Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Selection Sort in Data Structure
Selection sort is one of the sorting algorithms which arrange the data in ascending order. What selection sort does is that it searches for the lowest value element in the array and then brings it to the first position. Later, it finds the lowest value element from the remaining array, and after searching such an element, it brings it to the second position. Likewise, the algorithm goes on sorting the array finally ending up with the sorted array. Here we will discuss the algorithm and implementation of selection sort in data structure with steps.
Algorithm for Selection Sort
We shall now go through the algorithm for selection sort. Just observe how the operations occur as using this algorithm, we will implement a program for selection sort.
Algorithm:
function selection sort (array [], integer variable n)
declare integer variable position
declare index variables i, j
begin:
loop (i = 0, i < n-1, i = i +1)
begin:
position = i
loop(j = i + 1, j < n, j = j ++)
begin:
if(array[j] < array[position]) then
position = j
end if
end
swap(array[position], a[i])
end
end
Program for Implementing Selection Sort
The program code to implement selection sort is as given below. This program can be implemented in any programming language of our choice. We implemented the program in C programming. Go through the program and each of the coding elements, including variables, statements, and loops to understand how these elements function.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int arr[50], num, i, j, pos, temp;
printf("Enter the number of elements in the array: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("\nEnter the numbers: ");
for(i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
for(i = 0;i < (num - 1); i++)
{
pos = i;
for(j = i + 1; j < num; j++)
{
if (arr[pos] > arr[j])
pos = j;
}
if(pos != i)
{
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[pos];
arr[pos] = temp;
}
}
printf("\nThe array sorted in ascending order is as follows.\n");
for(i = 0; i < num; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
getch();
}
We tested the above program with multiple inputs, and the program worked correctly. Click on the Run option and pass the required input to validate the program. Let’s go through the various inputs that we passed into and the results that we got.
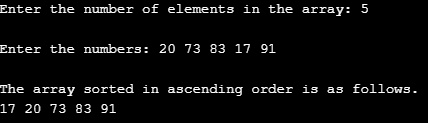
Input 1
In this case, we passed five different two digits numbers. While passing the elements, ensure that they are separated by space or enter. E.g. if we intend to pass three numbers 23, 45, and 87 then pass them as 23 45 87 and not as 234587 or else the compiler will consider it a single element. The following screenshot shows this.
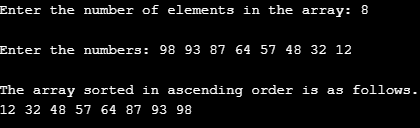
Input 2
In this case, we tested the program by passing an array containing eight elements. The array has elements present in the descending order. When executed, the program worked correctly giving the array sorted in ascending order of the numeric elements. Let’s go through the following programming output.
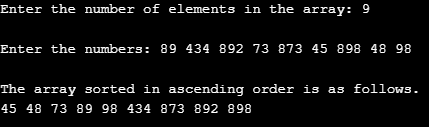
Input 3
In this case, we passed nine different numbers, as mentioned earlier, while passing numbers separate them with space. We must pass a specified number of elements only. As shown in the below screenshot, we got the input array sorted in the ascending order. So, this shows that our algorithm has worked correctly.
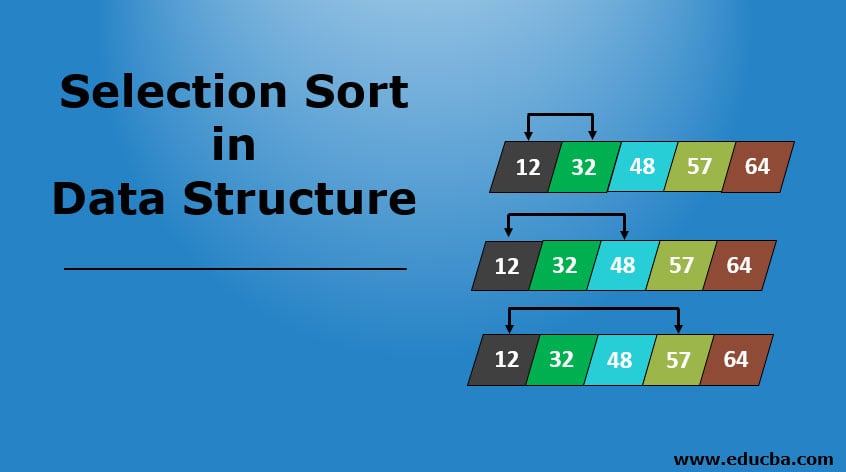
How the Selection Sort Algorithm Works?
In the above section, we saw how the selection sort algorithm gave us correct results after testing the program implementing the algorithm through various inputs. We will go through the steps that are followed by a selection sort algorithm by following which we get the array sorted in ascending order.
To understand how the algorithm works, we are considering an array that we passed in the second input example described above. The array consists of eight elements present in descending order. These eight numeric elements are 98, 93, 87, 64, 57, 48, 32, and 12. The steps followed by the selection sort algorithm to sort these elements in ascending order are described below.
Step 1: Initially, the input array looks like as shown:
Step 2: The lowest element from the entire array is brought to the first place. So, 12 will come to the first place, and 98 will go to the last place, as shown below.
Step 3: Now, the first element remains intact, and all the operations happen with the rest of the array elements. The process works the same as in the above step. From the remaining array, the lowest element is brought to the second position. So, here 32 will come to the second position and 93 will go to the position of 32. The array after swapping looks like as shown below.
Step 4: The next smallest element in the remaining array is 48. Now, 48 gets swapped with 87, and after the positions of these two elements are changed, 48 comes to the third position, and the array looks like as shown in the below screenshot.
Step 5: If we see the array now, we find that it almost looks as if it has got sorted. In the remaining array now we have only two elements left which are 64 and 57. Had 57 been at 64’s position, the selection sort would have given us the ascendingly sorted array in the above step itself. However, now, the position of these two elements must be changed. So, selection sort brings 57 at the position of 64, the former numeric element being lower than the latter. After the swapping takes place, the array looks like as shown below.
Conclusion – Selection Sort in Data Structure
The selection sort is a straightforward algorithm to implement. Irrespective of the programming tool used for implementing the algorithm, the concept remains the same. Before implementing the program, the algorithm must be studied to understand the functioning of the algorithm.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Selection Sort in Data Structure. Here we discuss the introduction, how it works, the program, and the algorithm for selection in the data structure. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –