Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Insertion Sort in Data Structure
The following article provides an outline for Insertion Sort in Data Structure. Insertion sort essentially works as per its name. As the name goes, it basically inserts the element at its correct position by following a step-by-step process. This algorithm is straightforward to implement and also performs the sorting operation quickly. It should be noted that while there are many sorting algorithms, the use of one, such as the method of insertion, should be controlled by the nature of the data and other technical requirements.
Algorithm of Insertion Sort in Data Structure
The algorithm to implement insertion sort is as given below:
Go through each of the algorithm’s steps to understand how the working of the steps. Based on this algorithm, we shall implement the program for insertion sort.
Algorithm:
function insertion sort(data_type array[], integer variable n)
begin
declare integer variable temporary
declare integer variables i, j
loop (i = 0, i < n, i++)
begin
temporary = array[i]
j = i
until (j > 0 and temporary < array[j-1])
begin
a[j] = a[j-1]
j = j – 1
end
a[j] = temporary
end
end
Program to Implement Insertion Sort
We have implemented a program for insertion sort using C programming.
Go through the following code and see how each of the elements viz. statements, loops, variables, etc., work.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void main()
{
int arr[50], num, i, j, pos, temp;
printf("Enter the number of elements in the array: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("\nEnter the numbers: ");
for(i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
for(i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
temp = arr[i];
j = i;
while(j > 0 && temp < arr[j-1])
{
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
j = j-1;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
printf("\nThe array sorted in ascending order is as follows.\n");
for(i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
getch();
}
Explanation:
- We tested the above-implemented program through a series of inputs. It is essential to test the program to validate that it works properly. When the program is executed, firstly, we are asked by the program to enter the desired number of elements in the array. Next, we should specify the numeric elements. Note that if we intend to have an array of three elements, then the array elements should be passed separated by space.
- E.g. if we want to pass numbers 33, 98, and 76, the three elements then enter the input as 33 98 78 and not as 339878 otherwise, it will be considered a single input. Now, let’s go through the following three inputs and the results obtained to confirm that the program implementing the insertion sort algorithm is correct.
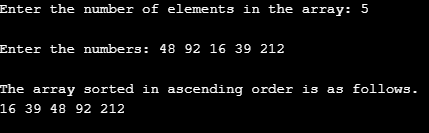
Input 1:
In this case, we kept the number of elements in the array to five and passed the elements shown in the following screenshot. The program has worked correctly, and we’re going to the sorted array as can be seen at the bottom of the screenshot.
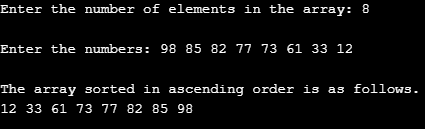
Input 2:
It is essential to validate a program through inputs of various types. In this case, we passed an array that has elements present in the descending order. As we can see in the screenshot, we passed eight elements all present in descending order. When the algorithm works, it gives us the correct result, i.e. array sorted in ascending order. So, it means the insertion sort program is working correctly.
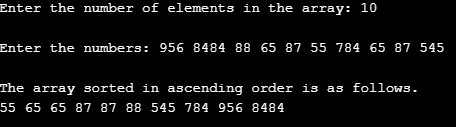
Input 3:
Here, we passed an array of size ten with elements that do not necessarily have the same number of digits. In the screenshot, there are one digits numbers right to four digits numbers in the array. But still, we got the array sorted in ascending order. Through various types of input, we have thus confirmed that the algorithm works correctly.
How the Insertion Sort Algorithm Works
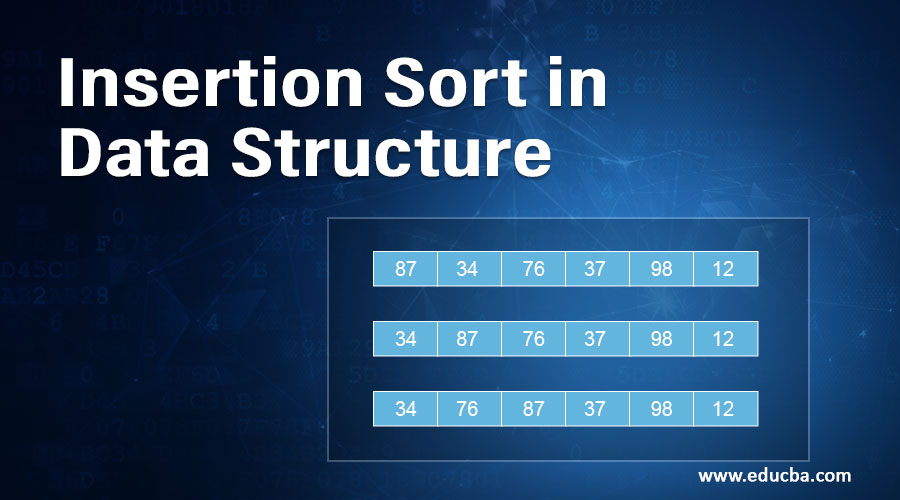
In the above section, we saw the algorithm and program in C programming language to implement the algorithm. However, it is important to understand how the sorting algorithm works. We shall now go through a step-by-step process to understand how the insertion sort algorithm works. For the demonstration, we will consider an array containing six elements. The array we are considering has elements 87, 34, 76, 37, 98, and 12 in that order. Let’s see how the insertion sort algorithm gives us an ascendingly sorted array.
Step 1: The algorithm works from the left-hand side. We have no element before 87, as it is the first element, so the array remains as shown below.
Step 2: Now, from the left-hand side, 34 is the next element which is less than 87, and so the positions of these two numbers get swapped. The array now looks like as shown below.
Step 3: The third element in the array is 76, which is less than 87 and is greater than 34, so it gets inserted between the two elements in the second position giving us the following array.
Step 4: Now, the fourth element in the array is 37. Compared to the three elements in the left-hand side, this is greater than only 34, and so it comes at the second position, and the array becomes as shown below.
Step 5: When we move to the fifth element from the left-hand side, which is 98, we find that it is greater than all the elements to its left, and the array remains as it was in the previous step.
Step 6: Finally, the last element is 12, which should come in the first place. So, the array gets shifted and 12 come in the first place as can be seen below.
Conclusion
Amongst many sorting algorithms, insertion sort is one that can be effectively used to sort the data. In data structures, algorithms have to be used based on the context, and insertion sort becomes handy when it comes to reducing the processing time.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Insertion Sort in Data Structure. Here we discuss the working, algorithm and different programs to implement insertion sort in the data structure. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –