Introduction to Cyber Crime in India
Cyber Crime in India – With the advent of technology, life has become much easier in this 21st century. You can book railway tickets from mobile, pay bills instantly, shop online, etc. These are possible only due to advancements in the technology of the Internet.
The use of the Internet has lots of advantages, as stated above. In contrast, there are disadvantages too for the use of the Internet. People can fall prey to online payment fraud and lose their confidential stuff on social networks due to revenge on someone. These kinds of malicious activities done on the Internet can be classified as Cyber Crime in India.
A few years back, there was a lack of cybercrime awareness about the crimes that could be committed through the Internet. However, with the increased support from the Government of India, there have been separate laws for crimes committed on the Internet. The Indian parliament passed a new law pertaining to cybercrime, “Information Technology Act, 2000,” on October 17th, 2000. This law deals with the technology in e-commerce, e-governance, and e-banking, as well as penalties and punishments for cybercrime.
What is cybercrime?
Cybercrimes are unlawful acts using the computer as a tool, a target, or both. This is a general term that covers crimes such as phishing, spoofing, DoS (Denial of Service) attack, credit card fraud, online transaction fraud, cyber defamation, child pornography, kidnapping a person using chat rooms, stalking a person using the Internet as a medium, access to the computer system without authorization, cyber terrorism, creation and distribution of a virus, spamming, etc.
Learn how to protect businesses from the dangers of malicious hacking efforts. Assess the security of computer systems using penetration testing techniques. Develop ethical hacking skills.
What are the different types of cybercrime?
Cybercrime can be:
- Cybercrime against a person
- Cybercrime against property
- Cybercrime against the government
- Cybercrime against society
1. Cybercrime against a person
In this category, crime is against a person using electronic services as a medium. Below are some offenses that come under this category :
a. Cyberstalking: The term stalking means unwanted or obsessive attention by an individual or group towards another person. Cyberstalking is a threat through computer technology such as the Internet, emails, SMS, webcams, phone calls, websites, or even videos.
b. Cybercrime Hacking: This means gaining unauthorized access to a computer system for personal gain or misuse. It generally destroys the whole data present in the computer system. Screenshot 2 shows a message that hackers can post once your system is compromised.
c. Cracking: Cracking refers to digitally removing the copy-write protection code that prevents copied or pirated software from running on computers that haven’t been authorized to run it by the software vendor. The person who carries out this task is a Cracker.
There is a difference between Hacker and a Cracker. Hacker uses their knowledge to find flaws in the security of systems, whereas Cracker uses their knowledge to break the law.
d. Defamation: It involves damaging the good reputation of someone using a computer or electronic service as a medium. E.g., Posting vulgar messages and photos about a person on their social network profile such as Facebook, Twitter, etc.
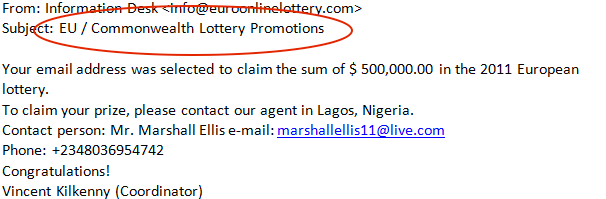
e. Online fraud: This refers to stealing confidential details of victims such as banking credentials using phishing sites and withdrawing money from victims’ accounts, online lottery scams such as Nigeria lottery scams. Screenshot 3 shows an online lottery scam claiming you have won $ 5,00,000!
f. Child pornography involves using electronic devices and services to create, distribute, or access materials that sexually exploit minor children—e.g., Recording a heinous act done with a child on a mobile device and spreading it on a porn site.
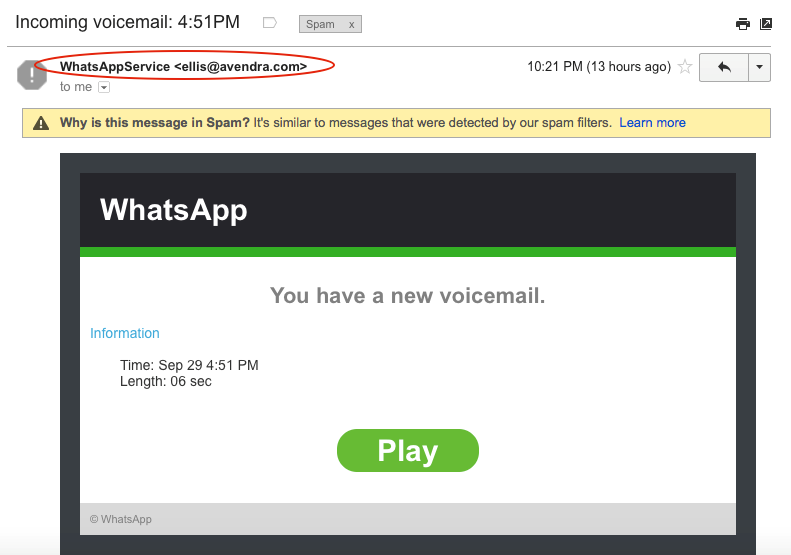
g. Spoofing: Spoofing means imitating something while exaggerating its characteristic features with some personal gain or profit. Spoofing of user identity can be described as a situation in which one person or program successfully masquerades (means pretending to be someone one is not) as another by falsifying data. Spoofing can take place using email or SMS, or WhatsApp. E.g., Constantly mailing a person claiming from the bank and requesting banking credentials. Screenshot 4 shows a hacker claiming to be from WhatsApp and sending an attachment (possibly a trojan or virus).
2. Cybercrime against a person
In this category, crime is against a person’s property using electronic service as a medium. Below are some offenses that come under this category :
a.Transmitting virus: A computer virus is a malware program that reproduces itself into another computer program, disk drive, files, or booting sector of the hard drive. Once this replication of the so-called virus succeeded, the areas affected are termed “infected”. Hackers generally transmit viruses to target systems using email attachments as a medium. When the victim opens the attachment (infected with a virus), this virus replicates throughout the system, slowing down your system.
b. Cyber Squatting: The term squatting means unlawfully occupying an uninhabited place. Cyber Squatting is where two or more persons claim for the same Domain Name or any service available on the Internet, such as a Facebook profile, etc. The hacker claims that he/she had registered the name before another person or that he/she owns a Twitter handle.
E.g. the first case in India registered for cybersquatting was Yahoo Inc. v/s, Aakash Arora, in 1999, where the defendant launched a YahooIndia.com website nearly identical to the plaintiff’s popular website Yahoo.com and also provided almost similar services. However, the court ruled in favor of Yahoo Inc.
c. Cyber Vandalism: Vandalism refers to action involving deliberate destruction or damage of public or private property. Cyber vandalism means destroying or damaging the data when a network service is unavailable.
E.g., The Tribune of Pakistan reported in November 2012 that hackers (a group named ‘eboz’ in Pakistan) replaced Google’s Pakistan logo with a picture of two penguins walking up a bridge at sunset.
d. Intellectual Property Crimes: Intellectual property is intangible property that is the result of creativity, such as copyrights, trademarks, patents, etc. Intellectual Property Right (IPR) crime is any unlawful act by which the owner is deprived of his/her rights completely or partially. These are the most common offenses in India, including software piracy, infringement of patents, designs, trademarks, copyright, theft of source code, etc.
E.g., The popular case of trademark of Bikanervala v/s New Bikanerwala filed in 2005. The plaintiff (here, Bikanervala) had filed an IPR case with the defendant (here, New Bikanerwala) since they ran a new outlet in Delhi using a trademark registered with the plaintiff. The court had allowed the plaintiff’s application, and the defendant was restrained using an ad interim injunction.
3. Cybercrime against the government
In this category, crime is against the government by using Internet facilities. Below are some offenses that come under this category :
a. Cyber Warfare: Cyberwarfare is an Internet-based conflict that involves politically motivated attacks on information and its related systems. It can disable official websites and networks, disrupt or even disables essential services such as Internet connection, steals or alters classified data such as Sensex details on the official website, and cripple financial systems such as blocking payment gateways.
For example, the US National Security Agency (NSA) is spying on a large scale in many countries. Former NSA agent Edward Snowden blew up this spying.
b. Cyber Terrorism: Cyber Terrorism is the politically motivated use of computers and information technology to cause severe disruption or widespread fear amongst people.
E.g., the recent example of the 2015 Dimapur mob lynching rape accused is due to an outspread of messages on a chatting app called Whatsapp amount locals of the Dimapur district in Nagaland.
4. Cybercrime against society at large
Unlawful activities cause harm to cyberspace that can affect an entire society or a large number of persons. Below are offenses that come under this category:
a. Online Gambling
The term gambling means involved in activities that allow a chance for money. Online gambling is one of the most lucrative businesses growing today in India’s list of cybercrimes. It is also Internet gambling or Gambling. Cybercrime incidents include online lottery scams (particularly those of Nigeria lottery scams), online jobs, i.e., working from remote locations, etc.
b. Cyber Trafficking
The term trafficking means dealing or involving in illegal trade activities prohibited by cybercrime law. Cyber Trafficking refers to unlawful activities using computers and computer services. E.g., selling kidnapped children to human trafficking groups using WhatsApp as a medium.
What are the laws about cybercrime in India?
Cybercrimes are increasing day by day due to the extensive use of the Internet by people. To deal with this Government of India (GoI) has imposed the Information Technology Act 2000, which was enacted with the prime objective of creating an enabling environment for the commercial use of Information Technology.
There are several different offenses related to the Internet that have been considered to be punishable under the IT Act and the IPC (Indian Penal Code). An extract of this act is illustrated below :
-
1. Cyber crimes under the IT Act
– Section 65: Tampering with computer source documents
– Section 66: Hacking with computer systems, data alteration
– Section 67: Publishing obscene information
– Section 68: Power of controller to give directions
– Section 69: Directions of Controller to a subscriber to extend facilities to decrypt information
– Section 70: Unauthorised access to a protected system
– Section 71: Penalty for misrepresentation
– Section 72: Breach of confidentiality and privacy
– Section 73: Publishing false digital signature certificates
Note: Section 66 A no longer exists.
There is one such incident related to this section that happened recently. A 21-year-old Palghar (a district in Maharashtra near Virar) girl was arrested on 19 November 2012 for posting a message on Facebook that criticized the shutdown in Mumbai due to the funeral of Bal Thackeray (former chief of Shiv Sena political party in Maharashtra).
Also, her friend was arrested for “liking” the post. Initially, they were detained under Section 295 A of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which stands for hurting religious sentiments, and Section 66 A of the Information Technology Act, 2000. However, later a local court dropped all charges against the girls.
2. Cyber crimes under IPC and special laws
– Section 503 IPC: Sending threatening messages by email
– Section 499 IPC: Sending defamatory messages by email
– Section 463 IPC: Forgery of electronic records
– Section 420 IPC: Fake websites, cyber frauds
– Section 463 IPC: Email spoofing
– Section 383 IPC: Web-Jacking
– Section 500 IPC: Sending an abusive message by email
3. Cybercrimes under the special acts
– NDPS (Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances) Act: Online sale of drugs
– Arms Act: Online sales of arms and ammunition
What to do when you become a victim of cybercrime?
People who become a victim of cybercrime don’t know what to do, and even some people don’t report the crime, thus allowing the hacker to target the next victim. If you become a victim of cybercrime, you can report it to the in charge of the cybercrime cell that falls under the jurisdiction where the crime has occurred. Cybercrime cell is present in almost all cities worldwide.
You can file a cyber crime complaint alleging cybercrime with the following mandatory documents :
1. It that involves email abuse, email bombarding, etc., should be provided with the following documents :
– Extract the extended headers of abusive emails and submit a soft and hard copy.
Please note that the hard copy submitted should tally exactly with the soft copy and should mention the date and time of the email correctly. Never delete such email until the cyber crime investigation is completed or the accused is brought to charges.
2. It that involves hacking of system should be provided with the following documents :
– Server logs (both soft copy and hard copy)
– Duplicate copy of defaced web page (both soft copy and hard copy) in case your website is defaced
– If your data is compromised, maybe it is on a server or computer or any network, submit a soft copy of the original data and compromised data
First Image Source: pixabay.com
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Cyber Crime in India. Here we have discussed how cybercrime takes place and also other internet fraudulent activities. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –