Differences Between Django vs Flask
Both Django vs Flask are web frameworks for Python. On the one hand, Django provides a full-featured Model-View-Controller Framework; a flask, on the other hand, is a micro-framework that believes in the concept of doing one thing and doing it well. It does not provide an ORM. Flask comes up with a basic set of tools for authorization or a third-party plugin such as Flask HTTP-Auth. Flask doesn’t need any specific libraries or tools. The Flask community provides an ORM with a rich set of extensions to match its capabilities with Django.
Django
Django’s primary aim is to simplify the website creation process, which is often complex and database-driven. It emphasizes the reusability of components, less code, low coupling, and rapid and fast-paced development. Python is the primary language extensively used, even for data models and setting files. It also provides creativity, updates, reads, and deletes an interface generated through introspection and built via admin models. They take different approaches to designing a web application and creating a REST-based API design. The Django framework uses its built-in user model, facilitating API authorization and authentication. It alone can be used to create a RESTful API.
Flask
Flask doesn’t need any specific libraries or tools. It also doesn’t have a database abstraction layer, pre-existing third-party-based built-in libraries, and standard functions or form validation methods. It, though, provides a wide variety of extensions that, when put to use, works as if built-in Flask itself. The need for extensions arises from object-relational mappers, upload handling, form validations, open authentication technologies, and many standard framework-dependent tools. One can also expect quick and frequent updates for the extensions, even more than the ones supported by the program.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Django vs Flask (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 comparisons between Django vs Flask:
Key Differences Between Django vs Flask
Below is a list of points that explains the key difference between Django vs Flask:
- The parameter to be discussed is a transfer of the request object. Each view is set as an individual parameter in Django, whereas the request-based object is imported from the Flask module and looks like a global variable in the case of Flask.
- Django relies on its ORM or SQLAlchemy, whereas Flask uses peewee and SQLAlchemy. Due to the void of any present ORM, authors create independent solutions from a particular ORM. Flask minimalism, therefore, has a positive effect on the environment.
- Flask applications are mostly SPAs (Single Page Applications). With Django, your project application is divided into smaller chunks, giving the developers an easy-to-code single application and merging them to form the application.
Django vs Flask Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Django vs Flask.
| Basis of Comparison | Django | Flask |
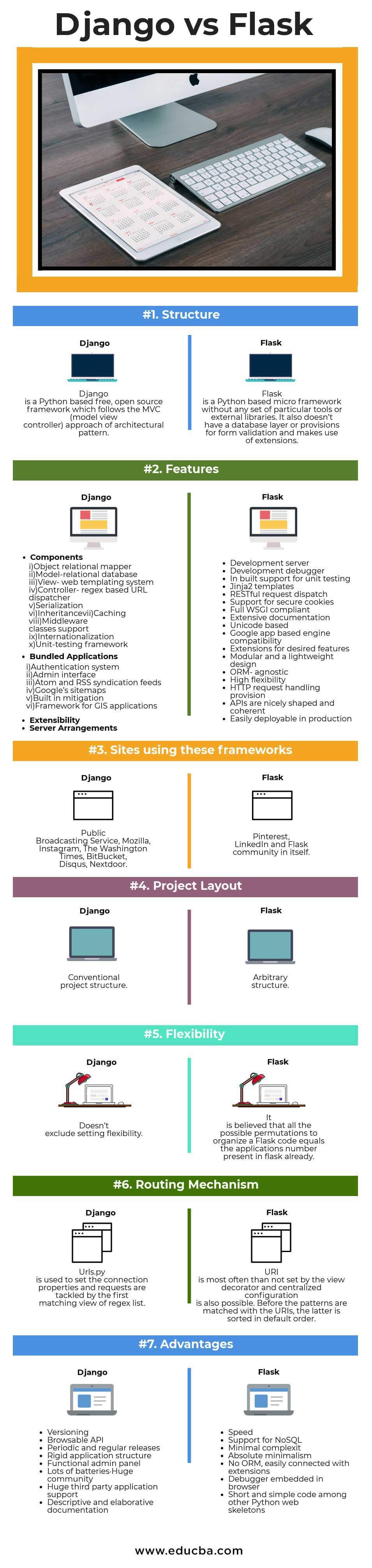
| Structure | Django is a Python-based free, open-source framework that follows an architectural pattern’s MVC (model view controller) approach. | Flask is a Python-based microframework without particular tools or external libraries. It also doesn’t have a database layer or provisions for form validation and uses extensions. |
| Features | Components
Bundled Applications
|
|
| Sites using these frameworks | Public Broadcasting Service, Mozilla, Instagram, The Washington Times, BitBucket, Disqus, Nextdoor. | Pinterest, LinkedIn, and Flask community in itself. |
| Project Layout | Conventional project structure. | Arbitrary structure. |
| Flexibility | It doesn’t exclude setting flexibility. | All the possible permutations to organize a Flask code are believed to be equal to the application number present in the Flask already. |
| Routing Mechanism | Urls.py is used to set the connection properties, and the first matching view of the regex list tackles requests. | URI is, most often than not, set by the view decorator, and centralized configuration is also possible. Before the patterns are matched with the URIs, the latter is sorted in default order. |
| Advantages |
|
|
Conclusion
All in all, both are open-source Python web frameworks. Django is a full-stack framework, whereas Flask is a micro and lightweight framework. There is no strict set of rules as to what one should use. Many believe Django to be the be-all and end-all, but that might not be the case in every scenario. Know your requirements and choose the framework wisely per your team’s needs. I hope you liked this Django vs Flask post. Stay tuned for more articles on Web Development.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Django vs Flask. Here we have discussed Django vs Flask head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –