What is the Current Ratio Formula?
The current ratio formula is categorized as a liquidity ratio that demonstrates a company’s capacity to settle its current liabilities, primarily due within one year.
- The current ratio formula is a financial metric used to evaluate a company’s ability to pay its due debts within a year.
- The formula divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities.
- A ratio higher than 1.2 or 2 is generally considered good, indicating that the company is utilizing its assets efficiently.
- However, a low current ratio of less than 1 doesn’t necessarily mean the company is bankrupt.
- It provides investors and analysts insight into how effectively a business can use its current assets to meet its current liabilities and other payables.
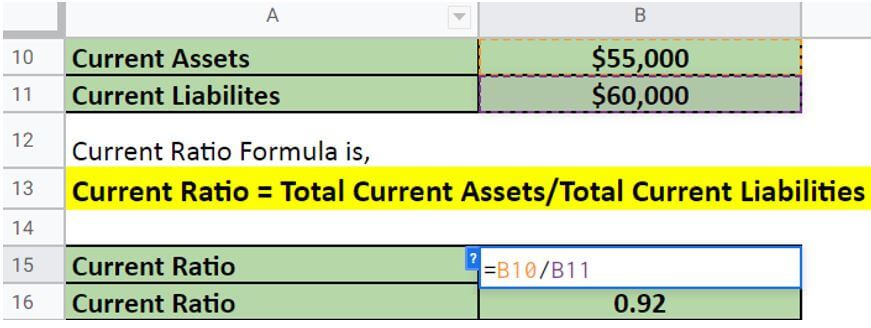
Current Ratio Formula
The current ratio formula is:
To define these terms:
- Current Assets are short-term holdings that can be liquidated within a calendar year or through an accounting period, such as cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments, etc.
- Current Liabilities are short-term obligations intended to be paid off within a year or an accounting period.
For example, in the Walmart Annual Report for the fiscal year ending on January 31, 2022, their current assets and liabilities were reported as $81.070 and $87,379, respectively. Using the formula, Walmart’s current ratio can be calculated as $81.070/$87,379 = 0.93.
Explanation of Current Ratio Formula
- The current ratio formula lets the investor know whether a company can generate enough cash to repay its short-term liabilities.
- Fundamental research analysts extensively use the ratio while valuing a company and measuring a firm’s liquidity.
- It measures the company’s liquidity/working capital management. Thus, the higher the ratio, the more current assets a company possesses compared to its liabilities.
- One must analyze the ratio in the background of the company’s industry. It could also be better if one analyzes the ratio over time.
- One can compare the company’s current ratio with its industry peers with a similar business model to decide the industry standard level of liquidity.
- A high ratio is not necessarily good, and a low ratio is not necessarily bad.
Interpretation of Current Ratio Formula
The current ratio is an important financial metric for assessing a company’s liquidity and ability to pay its debts using its current assets and liabilities. A good current ratio varies depending on the size and industry of the company. Large companies often have higher current ratios due to their high revenue generation.
- When the Current Assets > Current Liabilities, or Current Ratio > 1. This indicates that a company has enough assets to pay off its short-term debts and is in a very desirable position.
- When the Current Assets = Current Liabilities, or Current Ratio = 1. This indicates that the company’s assets can pay off its short-term debts.
- When the Current Assets < Current Liabilities, or Current Ratio < 1. This indicates that the company does not have sufficient assets to pay off its short-term debt and is not in a desirable position. However, a low current ratio does not necessarily mean the company will go bankrupt.
How to Calculate the Current Ratio Formula? Excel Examples
Example #1
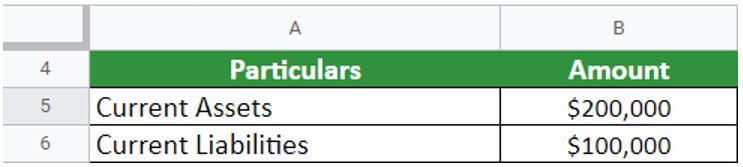
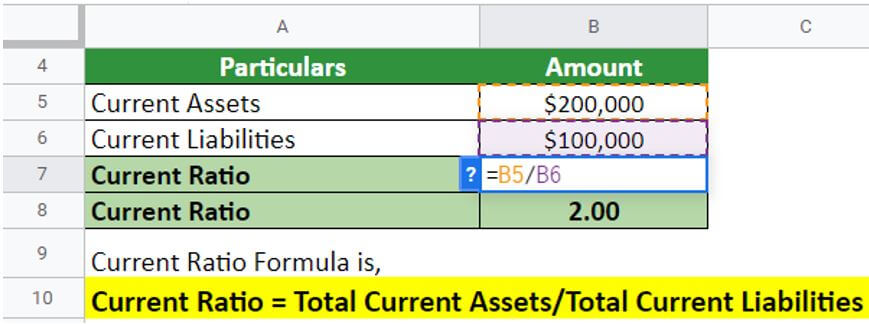
Food & Hangout outlet sells fast food items in Texas. As a business expansion strategy, the company is applying for a loan to open its outlets in the Texas suburbs. The bank asks for the company’s balance sheet to analyze its current liquidity position. According to Food & Hangout outlet’s balance sheet, current liabilities were $100,000, and current assets were $200,000. Calculate the current ratio for the Food and hangout outlet.
Given,
Solution:
The current ratio for Food and hangout outlets is 2, meaning they have enough assets to pay back their current liabilities. It shows that the Food & Hangout outlet’s business is less leveraged and has negligible risk. Banks always prefer a current ratio of more than 1, so the current assets can cover all the current liabilities. Since the Food & Hangout outlet’s ratio is more than 1, it will certainly get the loan approval.
Example #2
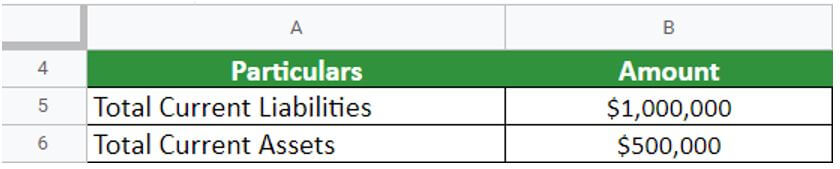
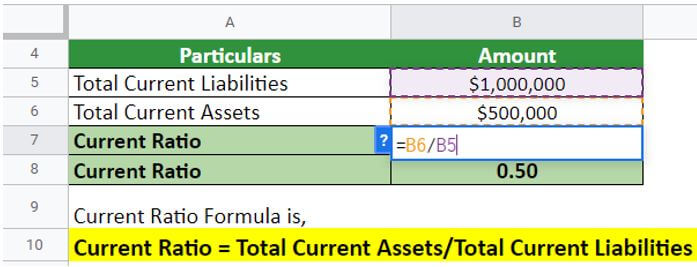
An investor, Alex, wants to choose a technology company to invest in. They want to calculate the current ratio for the technology company XYZ Ltd based in California. The company reports show they have $500,000 in current assets and $1,000,000 in current liabilities.
Given,
Solution:
Based on the calculation above, it can be concluded that for every dollar in current liabilities, the company has only $0.5 in current assets. This indicates that the business is highly leveraged and carries a high risk. Therefore, investing in this company could potentially result in a loss for Alex.
Example #3
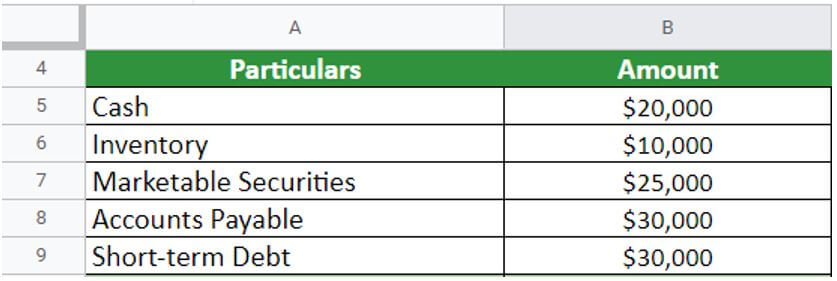
Let’s assume a company ABC holds the following data at the end of the fiscal year 2022:
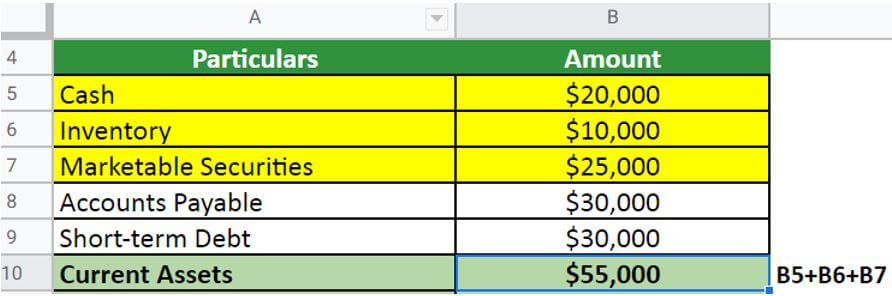
- Cash= $20,000
- Inventory= $10,000
- Marketable securities= $25,000
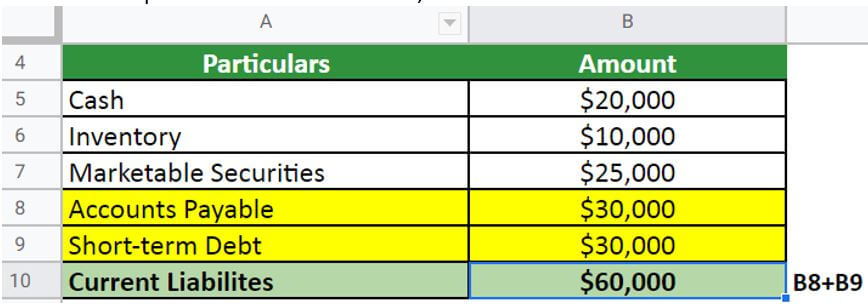
- Accounts payable= $30,000
- Short-term debt= $30,000
Calculate the current ratio for the company ABC.
Given,
Solution:
First, calculate the current assets,
Then, compute the current liabilities,
Implementing the current ratio formula,
The ABC company currently has a ratio of 1, which means paying off its outstanding liability will be difficult. A 1 or less than 1 ratio indicates that the company’s due obligation is more than its assets. In such a case, the ABC company will convert short-term assets into payable cash within this time.
Real-World Examples
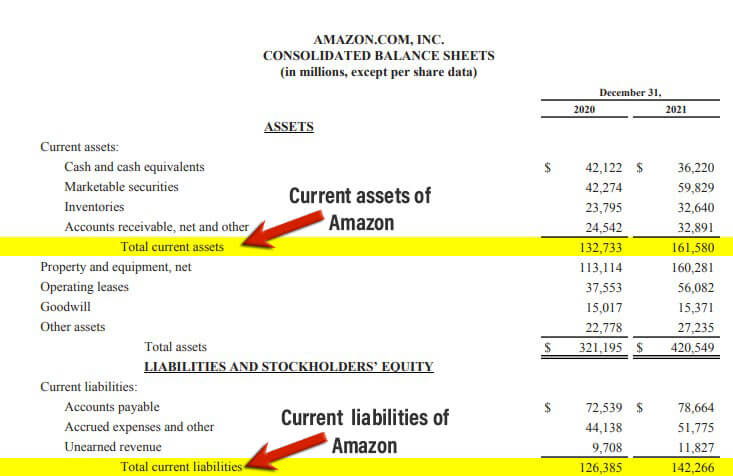
#1 Amazon’s Current Ratio
Here is an example of Amazon Inc., where the company provided the current assets and liabilities data in its annual report for the financial year ending on December 31, 2021.
(Image Source: Amazon’s Annual Report 2021)
From the balance sheet, one can infer that the company’s current assets were worth $161,580, and the current liabilities were $142,266. Let’s find the company’s ratio by implementing the current ratio formula.
As per the annual report of Amazon:
Current assets: $161,580
Current liabilities: $142,266
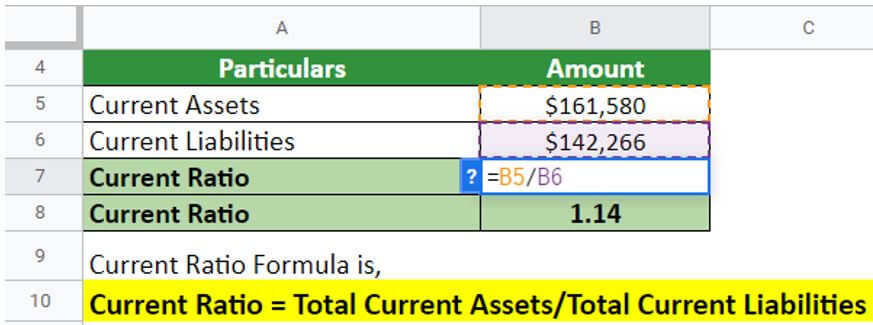
Solution:
Implementing the current ratio formula:
Current Ratio = $161,580/$142,266 = 1.14
Thus, Amazon’s Current Ratio for 2021 is 1.14. A low current ratio (values less than 1) can indicate that a firm struggles to meet current obligations. However, it can also reflect the organization’s ability to borrow against good prospects to meet current obligations. Strong businesses that can turn inventory faster than due dates on their accounts payable may also have a current ratio of less than one.
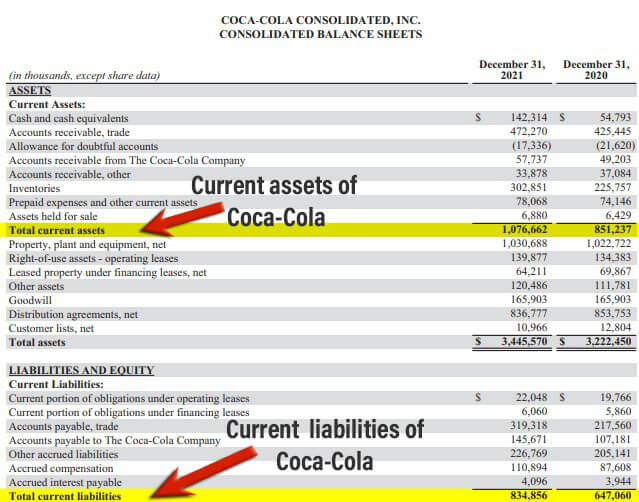
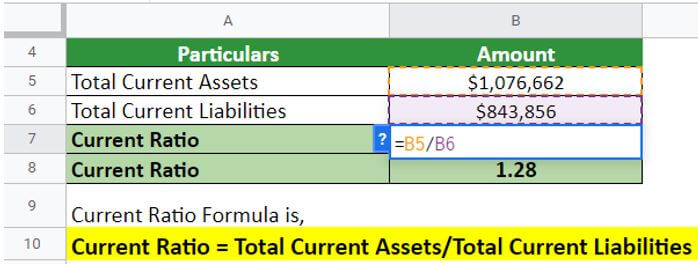
#2 Coca-Cola’s Current Ratio
Here is an example of Coca-Cola, where the company has provided the current assets and current liabilities data in its annual report for the financial year ending on December 31, 2021.
(Image Source: Coca-Cola Annual Report 2021)
From the balance sheet, one can infer that the company’s current assets were worth $1,076,662, and the current liabilities were $834,856. Let’s find the company’s ratio by implementing the current ratio formula.
As per the annual report of Coca-Cola:
Current assets: $1,076,662
Current liabilities: $834,856
Solution:
Implementing the formula:
Current Ratio = $1,076,662/$843,856 = 1.28
Thus, Coca-Cola’s Current Ratio is 1.28 during the year 2021. While a low current ratio (values less than 1) may indicate that a firm is having difficulty meeting current obligations, it may also reflect the organization’s ability to borrow against good prospects to meet current obligations. Strong businesses that can turn inventory faster than due dates on their accounts payable may also have a current ratio of less than one.
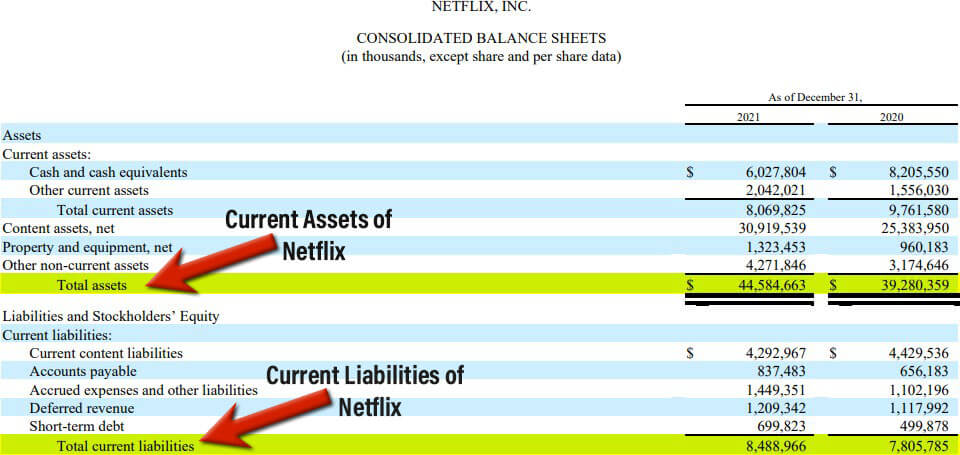
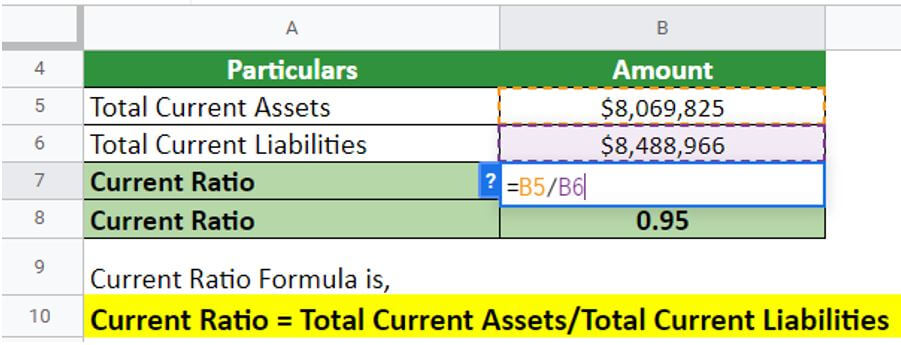
#3 Netflix’s Current Ratio
Here is an example of Netflix.Inc., where the company has provided the current assets and current liabilities data in its annual report for the financial year ending on December 31, 2021.
(Image Source: Netflix’s Annual Report 2021)
From the balance sheet, one can infer that the company’s current assets were worth $8,069,825, and the current liabilities were $8,488,966. Let’s find the company’s ratio by implementing the current ratio formula.
As per the annual report of Netflix:
Current assets: $8,069,825
Current liabilities: $8,488,966
Solution:
Implementing the current ratio formula:
Current Ratio = $8,069,825/$8,488,966 = 0.95
Thus, Netflix’s Current Ratio is 0.95 during the year 2021. A low current ratio (values less than 1) may indicate that a firm is having difficulty meeting current obligations; however, it may also reflect the organization’s ability to borrow against good prospects to meet current obligations. Strong businesses that can turn inventory faster than due dates on their accounts payable may also have a current ratio of less than one.
Current Ratio on the Balance Sheet
To calculate a company’s current ratio, one needs to determine its current assets and liabilities, which can be found on its balance sheet.
The following are examples of current assets that can be found on a company’s balance sheet:
- Cash & cash equivalents
- Short-term deposits
- Marketable securities
- Trade & account receivables
- Inventories
- Trade and prepaid expenses
- Other current assets, etc.
On the other hand, current liabilities include:
- Short-term debt to be repaid within 1 year
- Trade & account payables
- Current portion of long-term debt
- Accrued expenses
- Taxes payables
- Deferred revenue, etc.
Here is an example to better understand it:
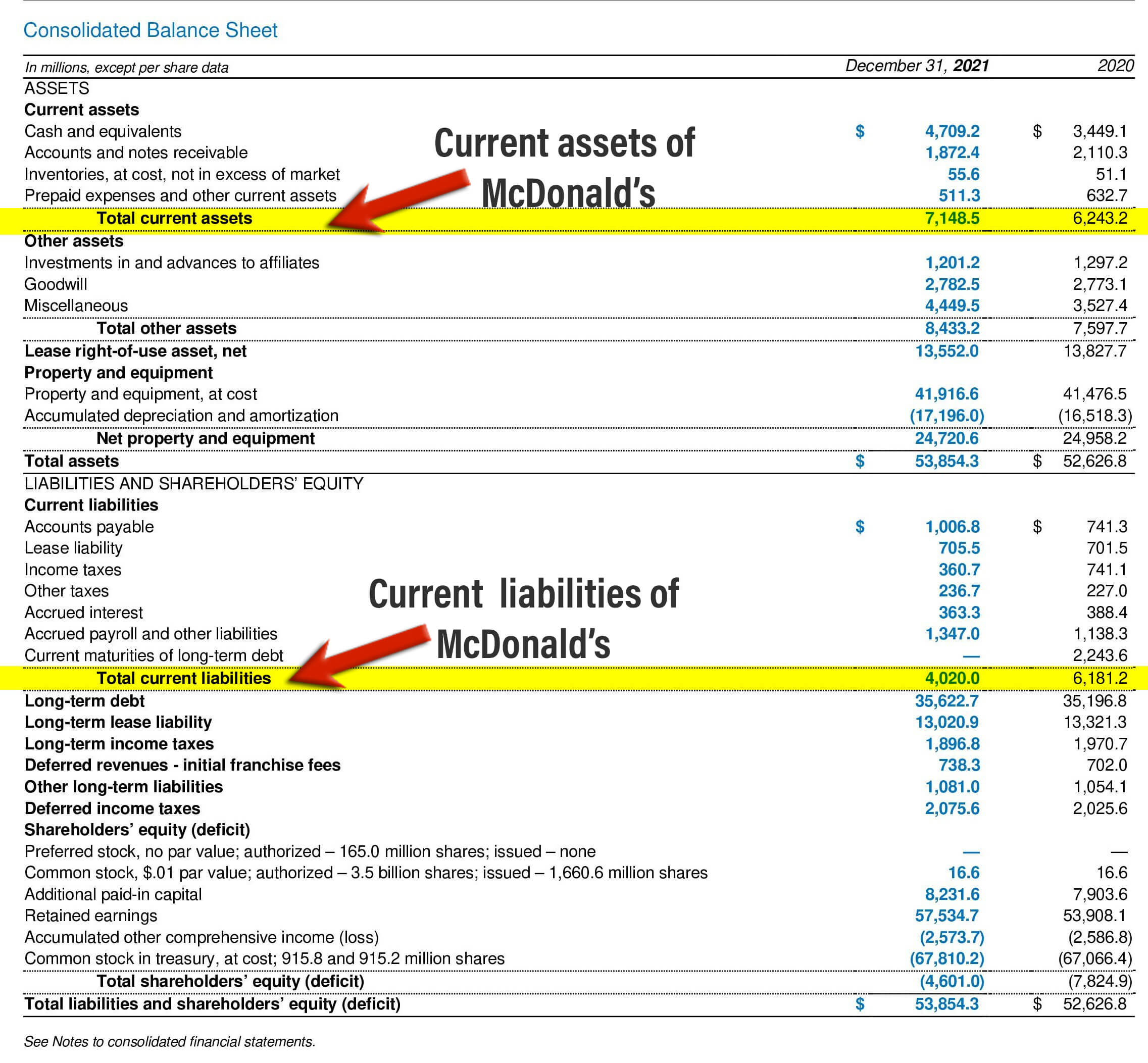
#Example- McDonald’s
In the annual report of 2021, one can find the balance sheet of McDonald’s, which reflects the current assets and liabilities the company holds. Attached below is its representation:
(Image Source: McDonald’s Annual Report 2021)
Referring to the balance sheet, the company’s current assets for the fiscal year 2021 are $7,148.5, while the current liabilities are $4,020. The factors contributing to these amounts are as follows:
| McDonald’s Current Assets (Amount in Millions) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $4,709.2 |
| Accounts and notes receivable | $1,872.4 |
| Inventories | $55.6 |
| Prepaid expenses & other assets | $511.3 |
| McDonald’s Current Liabilities (Amount in Millions) | |
| Accounts payable | $1,006.8 |
| Lease liability | $705.5 |
| Income tax | $360.7 |
| Other taxes | $236.7, |
| Accrued interest | $363.3 |
| Account payroll and other liabilities | $1,347 |
Implementing the current ratio formula, the ratio of McDonald’s will be 1.77. Here, one divides the company’s current assets of $7,148.5 by its current liabilities of $4,020.0.
Thus, it can be concluded that the ratio of McDonald’s is good, indicating that the company can easily pay off its obligations.
Average Current Ratio: Industry-Wise
| Industry | Average Current Ratio for 2021 |
| Real Estate | 5.21 |
| Legal Services | 1.17 |
| Health Services | 4.60 |
| Textile Products | 2.62 |
| Food Products | 2.63 |
| Electronic and Electrical Equipment | 5.08 |
| Agricultural Services | 154.05 |
| Oil and Gas Extraction | 3.77 |
| Chemical Products | 7.91 |
| Primary Metal Industries | 2.58 |
(Source: ReadyRatios)
Current Vs. Quick Ratio
| Current Ratio | Quick Ratio |
| The current ratio, or working capital ratio, helps calculate the proportion between the current assets and liabilities. | The quick ratio, or acid test ratio, helps calculate the proportion between the most convertible assets and current liabilities. |
| Finds a company’s ability to pay off its outstanding obligations within a fixed time period. | Finds a company’s ability to pay off any urgent obligation or requirement that arises. |
| Accounts for the assets that can be convertible to cash within a time period of 12 months. | Accounts for the assets that are convertible to cash within a time period of 90 days or less. |
| Considered a relaxed approach towards paying off a company’s obligations. | Considered a more strict or rigid approach towards paying off a company’s obligations. |
| The favorable ratio for it is 2:1. | The favorable ratio for it is 1:1. |
Importance of Current Ratio Formula
- The current ratio formula accurately analyzes a company’s overall financial health. Creditors consider this ratio when determining whether to provide short-term debt to a company.
- It also indicates how well management is utilizing working capital. However, using this ratio alone cannot evaluate a company’s short-term liquidity.
- The formula includes all of a company’s current assets and excludes those that are difficult to convert into cash, such as inventory.
- This ratio also reveals information about a business’s operational cycle and ability to sell assets to cover short-term obligations.
- However, it only depicts the company’s financial standing at the present time and does not fully depict its solvency or liquidity.
Calculator
Use the following calculator for Current Ratio formula calculations:
| Current Asset | |
| Current Liabilities | |
| Current Ratio = | |
| Current Ratio = | (Current Asset / Current Liabilities) |
| = | (0 / 0 ) = 0 |
Final Thoughts
The current ratio formula is essential to evaluate whether a company’s liquid assets are sufficient to settle its obligations. To maintain a good ratio, the company must ensure that it utilizes its assets efficiently and maintains a balance where current assets equal or exceed current liabilities. Therefore, paying attention to the current ratio is crucial if a company wants to avoid accumulating debts and obligations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Formula for the Current Ratio in Accounting?
Answer: The formula for the current ratio in accounting is current assets/current liabilities. In this formula, current assets refer to liquid assets, cash, or cash equivalents that can be converted into payable cash within a 12-month period.
Q2. Is the Current Ratio a Percentage?
Answer: Technically, no. The current ratio is depicted in numerical form after the calculation, expressed as a whole number and not a percentage. Moreover, a ratio of more than 1.5 indicates that the company holds more assets than liabilities.
Q3. What Current Ratio is Good? Should it be High or Low?
Answer: The higher the ratio, the greater the capability to pay off due obligations. If a company’s current ratio is low, paying off its debts and liabilities may be challenging. Typically, a ratio of 2 is considered good for a company, and anything below it can be considered bad.
Q4. Differentiate Between the Current vs. Working Capital Ratio Formula.
Answer: Technically, the current and working capital ratios are the same. One calculates the working capital ratio by dividing current assets by current liabilities. It is a financial ratio that measures a company’s liquidity position or simply the ability of a company to pay off its due obligations.
Q5. What is the Current Asset Turnover Ratio Formula?
Answer: The current asset turnover ratio helps compare a company’s performance from the income statement with the financial health of a company from the balance sheet.
The formula for this is:
Net sales refer to the profits made after deducting sales allowances, discounts, and returns. Average total assets refer to the average aggregate assets at the end of the current or previous fiscal year.
Q6. What is a Too-High Current Ratio?
Answer: A ratio as high as 3 or more indicates that the business is not utilizing its assets effectively. It might mean that the business is not using its working capital efficiently, and there might be some loopholes, too.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further articles for expanding understanding: