Updated September 5, 2023
Introduction to Server Message Block
Welcome, brave voyager, to the universe of Server Message Block, or SMB for short. In essence, SMB is the language your devices speak to share files, folders, and printers across networks. Think of it as the invisible cosmic string that connects your digital realm, enabling seamless communication between devices- your trusty laptop, corporate server, or even a celestial printer.
IBM first created the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol in the 1980s. It is one of the Common Internet File System (CIFS) versions to transfer files over the network. A server Message Block is a network communication transfer protocol that provides shared access to files, printers, and ports between the networks.
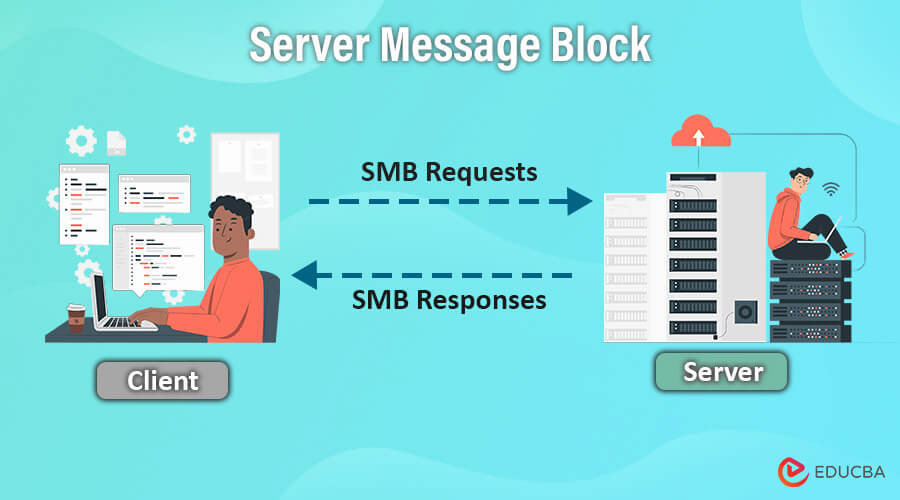
Table of Content
- Introduction
- What is a Server Message Block?
- How does it work?
- Version Enhancements
- Hardware Requirements
- Security Considerations
- CIFS VS SMB
- Authentication Protocol
What is a Server Message Block?
SMB is a client-server interaction protocol where clients request a file, and the server provides it to the client. It is now a Windows-based network that allows users to create, modify, and delete shared files, folders, and printers within the network. SMB is an application-layered protocol that uses TCP Port 445 to communicate. It also provides a herborized intercommunication mechanism to transfer and share files between the client and the server. With the upgrades of its versions, the services are much more enhanced and effective to use by the users or clients.
Key Takeaways
- SMB is a network protocol that allows devices to share files and printers and communicate with each other.
- SMB facilitates cross-platform compatibility, allowing users to exchange resources effortlessly between devices running different operating systems.
- Organizations may ensure secure and effective file sharing, supporting cooperation and productivity in network environments, using newer SMB versions with additional security features.
How does Server Message Block Work?
SMB is a request-response protocol that transfers multiple messages between the client and server to accomplish the request.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how SMB works:
1. Client Request: A client device (e.g., a computer or a user’s device) initiates a request to access shared resources on a remote server, such as files or printers. The client uses the SMB protocol to send the request.
2. Name Resolution: The client must determine the server’s name holding the shared resources before connecting. Several approaches, such as NetBIOS name resolution or DNS (Domain Name System), can accomplish this.
3. Session Establishment: After resolving the server’s name, the client starts a session with the server. This includes determining the SMB version for communication and verifying the client’s identity.
4. Authentication: The client sends its credentials (username and password) to the server. The server validates these credentials to verify whether the client can access the requested resources.
5. Resource Access: Following successful authentication, the client can use SMB commands to access shared resources on the server. The client might, for example, request a directory listing, read or write files, or send print jobs to a shared printer.
6. File and Printer Sharing: SMB provides instructions that allow the client to perform different file and printer-sharing tasks. These commands offer operations for opening files, reading and writing data, creating directories, and submitting print jobs.
7. Data Transfer: When a client requests to read or write data from a shared file, SMB supports data transfer between the client and server. The data is divided into smaller packets and delivered over the network using the SMB protocol.
8. Transaction and Response: The server processes the client’s requests as transactions, and each transaction delivers a response back to the client. The response includes the requested information, such as file data, directory listings, or printer status.
9. Session Termination: When the client no longer requires access to the shared resources, it can end the session with the server. This frees up resources on both the client and server sides and terminates SMB communication.
Server Message Block (SMB) Version Enhancements
Given below are the SMB Version Enhancements:
1. SMB 1.0 (CIFS – Common Internet File System)
- SMB 1.0, also called CIFS, was Microsoft’s initial protocol edition. It offered fundamental file and printer-sharing functions in the early stages of Windows environments.
- Some key features of SMB 1.0 include file sharing, printer sharing, network browsing, and basic authentication.
- This protocol played an essential role in the early development of Windows networking, but it lacked modern security features and was vulnerable to various cyberattacks. Due to these security concerns, it may no longer be the best option for network file sharing.
2. SMB 2.0
- SMB 2.0 is a protocol redesign introduced with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It was created to address the limitations of SMB 1.0 and to improve performance and security.
- The key features of SMB 2.0 include reduced back-and-forth communication, support for larger file sizes, and enhanced error handling.
- This redesign is significant because it significantly improves performance, especially over high-latency networks, and reduces the load on servers and clients during file operations.
3. SMB 2.1
- SMB 2.1 is a slightly upgraded version of SMB 2.0, which has improved to enhance its performance and scalability.
- Its key features include the optimization of bandwidth, better caching to ensure faster access to frequently used files, and support for durable file handles.
- The introduction of SMB 2.1 has significantly improved bandwidth usage, enabling better network utilization in various scenarios.
4. SMB 3.0
- SMB 3.0 is a vital protocol introduced with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. It marked a significant milestone in network technology and brought many enhancements beneficial for modern network environments.
- Some key features of SMB 3.0 include transparent failover, which ensures continuous availability even during server outages, SMB encryption for secure data transfer, multichannel support for improved performance, and SMB Direct (RDMA) for high-speed data transfers.
- SMB 3.0 holds immense significance and cannot be overstated. Its introduction brought critical features like transparent failover, ensuring continuous resource access during server outages. SMB encryption also provides end-to-end data protection, while SMB Direct (using RDMA) facilitates faster data transfers with reduced CPU overhead.
5. SMB 3.x
- Microsoft has consistently made minor improvements to the SMB 3.x family through updates and revisions.
- Features: The SMB 3.x protocol has undergone ongoing enhancements and refinements to improve its performance, security, and compatibility.
- These updates have significantly improved the protocol’s performance, security, and overall functionality, ensuring it remains relevant in modern networking environments.
6. SMB 3.1.1
- The SMB 3.1.1 update is part of the SMB 3.x protocol family, with a significant focus on improving data security by providing encryption for files stored in file shares.
- Its key feature is data-at-rest encryption, which protects sensitive data stored on file shares.
- By enabling encryption for data at rest, unauthorized users cannot access the underlying storage media, as the data remains unreadable and encrypted.
Hardware Requirement to run SMB
The following hardware requirements are required to operate SMB and enable file sharing in a network environment:
1. Server or Network-Attached Storage (NAS) Device: A server or a dedicated NAS device is required to host the shared files and resources. The server/NAS should have sufficient storage capacity to transfer the files across the network.
2. Network Interface Card (NIC): To connect to the local area network (LAN), each network device (server, client computers, NAS) requires a network interface card (NIC). The NIC enables the device to communicate with other network devices.
3. Switch or Router: A switch or router is necessary to set up the local area network (LAN) and handle traffic between devices. It promotes data transfer and guarantees that devices may adequately communicate with one another.
4. Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables are required to connect the devices to the switch or router. These cables allow for high-speed data transfer across the LAN.
5. Centralized File Server: A centralized file server is helpful in more extensive networks or enterprise situations. This server hosts the shared files and maintains data consistency, backup, and security. It also assists in managing permissions for various users and groups.
6. Adequate RAM and Processing Power (CPU): The server or NAS device should have enough RAM and processing capacity (CPU) to handle file-sharing requests properly. This ensures the device can properly manage multiple client connections and analyze data.
7. Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID): The storage discs can use a RAID configuration to improve data protection and performance. RAID arrays provide data redundancy, allowing for data recovery in the case of a disc failure.
8. Networked Printers (Optional): If you intend to use SMB for printer sharing, you may need networked printers that support SMB protocols. These printers can be shared across the network, enabling numerous users to print from their devices.
Security Considerations
Here are some key security aspects related to the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol:
1. Authentication and Access Control
Authentication is a vital security measure for SMBs. It entails confirming the identity of users or devices before allowing them to access shared resources. Access control mechanisms establish and enforce user permissions, guaranteeing that only authorized users can access specific files, folders, or printers. Ensuring proper authentication and access control is imperative to avoid unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources. This mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications.
2. Encryption
SMB uses encryption to protect data from eavesdropping and unauthorized interception when transmitting over the network. End-to-end encryption is supported by SMB, which ensures that data is secure while it travels between the client and server. Encryption is crucial for maintaining data privacy and confidentiality, making it much more difficult for attackers to decipher sensitive information if they can intercept network traffic.
3. Secure Negotiation
When communicating, clients and servers must agree on the most secure SMB protocol version and security settings. Secure negotiation is the process that ensures both parties utilize the highest level of security available to them. Secure negotiation is essential because it helps prevent downgrade attacks, where an attacker tries to force the use of an older and less secure SMB version to exploit known vulnerabilities.
4. Message Signing
Message signing is a feature in SMB that adds a digital signature to messages between the client and server. This signature verifies authenticity and prevents tampering or alteration during transmission, ensuring data integrity. Message signing is important because it protects against man-in-the-middle attacks and data manipulation, providing additional security for your data.
5. Secure Communication Channels
SMBs can utilize secure communication channels such as IPsec or VPNs to protect data while it travels through untrusted networks like the Internet. Secure communication channels are essential because they help prevent unauthorized access and data interception, especially when using SMBs for remote access or connecting networks in different locations.
6. Disable SMBv1
SMBv1 is an outdated and insecure SMB protocol version, making it vulnerable to attacks. Turning off SMBv1 on servers and client devices is essential to eliminate these security risks. Doing so reduces the chance of attacks exploiting the known vulnerabilities of SMBv1, reducing the attack surface and mitigating the risks associated with this version.
7. Patch Management
It is crucial to regularly apply security updates and patches to both the operating system and SMB implementation. Software vendors tend to release patches to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. It is critical to keep the system up to date with the latest security patches to prevent known vulnerabilities and keep the SMB implementation secure.
8. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides a network into smaller subnetworks to protect sensitive data and resources. This helps to contain and limit the impact of a security breach on specific areas. Network segmentation also reduces the risk of lateral movement for attackers and minimizes the exposure of critical data to potential threats.
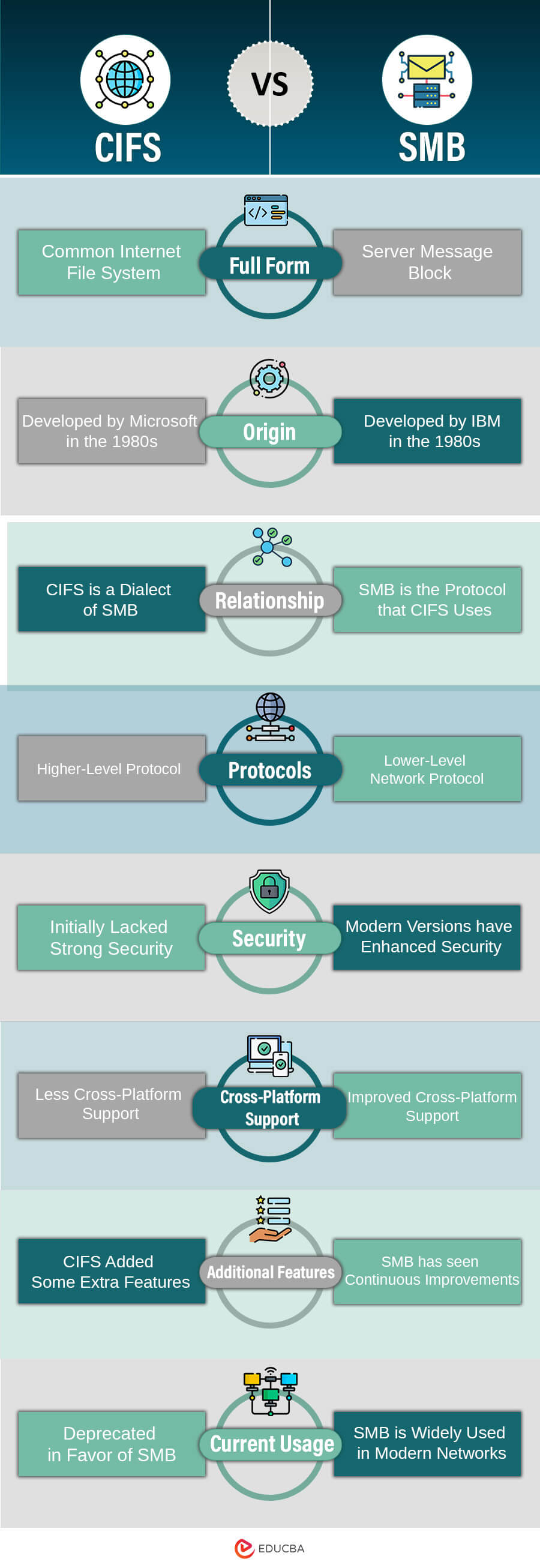
CIFS vs SMB
SMB Authentication Protocol
The SMB Authentication Protocol, a crucial part of the SMB protocol suite, verifies the identity of users and devices seeking access to shared resources in a network environment. This protocol ensures that only authorized users can access specific files, folders, printers, or other network resources. There are various authentication mechanisms used within the SMB protocol.
1. NTLM (NT LAN Manager)
NTLM, a dated authentication protocol, was used in previous versions of Windows and SMB. It employs a challenge-response mechanism where the server sends a random challenge to the client, and the client responds with a hashed value of the user’s credentials. While more secure authentication methods have replaced NTLM, it remains compatible with older systems.
2. Kerberos
In modern Windows environments, Kerberos is a robust and highly secure authentication protocol. It uses tickets to verify users and facilitates mutual authentication between the client and server. For SMBs in Active Directory (AD) domains, Kerberos is the recommended authentication method.
3. SMB2 and SMB3 Authentication Extensions
- SMB2 and SMB3, the newest versions of SMB, introduced authentication extensions that improve security and provide extra functions. These are some extensions: Pre-Authentication Integrity (SMB2/3) – The integrity of SMB packets is verified during the authentication process using a hash of the client’s authentication credentials.
- Secure Dialect Negotiation (SMB3) – Ensures the client and server negotiate the most secure SMB version and security settings.
Modern authentication methods such as Kerberos and SMB3 with extensions are crucial for ensuring strong security in SMB communications. Properly configuring authentication and access control within the SMB protocol is essential to safeguard sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
FAQs
Q1. Should I block SMB?
Answer: Blocking SMB completely is not recommended because it may interrupt important network file and printer-sharing functions. To ensure the security of SMBs, it is important to turn off outdated versions such as SMBv1, activate encryption, implement strong authentication methods, and regularly update systems with the latest security patches.
Q2. Can SMBs be used for cloud storage services?
Answer: Cloud storage services utilize SMB to ensure smooth integration with on-premises network environments. This allows users to easily access files stored in cloud-based storage and enables seamless file sharing between cloud and local network devices.
Q3. What alternatives are there to SMB for file sharing?
Answer: A few options are available if you’re looking for alternatives to SMB for file sharing. Unix-like systems can use NFS (Network File System), while macOS users can utilize AFP (Apple Filing Protocol). Alternatively, there are also cloud-based file-sharing services that allow for the easy sharing of files over the Internet.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Server Message Block” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.