Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Stack in Data Structure
A stack is a data structure that allows insertion and deletion operation in a LIFO (last-in-first-out) manner. The memory operations, therefore, are regulated in a particular manner. When an element is added to the stack, it occupies the top position. When it comes to removal operation, the most recent element in terms of being inserted into the stack gets first removed, hence the LIFO characteristic. This is similar to a stack of saucers or tiles, kept one over another. We keep going on placing saucers on over another, and while removing, the most recently added one is removed first.
Features of Stack
Some of the features are as follows:
- A stack is an ordered list of elements of a similar type. E.g. stack storing numbers or stack of strings.
- It is essentially based on LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) feature or FILO (First-In-Last-Out) feature.
- When a stack is full, it is called to be in Overflow state, and when it is empty, it is called to be in Underflow state.
How does Stack work in Data Structure?
A stack is a very simple data structure, and there are necessarily two operations associated with stack, which are Push and Pop. The working of the stack as a data structure can be understood through these operations. Let’s understand each of them one by one, as described below. Let’s understand the insertion and deletion (removal) operations in a stack as discussed below.
1. Insertion Operation
The operation to insert an element in a data structure is called Push operation. When we insert an element into a stack, it occupies the bottom-most position, as an object pushed into a pit. The next element inserted goes over the top of the previous element, and likewise, the insertion of all elements happens. As each time, the insertion operation resembles pushing an element into the stack, and the operation is termed as “posh operation”. We will understand the working of push operations through the following steps.
Consider we have five numeric elements which are 51, 98, 24, 76, and 38. We intend to save these elements into memory using a stack data structure. The elements have to be inserted into a stack in the mentioned order. The push operation in this context will happen as discussed below.
1. In the beginning, the stack is empty, as shown below. Using push operation, we shall insert each element into this stack.
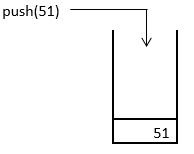
2. In the beginning, using push operation 51 is inserted into the stack, and it occupies the bottom-most position, as shown below.
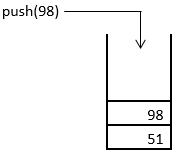
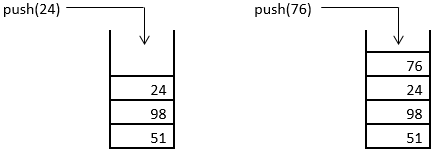
3. The next element to be inserted into the stack is 98, which gets inserted using the push() operation, as shown below.
4. Similarly, the next two elements viz. 24 and 76 are inserted into the stack using the push() operation. This is as shown below.
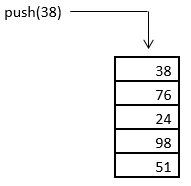
5. Finally, we have 38 going into the stack through push operation. And when the last element is pushed into the stack, the stack gets full. This is as shown below.
The push operation in stack works, as mentioned in the above section. We will now see how the removal of an element from stack takes place, as described in the below section.
2. Deletion or Removal Operations
We will understand the deletion operation in the stack through the example discussed in the insertion operation section. Let’s start with the last step in the above section. Now, we know that the stack is full. We will remove every single element in the stack. The operation to remove an element from the stack is called “Pop” operation. The pop operation removes the most recently added element first. The removal operation in the stack, facilitated by pop operation, will work as described below.
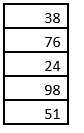
1. Initially, the stack is full. This is as shown below.
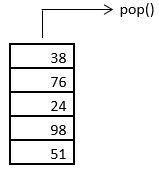
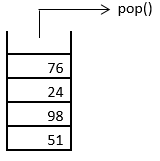
2. The element that occupies the top position in the stack is 38. It is the most recently added element into the stack. The pop operation removes this element first. This is as shown below.
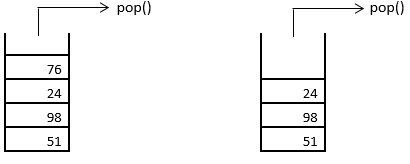
3. The next element to be removed from the stack is 76. The pop operation removes it from the stack. This is as shown below.
4. Similarly, 76, and 24, in that order are removed from the stack facilitated by the pop operation, as shown below.
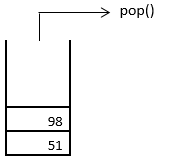
5. Next, last-but-one element, i.e. 98, is removed from the stack through pop operations, as shown below.
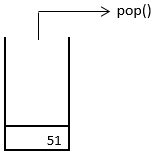
6. So, one-by-one every element in the stack is removed through the pop operation. Lastly, we have only 51 left in the stack. As we know, 51 was the first element to enter, but when it came to removing, it turned out to be the last element to get removed from the stack, this is because, to have it removed, we first need to remove the element located above it. Hence, the stack follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) feature for insertion and deletion operations. The last element gets removed, as shown below.
7. Finally, the stack becomes empty. This is as shown below.
3. Top and Search Operations
As the names suggest the Top operation in stack returns the topmost element in the stack. Similarly, the Search operation enables searching through the data structure.
Applications of Stack in Data Structure
- The stack is the most convenient data structure to reverse a string. This is facilitated by the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) nature of the stack.
- The stack is a very effective data structure for parsing operations.
- It is also used for expression conversion, i.e. converting infix expression to postfix expression, or postfix expression to prefix expression.
- It proves very efficient when it comes to performing backtracking.
Conclusion
Stack though a simple data structure is a powerful tool to store and manage data in the required manner. It can be considered a path with the entrance, which facilitates both insertion and removal operation. Because of this nature of stack, the insertion and deletion operations are LIFO based.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Stack in Data Structure. Here we discuss features and working of Stack in Data Structure along with its applications. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –