Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Merge Sort in Data Structure
It is a recursive procedure based on the divide and conquers technique to solve a problem. This means it divides the main problem into smaller problems and later merges them to get the solution to the bigger one. In Merge Sort, we divide the list of elements into smaller lists until and unless the single element is left in the list and then these are merged in correct order to get the sorted list of elements. This is also a comparison-based sorting algorithm with O(nlogn) of complexity. Here we will discuss merge sort in a data structure along with its algorithm and applications.
Algorithm for Merge Sort in Data Structure
Merge Sort works similar to quick Sort where one uses a divide and conquer algorithm to sort the array of elements. It uses a key process Merge(myarr, left,m, right) to combine the sub-arrays divided using m position element. This process works on one assumption that the two sub-arrays contain the elements in a sorted manner. Below is pseudo-code to implement Merge Sort for a given array myarr which has its last index as right.
Algorithm:
MergeSort(myarr[], left, right)
If right > left
1. Middle point is found to divide the array into 2 halves:
m = (left+right)/2
2.MergeSort is called for first half:
Call mergeSort(myarr, left, m)
3. MergeSort is called for second half:
Call mergeSort(myarr, m+1, right)
4. Above 2 halves are merged using below algorithm:
Call merge(myarr, left, m, right)
MERGE (A, left, m, right)
n1 = m – left +1
n2 = right – m
let LArray[1.. n1 + 1 ] and RArray [1.. n2 + 1 ] be new arrays
for i=1 to n1
LArray[ i ] = A [ left + i -1]
for j=1 to n2
RArray[ j ]= A[ q + j ]
LArray[n1 + 1 ] = ∞
RArray[n2 + 1 ] = ∞
i = 1
j = 1
for k = left to right
if LArray[ i ] < R [ j ]
A[ k ] = LArray[ i ]
i = i + 1
else A[ k ] = RArray[ j ]
j = j + 1
Explanation: First, we have algorithm MERGE-SORT that takes an array as an argument and sees if the last index is greater than the left index to see if the array contains some elements to be sorted. Then a middle point m is calculated to divide the array into 2 sub-arrays, and the same algorithm is called for those sub-arrays. When recursive calls end and we end up having single elements in each sub-array, the MERGE algorithm is called.
This algorithm declares 2 arrays LArray and RArray to hold the elements in 2 sub-arrays. Then, elements in the 2 sub-arrays are compared simultaneously, and Array A is populated with elements in the sorted arrays. This algorithm is preferred over quick sort while working with the linked list as in quicksort, and there was a need to access the elements a lot which is of O(n) complexity in case of the linked list.
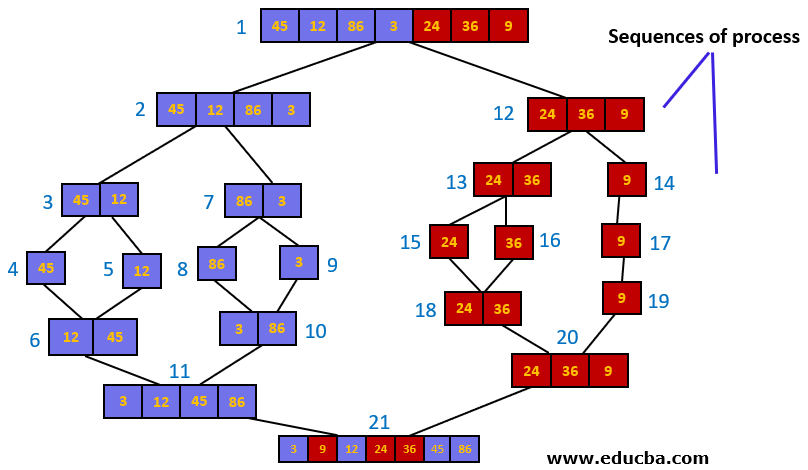
In the above picture, elements of the array are sorted using Merge sort. Also, we can see the sequence or the order in which the elements are processed.
Example to Implement Merge Sort in Data Structure
Here are some examples of implementing merge sort:
Code:
def mergeSort(myarr):
if len(myarr) >1:
mid = len(myarr)//2 #Middle element of the array is found
LArray = myarr[:mid] # Elements are divided in 2 arrays
RArray = myarr[mid:]
mergeSort(LArray)
mergeSort(RArray)
i = j = k = 0
while i < len(LArray) and j < len(RArray):
if LArray[i] < RArray[j]:
myarr[k] = LArray[i]
i+=1
else:
myarr[k] = RArray[j]
j+=1
k+=1
while i < len(LArray):
myarr[k] = LArray[i]
i+=1
k+=1
while j < len(RArray):
myarr[k] = RArray[j]
j+=1
k+=1
def printList(myarr):
for i in range(len(myarr)):
print(myarr[i],end=" ")
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
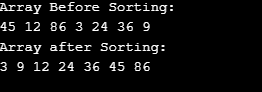
myarr = [45,12,86,3,24,36,9]
print ("Array Before Sorting:", end="\n")
printList(myarr)
mergeSort(myarr)
print("Array after Sorting: ", end="\n")
printList(myarr)
Output:
Time Complexity
As it is a recursive algorithm, its time complexity can be expressed as a recurrence relation. Here are the 3 types of time complexity which are explained below:
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + Θ(n)
1. Worst Case: The case when all the array elements are sorted in the reverse order. Using Masters theorem, we found the complexity of Merge sort in such case is Θ(nlogn).
2. Average Case: This is the case when the elements are partially sorted. The complexity of merge sort, in this case, is Θ(nlogn).
3. Best Case: This is when all the elements are already sorted, but still recursive calls are made thus, complexity is Θ(nlogn).
And Complexity of Merge algorithm is O(n) in all cases. Thus Merge sort is a stable algorithm that uses O(n) of auxiliary space and Divides and Conquer paradigm to sort the list of elements.
Applications of Merge Sort
Here are some of the applications of merge sort which are explained below:
- Sorting linked lists: Since random access of elements takes much time in case of the linked list, Merge Sort provides a quick solution to sort the linked list elements. This also stores the elements in self-made arrays and does not need random access in the linked list thus, and it provides a good solution to sort elements in O(nlogn).
- Inversion Count Problem: This is a problem where the degree of sorting of elements is calculated in a list of array. N case array is sorted degree is 0, and in case of reverse sorted list degree becomes maximum.
- Used internal Sorting: The type of sorting required to be done on data resides in secondary memory. This is required in case when the amount of data is too large to fit into the main memory. Since the memory location of data need not be contiguous in secondary memory thus merge sort is preferred.
Conclusion
Merge Sort is a divide and conquer algorithm that uses a merge process to merge the two sub-arrays into one by sorting its elements incorrect order. It works on one assumption that the elements in these sub-arrays are already sorted. This is a stable algorithm often used to sort the LinkedList or inversion count problems or external Sorting.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Merge Sort in Data Structure. Here we discuss the introduction, algorithm, and applications of Merge Sort in Data Structure and its code implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –