linux distributions, which provide a variety of software applications and tools for multiple purposes.
- GPIO Headers and Expansion: The Raspberry Pi’s GPIO headers allow users to attach additional hardware components and sensors, enhancing the board’s capabilities for various tasks.
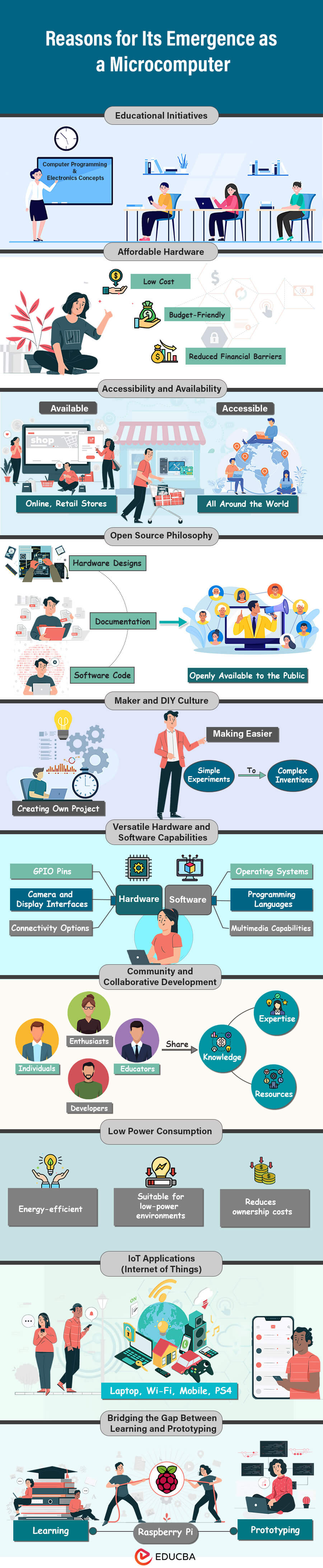
Reasons for Its Emergence as a Microcomputer
We need to know why it is emerging as a microcomputer, so here are the reasons for that.
Some of the projects that you can tackle with Rpi very easily can be:
- Block ads on your network with pi-hole.
- Set up a Postgres database on a Rpi.
- Make your own Twitter bot with Python and Raspberry Pi.
- Build projects using the RPi camera.
- Set up WordPress on an RPi.
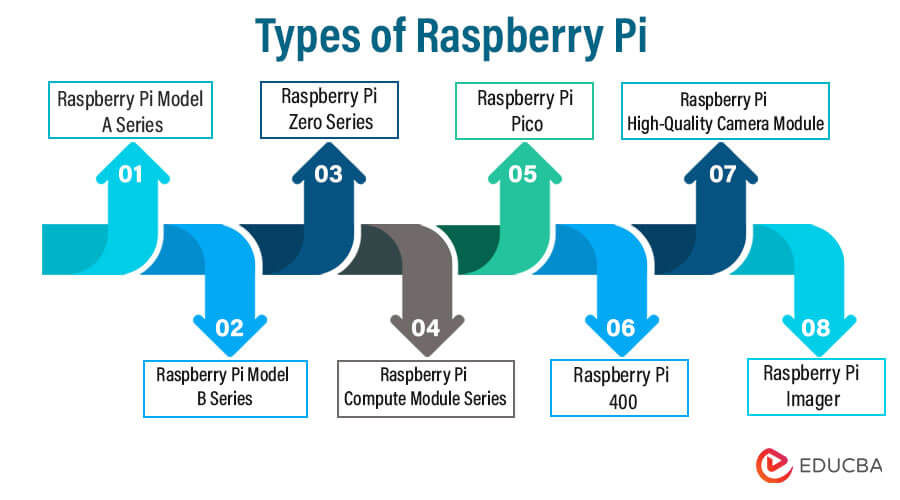
Types of Raspberry Pi
Here are some of the notable types of Raspberry Pi:
1. Raspberry Pi Model A Series
The Model A series aims to offer a small and energy-saving choice for fundamental computing tasks. These models usually feature less RAM and connectivity choices than their Model B counterparts. They are ideal for projects that emphasize mobility and energy efficiency.
2. Raspberry Pi Model B Series
The Model B series of Raspberry Pi is the most popular and extensively used range of models. These models provide a good balance of performance and features, making them adaptable for various purposes. They have multiple RAM options, connectivity ports, and processing power, making them suitable for various activities, including education and do-it-yourself projects.
3. Raspberry Pi Zero Series
The Raspberry Pi Zero series is a highly compact computing platform, ideal for projects and embedded systems that require minimal space. Despite their small size, these models offer essential features such as GPIO pins, USB connectivity, and wireless capabilities.
4. Raspberry Pi Compute Module Series
The Compute Module series is intended for industrial use and personalized designs. These modules contain the essential elements of a Raspberry Pi but in a more condensed form that can be incorporated into specific hardware configurations. They are ideal for building prototypes and developing embedded systems.
5. Raspberry Pi Pico
The Raspberry Pi Pico is a microcontroller board, not a typical single-board computer. It runs on the RP2040 microcontroller chip created by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. The Pico is ideal for embedded programming and provides an affordable and robust platform for projects that involve sensors, actuators, and other components.
6. Raspberry Pi 400
The Raspberry Pi 400 takes a unique form factor by integrating the Raspberry Pi components into a keyboard. It’s designed for simplicity and ease of use, making it an excellent option for beginners and educators. The Raspberry Pi 400 comes pre-assembled, providing a compact, ready-to-use computing experience.
7. Raspberry Pi High-Quality Camera Module
While not a standalone model, the High-Quality Camera Module is an essential accessory for Raspberry Pi models. It has high-resolution image capabilities and adjustable lenses, making it excellent for photography, videography, and computer vision projects.
8. Raspberry Pi Imager
The Raspberry Pi Imager is a software tool the Raspberry Pi Foundation produces, not a hardware model. It simplifies the process of flashing OS system images onto microSD cards, making it easier for users to set up and configure their Raspberry Pi devices.
How does Raspberry Pi work?
Here’s a step-by-step overview of how a Raspberry Pi works:
- Power Supply: Connect a power supply (often a micro USB cable) to the Raspberry Pi’s power port. This provides the essential electrical power for the board to function.
- Boot Process: Powering on the Raspberry Pi initiates the CPU to execute instructions from the bootloader, typically stored in the firmware. The bootloader initializes the CPU, memory, and other essential components.
- Loading the Operating System: The bootloader transfers the operating system from the bootable storage medium (often a microSD card) into the RAM of the Raspberry Pi. The operating system can be a Linux distribution optimized for the Raspberry Pi, such as Raspbian (now known as Raspberry Pi OS).
- Kernel Initialization: The kernel initializes hardware components such as GPU, CPU cores, memory, and peripherals.
- User Space Initialization: After kernel initialization, the Raspberry Pi initiates the start of user space programs and services, encompassing system services, daemons, and background tasks.
- Command Line Interface (CLI) or Desktop Environment: The Raspberry Pi will display a command line interface (CLI) or a graphical desktop environment, depending on the operating system and configuration. Users can interact with the Raspberry Pi by connecting it to a display, keyboard, and mouse or using remote connections.
- Software Execution: Users may run software applications programming scripts in the CLI and perform commands. The CPU executes instructions, performs calculations, and interacts with memory and peripherals.
- Peripheral Interaction: The Raspberry Pi can communicate with numerous peripherals via its GPIO pins, USB ports, network interfaces, and other connectors. Sensors, displays, actuators, and other external devices can be linked and controlled.
- Networking: The Raspberry Pi can access the internet through Ethernet or Wi-Fi (depending on the model). Users can connect to the internet, send and receive data, and communicate with remote servers.
- Storage and Data Handling: The Raspberry Pi reads and writes data to storage devices such as the microSD card or external storage. This includes accessing operating system files, application data, and user data.
- Multimedia and Graphics: The GPU renders graphics, enabling multimedia playback, graphical interfaces, and other functions. Visuals can be displayed on connected monitors via HDMI or other display interfaces by the Raspberry Pi.
- Shutting Down: Shutting down the Raspberry Pi correctly ensures the preservation of data and the safe powering off of the system. Users can start a shutdown via the command line or the desktop interface.
Applications of Raspberry Pi
Here are some of the prominent uses of Raspberry Pi:
1. Raspberry Pi in Education
One of the Raspberry Pi Foundation’s core goals was to improve computer education. Raspberry Pi is an inexpensive platform for teaching kids of all ages programming, electronics, and computing principles. It gives students hands-on experience and encourages experimenting, which fosters creativity and problem-solving abilities.
2. DIY Projects and Makers Community
The Raspberry Pi has sparked a thriving community of creators and experimenters worldwide. These enthusiasts engage in various do-it-yourself undertakings, such as developing home automation systems, weather stations, intelligent mirrors, and robotic devices. With GPIO pins, it’s simple to integrate sensors, motors, and other elements, making it the perfect option for custom electronics projects.
3. Learning to Code with Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi is a wonderful platform for learning various programming languages. From Python to Scratch, beginners can experiment with coding topics in a hands-on environment. This accessibility has enabled people from diverse backgrounds to learn programming and enter the world of software development.
4. Home Automation and IoT (Internet of Things)
Raspberry Pi is essential in creating home automation systems and IoT projects. Users can construct smart home solutions to control lights, thermostats, security cameras, and other devices. It’s networking choices and compatibility with numerous sensors make it a dependable hub for developing IoT applications.
5. Media Centers and Entertainment
By installing software like Kodi or Plex, Raspberry Pi may be transformed into a media center, allowing users to stream and organize media content. It’s also utilized for retro gaming emulation, allowing players to recreate classic gaming experiences with emulators and ROMs.
6. Scientific Research and Data Analysis
Researchers employ Raspberry Pi for data collection and analysis across diverse scientific domains. They use it for tasks like environmental monitoring, data logging, and even as a component in experimental setups. Its affordability and portability make it a vital tool for academics with limited budgets.
7. Industrial and Prototyping
Raspberry Pi finds application in prototyping and developing embedded systems in the industrial sector. It aids in constructing automation and control systems, enabling organizations to streamline processes and enhance productivity.
8. Digital Art and Creativity
Raspberry Pi is being explored by artists and creatives for interactive installations, digital art projects, and multimedia experiences. Its video, audio, and input capabilities enable unique and immersive artistic expressions.
9. Network Monitoring and Security
Raspberry Pi enables the creation of network monitoring tools or security camera systems. It monitors network traffic, establishes VPNs, and manages cybersecurity measures for home and small office environments.
10. Educational Servers and Learning Platforms
Raspberry Pi is used by educational institutions and individuals to host educational websites, learning management systems, or collaborative platforms, giving a localized environment for learning and interaction.
Top Raspberry Pi Models
Here are some of the top models that have gained popularity:
3.1 Raspberry Pi 4 Model B
The Raspberry Pi 4 Model B is an impressive upgrade in processing power and features. It has a quad-core ARM Cortex-A72 processor provides significant performance improvements compared to previous models. With different RAM options ranging from 2GB to 8GB, users can select the best-suited model for their needs. The Raspberry Pi 4 also includes two micro HDMI ports that support dual 4K displays, making it perfect for multimedia and productivity tasks. Additionally, it has USB 3.0 ports that offer faster data transfer and Gigabit Ethernet for high-speed networking.
3.2 Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+
The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ is highly regarded for its ability to balance performance and energy efficiency. It boasts a quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor and 1GB of RAM and is equipped with Gigabit Ethernet for improved networking capabilities. With Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, it is well-suited for wireless projects and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Furthermore, the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ remains compatible with previous accessories and software, making it a dependable choice for various applications.
3.3 Raspberry Pi Zero W
The Raspberry Pi Zero W is a highly compact and budget-friendly model with a single-core ARM11 processor and 512MB of RAM. It features Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, rendering it an ideal choice for wireless projects. With its small size and advanced features, the Raspberry Pi Zero W proves perfect for portable and embedded applications.
3.5 Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4
The Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4 caters to industrial and commercial applications. It packs the same power as the Raspberry Pi 4 in a compact form that suits custom PCB designs. Additionally, it comes with the option of eMMC storage and Wi-Fi connectivity, making it flexible for various projects, such as embedded systems and IoT devices. .
Advantages and Disadvantages of Raspberry Pi
After knowing and understanding the features, we must also understand their advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- The module takes only the size of your credit card.
- The working principle is the same as the normal computer at the expense of a meager price.
- Internal or external web traffic handling can be done at a relatively very low cost.
- It works as a server and is more cost-efficient than the standard server.
- The presence of GPIO (General Purpose Input Output pins) is what distinguishes an RPI from traditional computers.
- RPI has built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, allowing us to quickly take projects into wireless mode.
Disadvantages
- The Rpi has no fuse protection, so you can damage the board if you misconnect pins.
- It is slower in terms of CPU processing speed.
- It has as much memory as a traditional PC or laptop, which is very low.
- Unlike in an Arduino, there is no built-in analog-to-digital conversion on the GPIO pins.
- It is Slow all hell
- Only HDMI CEC for remotes unless you want to build your own IR receiver
Conclusion
Raspberry Pi’s success indicates its IoT potential and suitability for learning, coding, and various projects. It is an effective microcomputer bridging the gap between educational and industrial applications. It shows that radically inexpensive devices are good enough for many people and a lot of tasks. It is suitable for the learning aspect of kids as well as for everyone who has an interest in microcomputers and programming and for those who are code-geeks.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Why is Raspberry Pi familiar as a mini computer?
Ans: Rpi is a powerful, interoperable device with any input or output device. It is a device the size of a credit card called a mini-computer.
Q2. What are the drawbacks of Raspberry Pi?
Ans: It is a small device that needs the appropriate power supply; it won’t work either in the increase or decrease of power. It doesn’t boot up in case of less supply and defects the device in excess power supply.
Q3. Which is best, Raspberry Pi or Arduino?
Ans: Arduino is a learning tool for quick programming and circuit prototyping. Even though Arduino is good at providing its service, Rpi is best used for projects.
Q4. Is the Raspberry Pi open source?
Ans: Yes, the Raspberry Pi is an open-source device. While the hardware design isn’t open-source due to some proprietary components, the Raspberry Pi Foundation strongly supports open-source software and offers a wealth of open-source resources.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is Raspberry Pi?” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,