Updated May 10, 2023
Differences Between Django vs Ruby On Rails
Django is an open-source web framework written in Python. Django Software Foundation (DFS), an independent non-profit organization, maintains it. Django assists in creating and maintaining web applications, eliminating repetitive tasks, making the development process easy, and saving a lot of time. Ruby on Rails (Rails) is a server-side web application framework written in the Ruby language. Rails help with a rapid application development approach, assisting the developer with many built-in features so that the developer can solely focus on application business logic. For example, an open-source Rails framework is ideal for developing a database-backed web application.
Django
- The primary goal of Django is to ease the development process of complex, database-driven applications. Django handles all the difficulties of web development, freeing the developer to concentrate on creating the business logic for the application.
- It focuses on the DRY (Don’t repeat yourself) principle and enhances the reusability of components by writing less code with low coupling. Hence promoting rapid application development. Python is utilized thoroughly and is used to write the Django framework. Installing Python is a prerequisite to getting Django up and running on a system.
- The creators of Django had multiple design philosophies in mind, aiming to make each stack component independent and thus loosely coupled. The developer has to write less code, thus promoting rapid application development.
- Once done, the action should not repeat itself and can be reused effectively at several junctions of application creation. Thus, Django promotes best development practices by maintaining a clean design throughout its code and hence a hyper-fast development.
- Django has several benefits that follow the MVT (Model-View-Template) pattern. A key feature is that Django takes care of the controller part, leaving the developer with the template. The template is an HTML file mixed with Django Template Language (DTL). Django has excellent support for ORM (Object-relational mapping), links the data model and data engine, and supports many databases. Other benefits include multilingual support via its built-in internationalization system. Django has support for Ajax, RSS, and caching.
Ruby On Rails
- Rails is an MVC (Model-View-Controller) based framework that provides structures for a database, web pages, and web services. Web standards such as JSON and XML for data transfer purposes are facilitated by Rails. Certain other paradigms are well promoted and supported by Rails, such as CoC (Convention over Configuration), DRY (Don’t repeat yourself), and the active record pattern.
- Rails are packed with features that make the developer more productive, like metaprogramming. Another framework utilizes extensive code generation from scratch, but Rails uses Metaprogramming techniques. Rails also use code generation but depend on metaprogramming for heavy tasks. An active record would save an object into the database. Fences also do not require much configuration; they prefer the conventional approach.
Head to Head Comparison Between Django vs Ruby On Rails (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 comparison Between Django vs Ruby On Rails:
Key Differences Between Django and Ruby On Rails
Below is a list of points that explain the critical differences between Ruby On Rails and Django:
- It is said that Django is an open-source MVT-based framework that was released in 2005, and Rails is a web application framework that is well-suited for database-backed web applications in the MVC pattern, released in 2008.
- Django is written in Python, released under a BSD license, whereas Rails is written in Ruby, which is easy to learn, with an understanding of syntax, and released under an MIT license.
- While Django is a better choice for scientific programming, system administration, and data manipulation, Rails is better suited for metaprogramming and database-backed modern web programming..
- Django follows a model-view-template pattern, a model being a relational database that describes data structure, whereas Rails follows a model-view-controller pattern; the model represents the data that is handled in an Active Record.
- Shared web servers used for Django are Apache, NGINX, Cherokee, and Gunicorn, whereas Rails uses WEBrick, Apache, NGINX, and Cherokee.
- Django has a small community but has a more extensive repository of Github, whereas Rails has a vast and robust community of developers, along with a massive repository of Github.
- Python is the easiest to learn, making the learning curve for Django small, with plenty of online resources available. In contrast, Rails has a steep learning curve recommended for seasoned programmers.
- Django has a design philosophy that revolves around Explicit being better than implicit, whereas the philosophy for Rails revolves around convention over configuration principle.
- Django is easier to install and will take a little time, whereas the Rails installation is more extended than Django.
- Django serves static files as they are; third-party applications add compilation and compression capabilities, whereas Rails has a built-in static collection that uses CoffeeScript by default.
Django vs Ruby On Rails Comparison Table
In this section, we shall compare Django vs Ruby On Rails features.
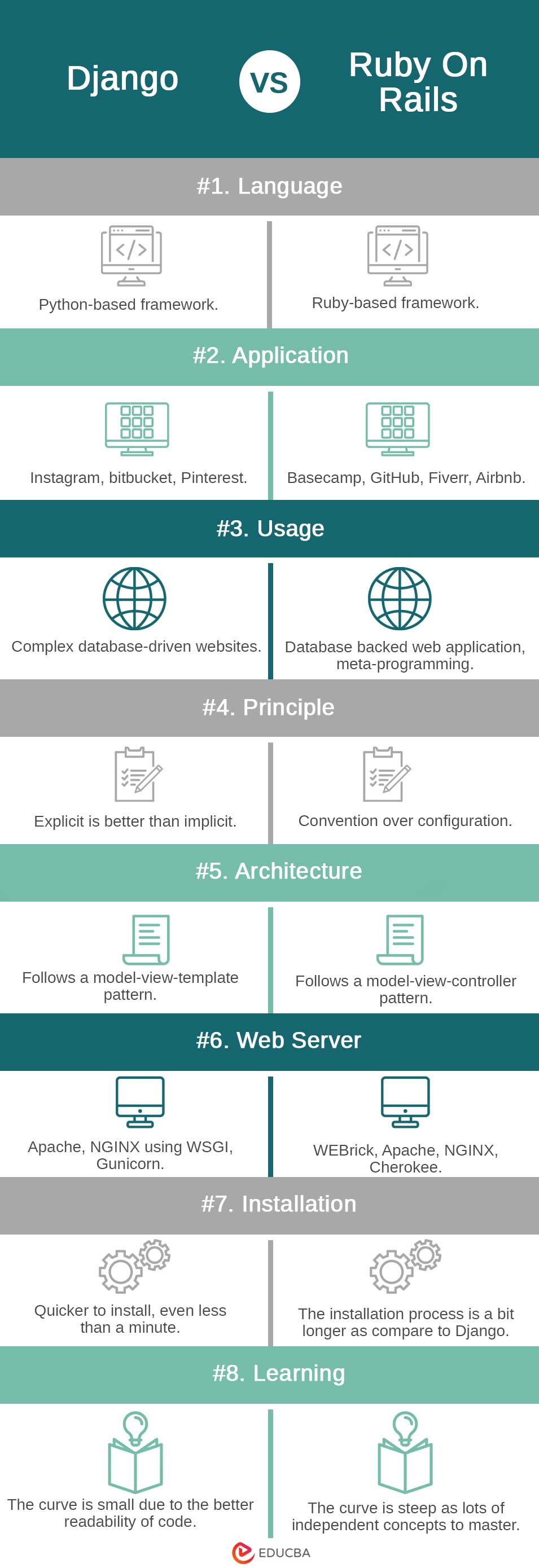
| Basis Of Comparison | Django | Ruby On Rails |
| Language | Python-based framework | Ruby-based framework |
| Application | Instagram, bitbucket, Pinterest | Basecamp, GitHub, Fiverr, Airbnb |
| Usage | Complex database-driven websites | Database-backed web application, meta-programming |
| Principle | Explicit is better than implicit | Convention over configuration |
| Architecture | Follows a model-view-template pattern | Follows a model-view-controller pattern |
| Web Server | Apache, NGINX using WSGI, Gunicorn | WEBrick, Apache, NGINX, Cherokee |
| Installation | Quicker to install, even less than a minute | The installation process is a bit longer as compared to Django |
| Learning | The curve is small due to the better readability of the code | The curve is steep as there are lots of independent concepts to master |
Conclusion
Both of them are excellent frameworks for web development. They provide nutritional support for clean code and help reduce time spent on everyday activities. Design principles at the core of both Django vs Ruby On Rails frameworks make them an ideal choice for rapid application development. Anyone familiar with Python tends to choose the Django framework, and the same holds for a Ruby person.
The decision to choose the framework comes down to which language the developer prefers or which principle needs to follow: convention over configuration or explicit is better than implicit.
There are plenty of people out there who love Python’s explicitness and Rails’ magic equally. Both Ruby On Rails vs Django provide benefits stemming from their core principles, assisting the developer in focusing on business logic. Project requirements, the developer’s skill, and efficiency within the chosen language are key factors that would decide the framework. Anyone who prefers to get the most important details out of the way first should go with Django. But when it comes to quickly launching and worrying about the details later, Rails would do better. Automation and shortcut features in Rails would assist in implementing a complex part.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Django vs Ruby On Rails” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.