Introduction to Cybersecurity Basics
Cybersecurity is a method of protecting systems from malicious attacks. In layman’s terms, Cybersecurity basics are steps taken to protect vital information from any theft or damage to hardware, software, and information contained in them. Hence it is essential to protect the data on personal systems or at the organizational level.
Cybersecurity is the prevention of data thefts, data breaches, or several other kinds of cybercrimes. It is also familiar with computer security or IT(Information Technology) security. The field’s emergence is due to the extensive use of software devices that are prone to threats.
Table of Content
Basic Types of Hackers
There are two types of hackers i.e., white-hat and black-hat.
White-hat hackers are generally known to you and let you know loopholes and vulnerabilities in your system. They are also called an ethical hacker. A corporate company typically hires these to find security flaws in its system.
In Cybersecurity basics contrast, a black-hat hacker is people who hack to gain profit (or for fun or revenge) from vital information. This essential information can be individual confidential details such as bank details, email access, etc., or personal company details such as access to a secure server.
Types of Cyber Attacks
#1 Social Engineering
Social Engineering is a skill by which a hacker gains vital information by merely having good communication with the victim. It aims at convincing the user to disclose personal information like numbers of the credit/debit cards, passwords, etc.
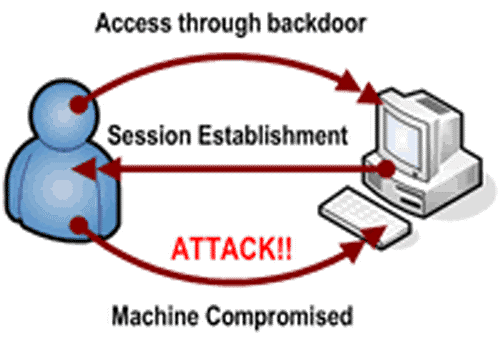
#2 Backdoors
In a real scenario, backdoors allow secret entry and exit points to a vital resource. A backdoor is any secret method of bypassing standard authentication or Cybersecurity basics controls in terms of computer systems. Regular phishing training for employees is crucial to mitigate vulnerabilities. This training helps educate them about cyber threats and ways to identify suspicious activities. Such training can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, which can, in turn, strengthen an organization’s overall security.
Moreover, these backdoors may exist for multiple reasons, such as the poor design of a system or intentional addition by a designer. It is a secret to himself or added by an authorized party afterward to allow legitimate access to the system.
#3 Denial-Of-Service (DoS)
These attacks involve no access to machines or network resources to authorized users. E.g., enter the wrong password multiple times so that the account locks or the machine/network overloads to such an extent that all authorized users cannot access resources. In such a case, a hacker attacks one machine, i.e., a single IP address. A firewall can control this situation by blocking a specific IP address. However, there may be a scenario in which a hacker attacks multiple machines. This is popular as Distributed-Denial-Of-Service (DDoS) attack.
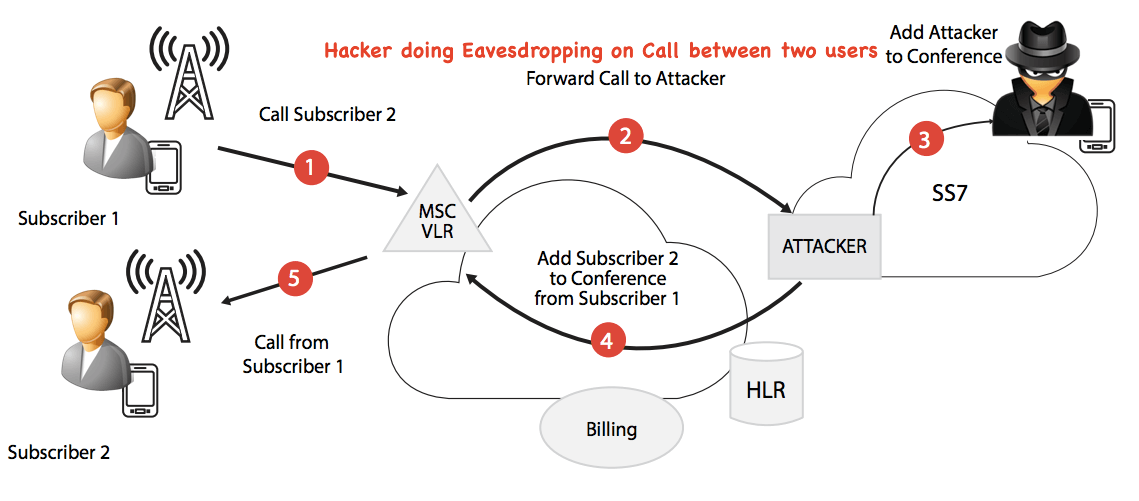
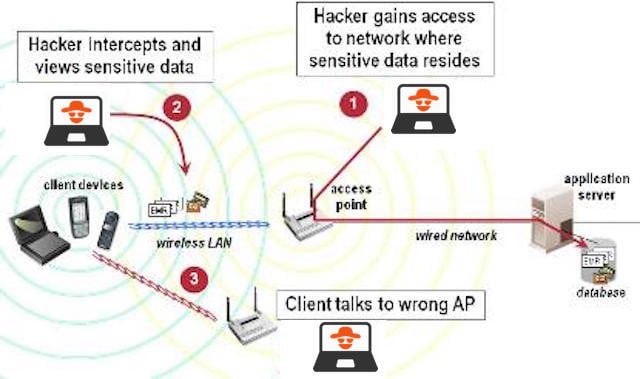
#4 Eavesdropping
The term eavesdropping means secretly listening to a conversation. In terms of computer security, this is typically carried out between Cybersecurity basics hosts on a network. E.g., there is a program called Carnivore used by the FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation) to eavesdrop on the system of ISP (Internet Service Providers).
#5 Spoofing
The term spoofing means to imitate something while exaggerating its characteristic features for some personal gain or profit. Spoofing of user identity is a situation in which one person or program successfully masquerades (means pretending to be someone one is not) as another by falsifying data, e.g., Making a call by a hacker (claiming to be an original user) to a bank official for carrying out banking transactions.
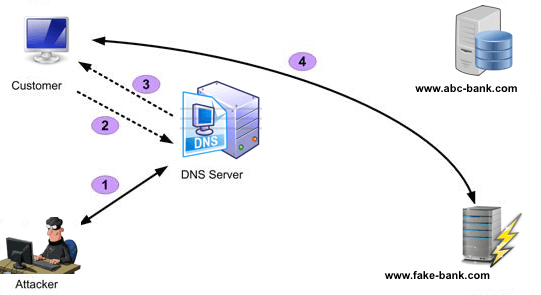
#6 Phishing
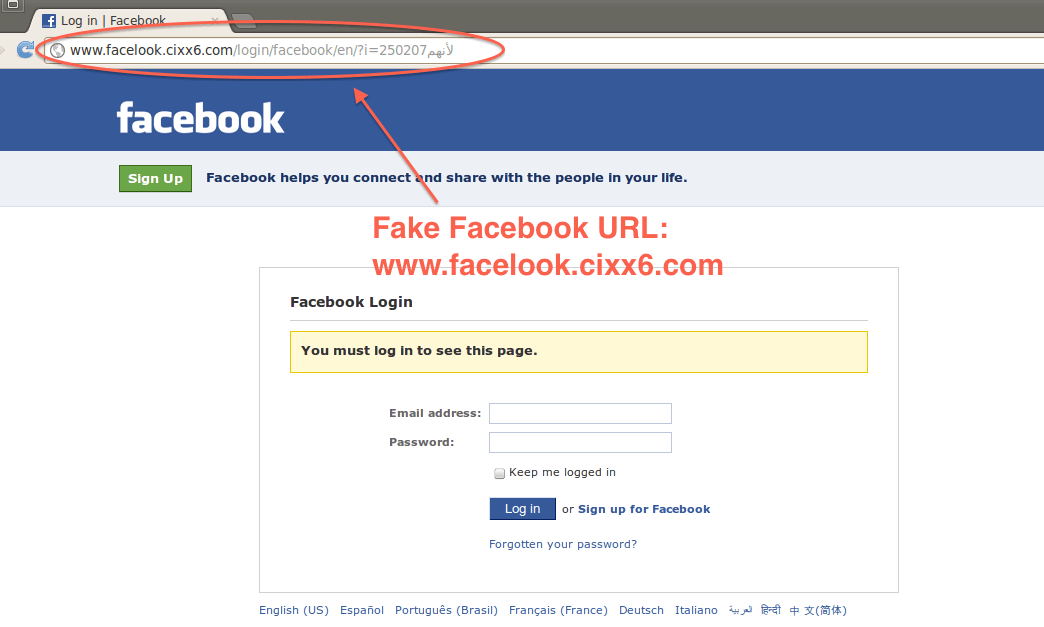
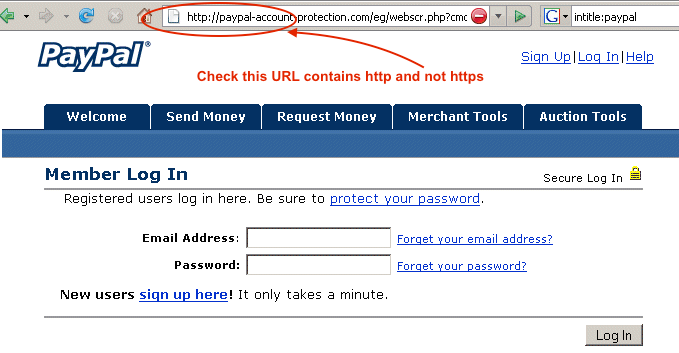
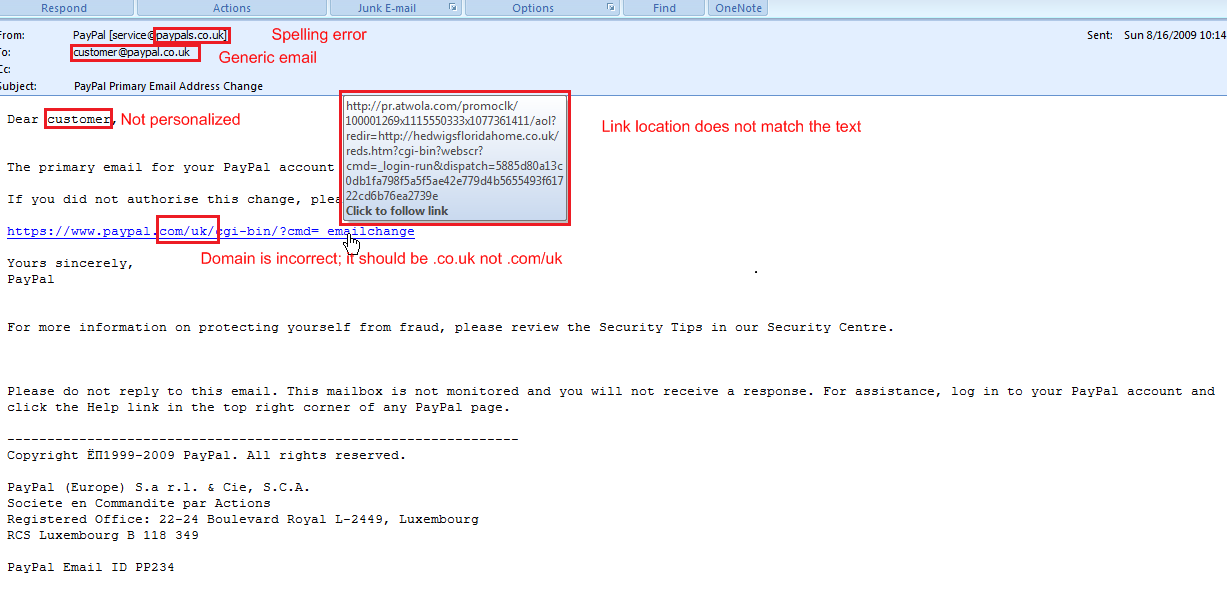
Phishing is the fraudulent practice of sending emails purporting to be from reputable companies to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, etc., online. This is generally carried out by email spoofing or instant messaging. It usually directs users to a website that appears to be legitimate but is fake, and a hacker controls it. The user enters confidential details at a fake website, becoming a phishing victim. Given below screenshot shows how the phishing website of Facebook happens.
Personal Security Tips
Below are a few personal security tips and tricks that can help you from getting hacked.
#1 Wireless Home Cybersecurity
- Wi-Fi always has the default password at the initial stage of installation. Change the default password of Wi-Fi. A password should be firm and have an alphabet (both upper and lowercase), numeric, special characters, and at least eight characters.
- Always turn on compatible WPA2 (Wireless Protected Access) / WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption for Wi-Fi. It is better to use some encryption rather than using none.
- Change the default network name. This is because default networks are more prone to getting hacked.
- Enable MAC address filtering. This mechanism allows Wi-Fi to work only on the registered MAC addresses.
- Do not auto-connect to open Wi-Fi networks since such networks are more vulnerable to getting hacked.
- Turn off the network during extended periods of non-use.
#2 Social Media Cybersecurity
- Use caution when clicking on links received in messages from an unknown sender. This is because links may redirect to a phishing website.
- Know what you’ve posted about yourself. Some people post confidential details such as personal contact numbers or addresses on social networks such as Facebook, Twitter, etc., which can be dangerous.
- Don’t trust that a message is from who it says it’s from. It may be spoofing content that claims to be the original sender.
- Do not allow social networking services like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc., to scan your email address book. This may give a door to read email content as well.
- Type the address of your social networking site directly into your browser instead of clicking on the link since it may be a phishing site waiting to gain your confidential details.
- Be selective about who you accept as a friend on a social network. While adding an unknown person to a social network may be the hacking entry point.
- Choose your social networks carefully. Understand the privacy policies.
- Be careful about installing add-on applications on your sites since these add-ons may be trojans that might gain access to your system.
#3 Online Banking Cybersecurity
- Monitor the account regularly.
- Avoid clicking through emails. Such an email can be a phishing trap and can land in great trouble.
- Change passwords regularly, and make sure to use a strong password always.
- Access your accounts from a secure location, such as using Firefox rather than internet explorer.
- Do not be lured while receiving an email, SMS, or phone call promising a reward for providing your personal information since it can be a social engineering approach to hacking.
- Make sure you use only official bank-sanctioned apps.
#4 Mobile Phone Cybersecurity
- Always use a pattern, PIN, or passcode to lock your device. If the device is at risk of theft and is not passcode protected, then a hacker can misuse the device.
- Auto-lock your phone to keep it secure.
- Data protection software should be useful for device data protection.
- Keep your apps and device software up-to-date and constantly updated from a genuine website source.
#5 Kids Care for Cybersecurity Basics
- Educate the kids about protecting their personal information, watching out for “free” stuff, and using strong email passwords.
- Advise kids to use security software to scan any programs downloaded.
- Monitor kids’ P2P (Peer-2-Peer) activities or file-sharing habits.
- Teach them about phishing scams using a demonstration.
- Teach kids about the apps they install.
(First Image Source: pixabay.com)
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity is a challenge to the contemporary world. It is a collection of methodologies to preserve the systems from unauthorized access. Security is essential for the large-scale system to protect the data. Even after taking a lot of care, cyberattacks keep happening worldwide. Hence it is necessary to be on the safer side.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1 What exactly does cyber security?
Answer: Cybersecurity is a technology that protects systems from threats or hacking. Maintaining the integrity, confidentiality, and security of the devices or networks is important. Strong cyber security is essential for government aid, educational institutions, and private companies since leaking simple information can cause serious risks.
Q2 Which technology is helpful in cyber security?
Answer: Artificial Intelligence(AI) and Machine Learning help to analyze large data streams. These can find any threats that may cause. AI-powered Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is a familiar example.
Q3 What is the most recent incident of cyber attacks?
Answer: The Royal Mail is a British multinational company that provides postal services. Recently, Royal Mail appeared earlier in January as a ransomware attack victim. This resulted in the halting of post and parcel deliveries overseas.
Recommended Articles
This EDUCBA guide to the Cybersecurity Basics discusses the introduction and five personal security tips. EDUCBA also suggests the following articles to learn more –