Updated June 14, 2023
Introduction to B Tree in Data Structure
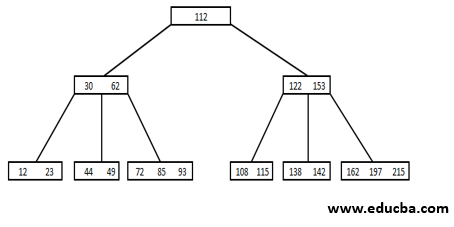
B-Tree is a data structure that systematically stores data and allows operations such as searching, insertion, and deletion. Certain aspects are associated with B-Tree, which deals with the tree in its balanced form. So, for having the balanced tree, there should be n/2 keys in each node, n being the B-Tree order. The other considerations are as follows.
- All leaf nodes must be present at the same level.
- There can be a maximum of n – 1 key for all nodes.
- There are at least two children for the root.
- n is the maximum number of children, and k is the number of keys each node can contain.
- There are at least n/2 children and at most n non-empty children.
- The tree gets divided so that values in the left subtree shall be less than the value in the right subtree.
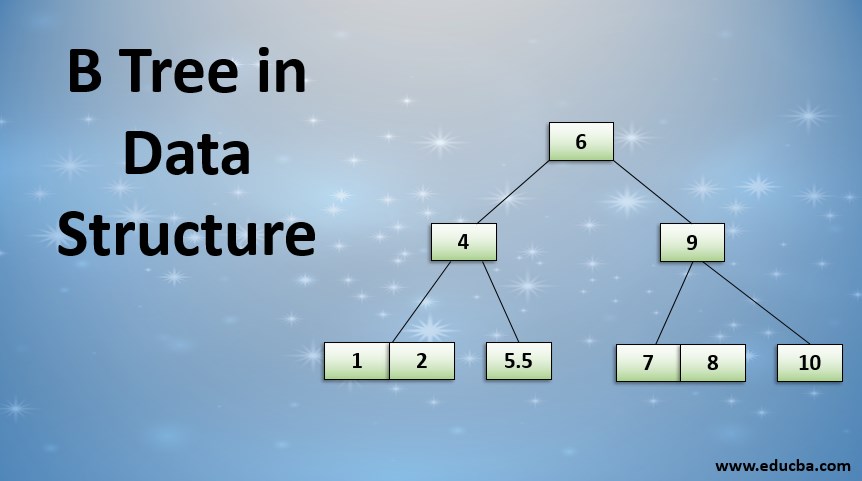
B-Tree Visual Representation
A sample visual representation of the B-Tree is shown below. It is a balanced tree that follows all the constraints associated with the concept.
All the leaf nodes are at the same level in the above B-Tree. The number of keys in non-leaf nodes is less than in the children nodes.
How Does B-Tree Data Structure Works?
Let’s understand the working of B-Tree through insertion and deletion operations. Two cases are associated with inserting a key in the B-Tree. These are; first, that node is not full, and second, the node is already full. Insertion of a key happens in the node if it’s a leaf node that is not full. If the node is full, we split the node at the median into two nodes. The level stays the same, and we move the median element up a level.
1. Insertion Operation
We will see how insertion happens into a B-Tree for a set of 6, 10, 5, 8, 2, 4, 9, 7, 1, and 5.5.
- The first element Inserted is 6.
- The next element to be Inserted is 10. It is greater than 6, so it will go to the right of it, as shown below.
- 5 is less than 6, so it goes to the left of the tree, as shown below.
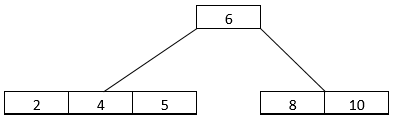
- Before the next element is inserted, it is checked if the tree is full. Since the tree is full, we allocate a new empty node. We make this node the root, split the former root, and put 6 into the new root. When you insert 8 into the tree, the arrangement becomes as shown below.
- The next element to be inserted is 2. It will go in the left subtree before 5. The arrangement now looks as shown below.
- Now, the next element to be inserted is 4. It goes into the left subtree as it is less than 6. It occupies the middle position in the node, as shown by the following B- tree arrangement.
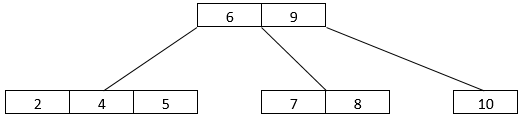
- The next step is essential. We need to insert elements 9 and 7 into the B-Tree. In this case, when the node is full, it undergoes a split operation, and the algorithm brings the middle child into the root. We get the B-Tree arrangement, as can be seen below. Here, 9 went into the root, while 7 joined 8, with 10 going into a separate node.
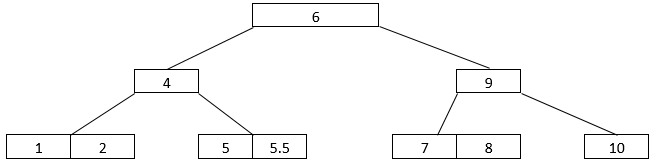
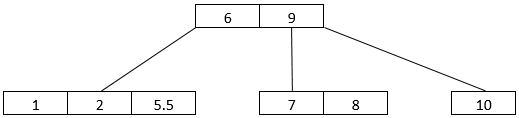
- The last two elements that we have are 1 and 5.5. 1 will go into the left subtree with 2, 4, and 5. We split the tree and send the middle child up to the root. Now, we have 5 and 5.5 in separate node. The B-Tree arrangement looks like this, as shown below.
2. Deletion from B-Tree
While performing the deletion from B-Tree, a traversal through the tree happens. After reaching the concerned node, two cases may occur, the first node is the lead node, and the second node is the non-leaf node. We shall see how deletion happens in B-Tree through the following example.
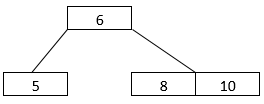
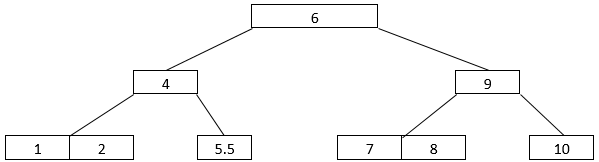
- Let’s consider that we intend to delete 5 from the above B-Tree arrangement 5 is present in the leaf node, so it will be deleted, giving the B-Tree arrangement below.
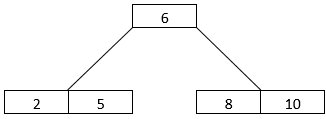
- What if we delete a non-leaf node? 4 is a non-leaf node. We shall delete it. When we delete 4, the arrangement changes to the one shown below.
- So, we find 5.5 and 9 going up by one level. 5.5 goes into the node having 1 and 2. 9, on the other hand, goes into the root node along with 6.
Advantages of B-Tree
Below are the advantages of B-Tree:
- B-Tree facilitates ordered sequential access, which works more effectively than a hash table.
- A B-Tree enables iterations over items similar to what a binary tree supports. The iterations arrange the items in the proper order (ascending or descending) as required.
- The tree can store millions of items, and its flat structure facilitates easy and efficient traversal through the data.
- When there are millions of records, deleting a record from a table can be expensive because the table may need to be rewritten. Using a B-Tree to handle sequential access to the table or storing the entire data in B-Tree nodes can simplify the deletion operation.
Conclusion
B-Tree is a data structure that efficiently assists in data operations, including insertion, deletion, and traversal. The usefulness of data structure is evident not in small applications but is impactful in real-world situations involving huge datasets.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to B Tree in Data Structure. Here we discuss data operations, including insertion, deletion, and traversal, with advantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –