What are Current Assets?
If you are new to finance or business, you may have heard the term “current asset” used often, but you may not be entirely sure what it means. In the simplest terms, these assets are those owned by a company that they can sell, consume, or are cash convertible in the accounting period.
Typically companies use these assets to fund their day-to-day operations, and they play a crucial role in a company’s financial health. Its examples include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments.

Explanation
Current assets reflect a company’s liquidity (ease of converting to cash) and solvency (financial stability). We consider a company with many current assets financially healthy because it has the resources to meet its short-term obligations. On the other hand, a company with few such assets may struggle to pay its bills on time, which could lead to financial trouble.
Another important thing to note about such assets is that they can vary significantly from one company to the next. For example, a retail company may have a lot of inventory as a current asset, while a consulting firm may have more accounts receivables as current assets. Therefore, understanding the composition of a company’s liquid assets can give you valuable insights into its operations.
Where are Current Assets Located on the Balance Sheet?
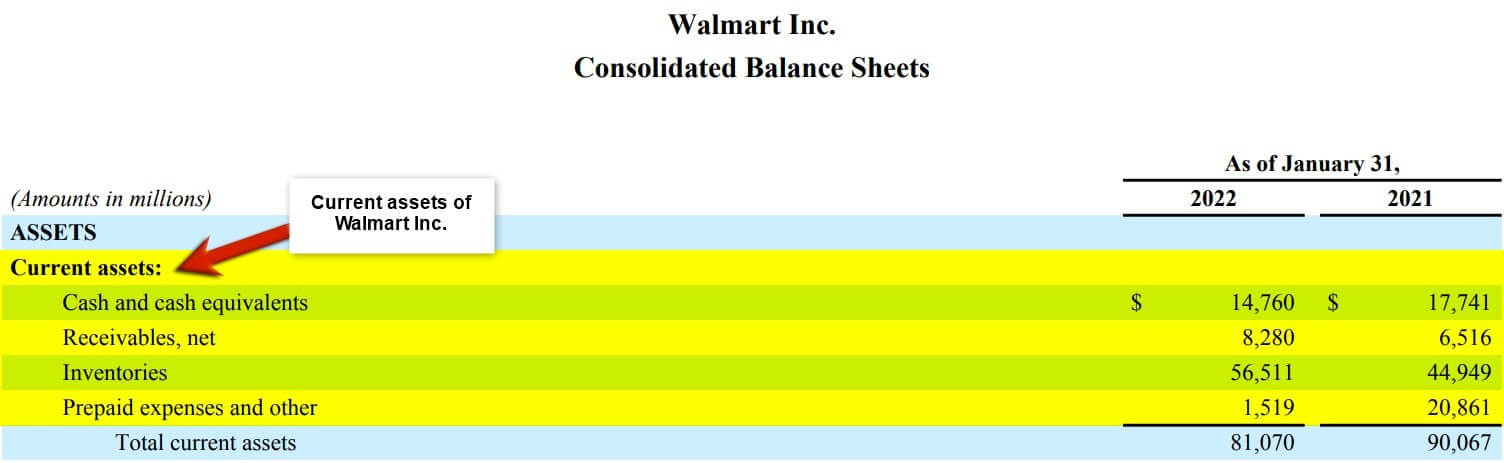
(Annual Report of Walmart Inc. for the FY22)
We always list the current assets at the top of the asset section of the balance sheet above long-term assets. These assets are expected to be used up or turned into cash quickly. In contrast, long-term assets will likely provide benefits over a longer time.
Additionally, it is important to understand that the order in which assets we list the assets on a balance sheet is not arbitrary. The order is based on the liquidity of the assets, which means that the most liquid assets are listed first. It helps investors and stakeholders understand a company’s financial health and how quickly it can access cash in an emergency.
Current Assets List
#1 Cash and cash equivalents
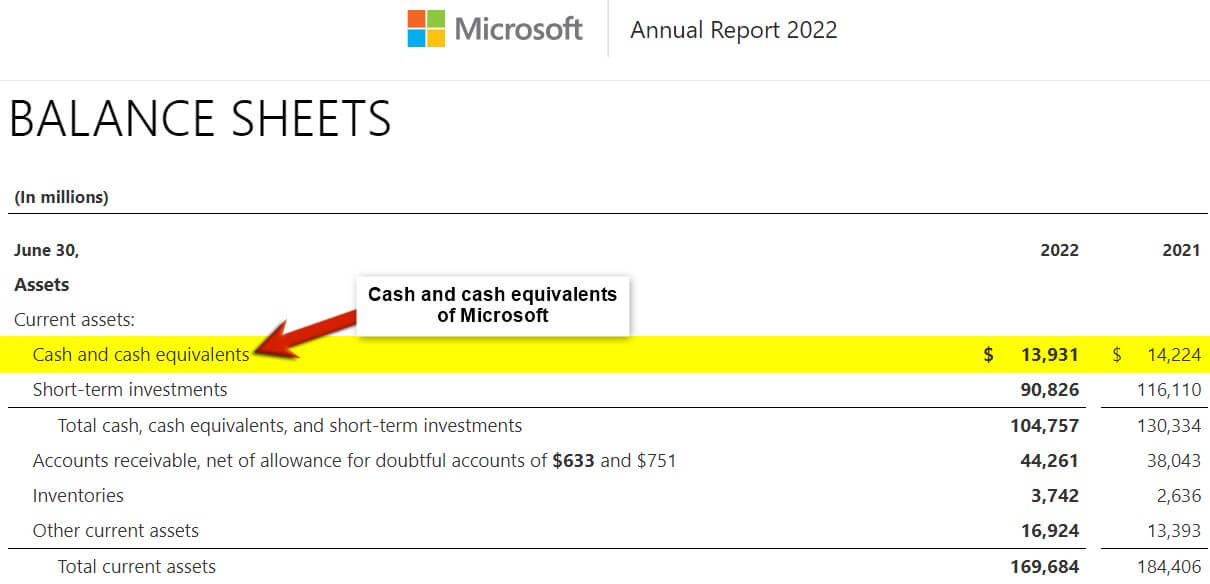
(Annual Report of Microsoft for FY22)
Cash equivalents are short-term investments easily convertible into cash, usually within 90 days. They are secure, very liquid (easy to sell), and include money market funds, treasury notes, and commercial paper. They are also easy to trade and determine their worth. As a result, one of the fundamental principles of cash management is that funds should be kept active. Instead, businesses should invest extra money in these tradable assets.
#2 Accounts receivables
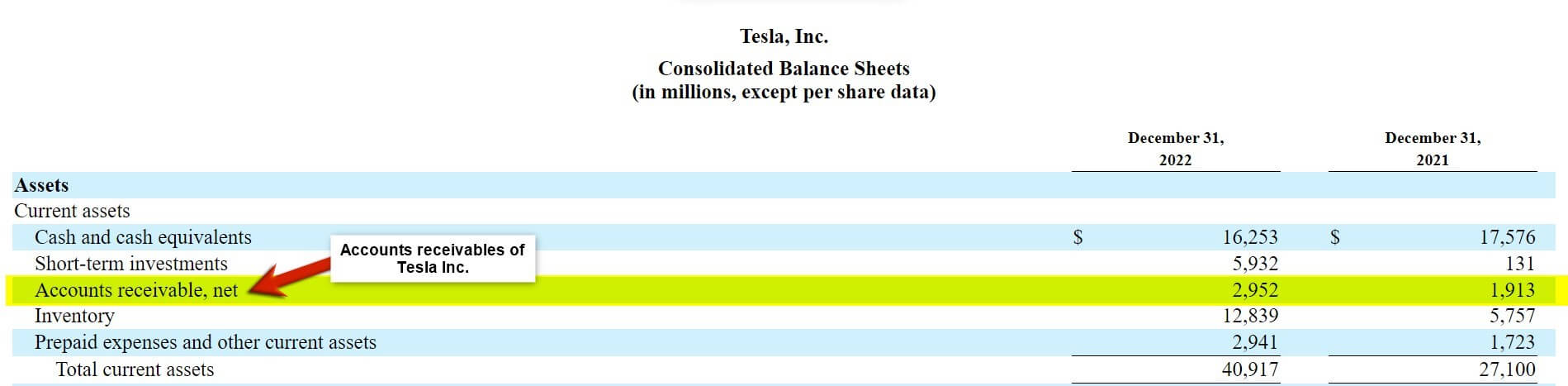
(Annual Report of Tesla Inc. for FY22)
The above image shows that in FY22, Tesla Inc. has accounts receivable worth $2,952, almost one time higher than in FY21. It means $2,952 is a due balance to Tesla yet receivable from its customers. Thus, when a company sells its goods or services, and the customer doesn’t pay for them, it is called accounts receivable. It means the company has delivered its services or goods to its customers. However, it is yet to receive the payment for the goods or services.
Accounts receivable are listed as current assets because they are cash convertible within a few months to a year. A company’s general ledger will typically reflect its total accounts receivable balance. However, to determine the outstanding payments made by each customer, the company has to refer to its accounts receivable subsidiary ledger.
#3 Inventory
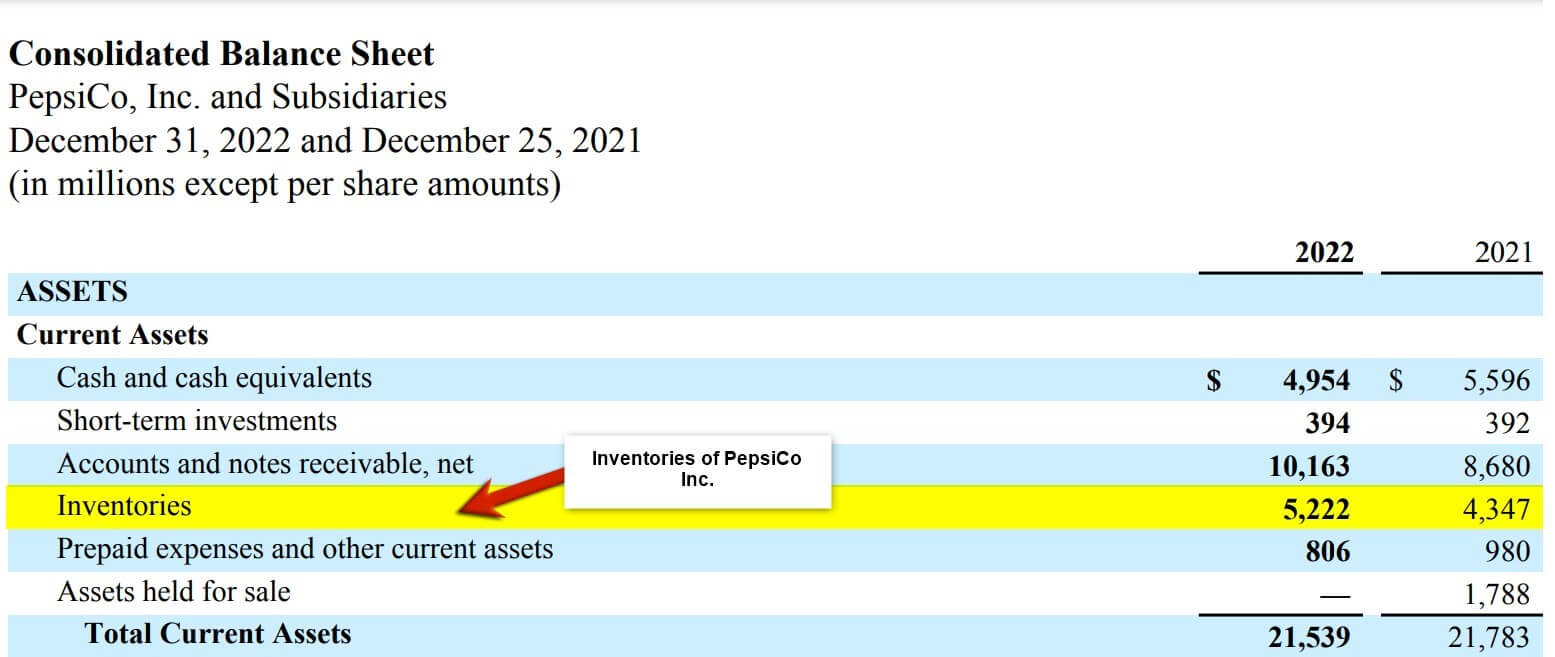
(Annual Report of Pepsico Inc. for FY22)
In the above image, we can see that PepsiCo Inc. has around $5,222 as inventories for FY22, which is almost 1.25 times more than FY21. In general, inventories refer to the goods, merchandise, items, materials, or work in progress that a company holds and for sale that will eventually generate profit. Inventories are regarded as one of a company’s most valuable assets because they are one of the main sources of revenue generation. Thus, it is a great source of profits for the company’s shareholders. There are three types of inventories:
- The finished goods the business has in stock for everyday business operations.
- The products that are still in the production stage (work-in-progress)
- The raw materials that the company uses for the manufacturing of goods.
However, if the business holds these items for over a year, they are not counted as liquid assets. They will become non-liquid assets.
#4 Marketable securities
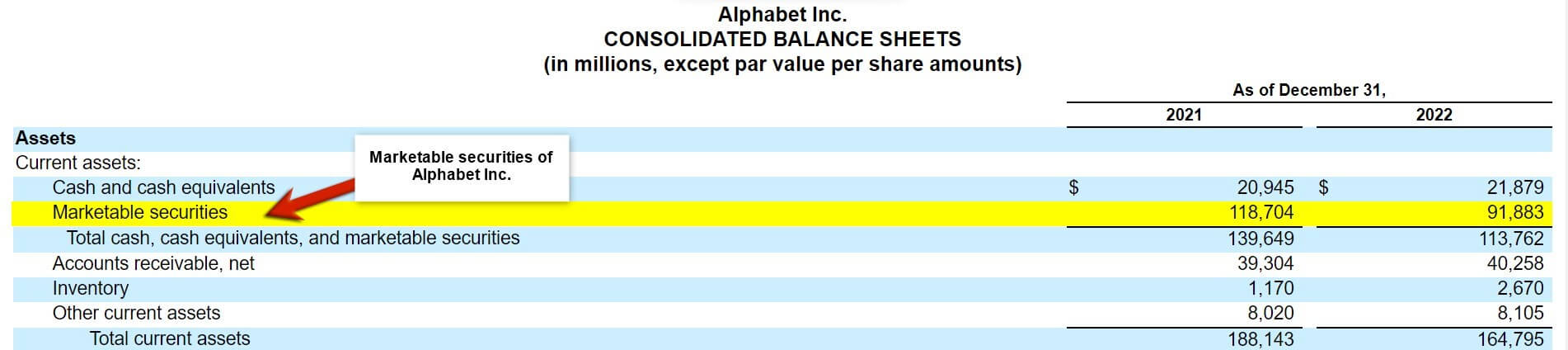
(Annual Report of Alphabet Inc. for FY22)
From the above image, we can interpret that Alphabet Inc. has marketable securities worth $118,704 in FY22, significantly higher than in FY21. Simply put, marketable securities are financial assets that are easily and readily tradable in the financial markets and are easily convertible into cash. These are typically short-term investments that can be bought or sold quickly with minimal impact on their market price. Therefore, proper accounting and managing these securities are crucial for a company’s financial health and stability.
Moreover, they are of two types; debt securities and equity. It’s important to note that there are different accounting treatments for different types of securities:
- We record trading securities at fair value, where the changes in value will reflect in the income statement.
- Registration of available-for-sale securities is always at a fair value, but changes in value will reflect in the comprehensive income statement.
- Recording of held-to-maturity securities is at amortized cost, and changes in value will not reflect in the income statement.
#5 Prepaid expenses
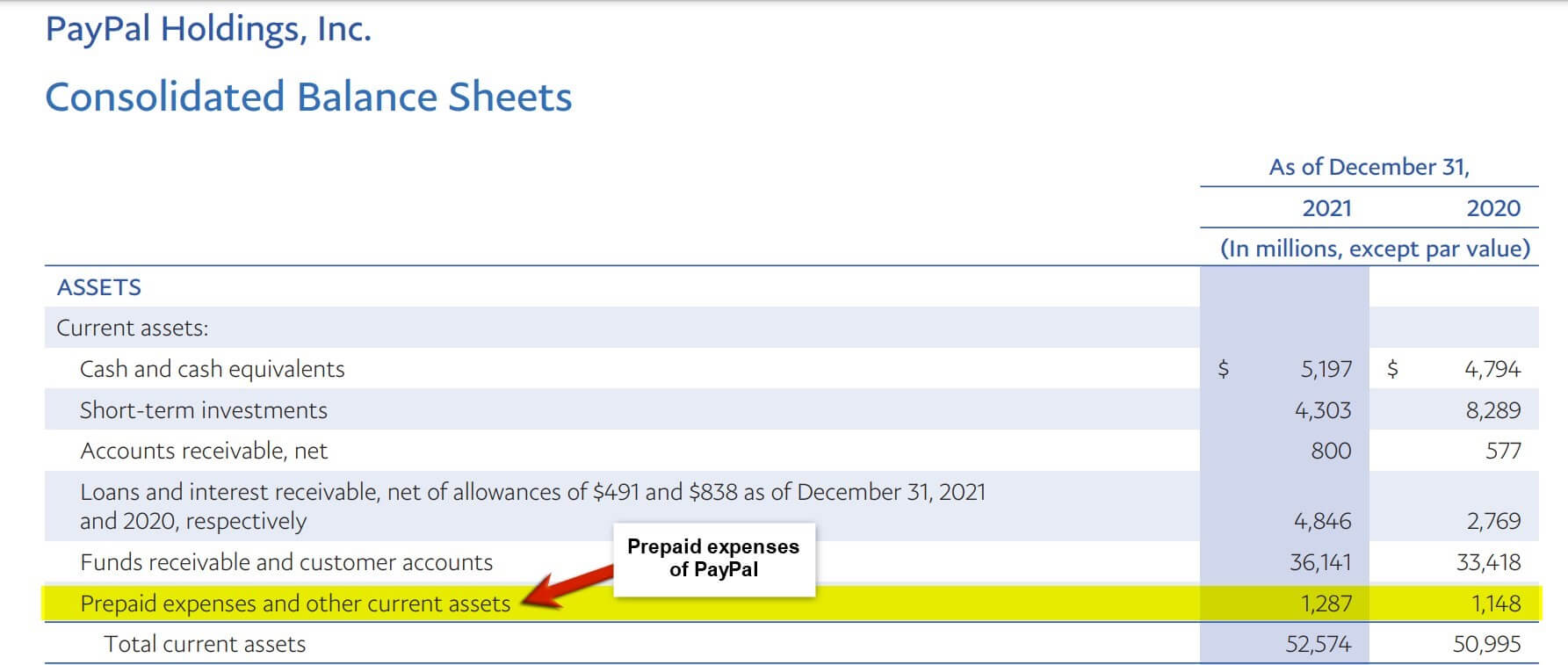
(Annual Report of PayPal Holdings Inc. for FY22)
The highlighted part in the image represents the prepaid expense of PayPal Inc. for FY22 and FY21, which is $1,287 and $1,148, respectively. Here, prepaid expenses refer to expenses paid for in advance but have yet to be consumed or used. In accounting, prepaid expenses are treated as an asset because the payment gets settled in advance, and somebody will receive the benefit or service in the future. A company will reflect its prepaid expenses under short-term or current assets on the balance sheet. Gradually, the company will use the services that will decrease the prepaid expenses.
For example, if a firm pays for a year-long lease, it is a prepaid expense, recorded as a current asset for the year. However, after the end of the renting period, the prepaid amount will be recorded as an expense on the balance sheet.
#6 Supplies
(Annual Report of Exxon Mobil Corporation for FY22)
The above image represents the balance sheet of Exxon Mobil Corporation, where we can interpret that the company’s supplies have decreased from FY21 to FY22. Here, supplies are the line of items used or consumed by a business daily. Businesses must track supply usage to ensure they have an appropriate amount to meet operational needs without wasting money on excess inventory. Once a company uses all its supplies, they are no longer considered an asset, and its cost becomes an expense. Also, the amount of supplies used is recorded in the income statement as part of the cost of goods sold or operating expenses, depending on the nature of the supplies.
#7 Other Liquid Assets
(Annual Report of Nike Inc. for FY22)
The above balance sheet of Nike Inc. represents the other liquid assets of the company, which have significantly grown from $1,498 (FY21) to $2,129 (FY22). Here, other liquid assets mean any assets a company can quickly turn into cash. This category includes deferred tax assets recorded as assets on a company’s balance sheet. These assets occur when a company pays taxes before they are required to. It creates a temporary difference in taxes payable. Moreover, these deferred tax assets can help companies reduce their future tax expenses.
The Formula of Current Assets
We derive the formula; we add all the cash-convertible assets acquired during the financial year. The formula is as follows:
Examples of Current Assets
Download the Excel template here – Current Assets Excel Examples
Example #1
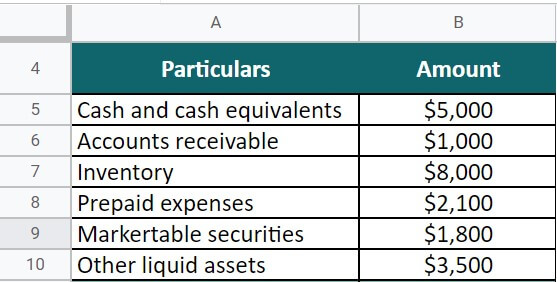
John & Co. is a retail business that has highlighted the information below to prepare its financial statements. Calculate the short-term assets for John & Co.
- Cash and cash equivalents = $5,000
- Accounts receivable = $1,000
- Inventory = $8,000
- Prepaid expenses = $2,100
- Marketable securities = $1,800
- Other liquid assets = $3,500
Given,
Solution:
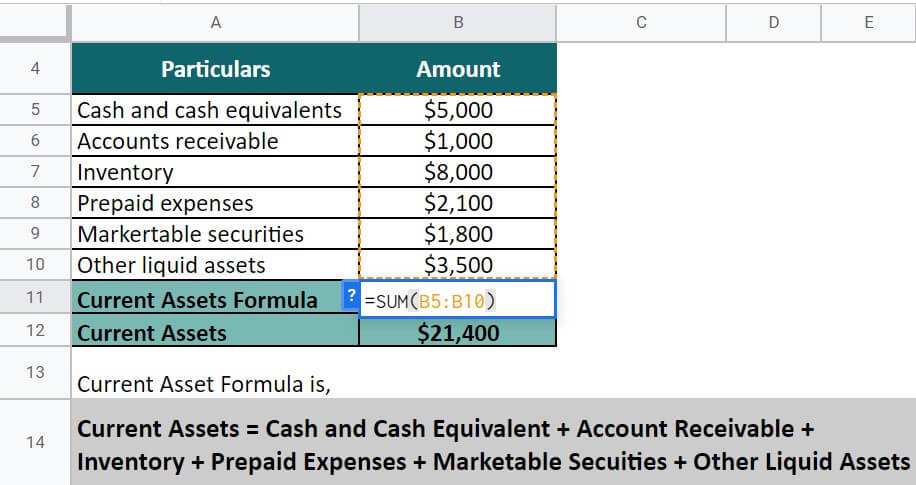
For calculating the liquid assets, we will implement the below formula:
Current Assets = Cash and Cash Equivalent + Account Receivable + Inventory + Prepaid Expenses + Marketable Securities + Other Liquid Assets
Current Assets = $5,000 + $1,000 + $8,000 + $2,100 + $1,800 + $3,500
= $ 21,400
Therefore, the short-term assets for John & Co. are $21,400, shown in their balance sheet. Investors can use this number to assess the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and manage day-to-day operations.
Example #2
Retail King needs to calculate its short-term assets to prepare its balance sheet. Given below is its financial information.
- Cash and cash equivalents = $8,000
- Accounts receivable = $2,500
- Inventory = $7,800
- Prepaid expenses = $1,800
- Marketable securities = $2,000
- Other liquid assets = $4,000
Given,
Solution:
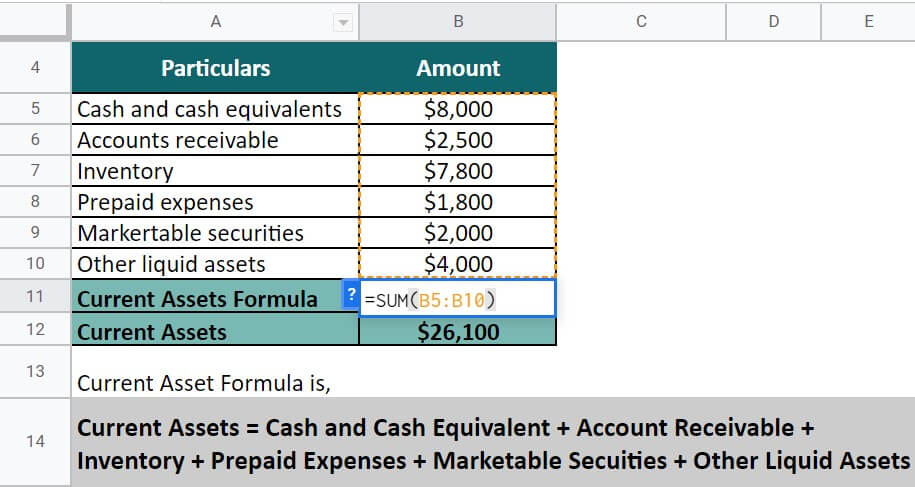
To find out the short-term assets, we will use the below formula:
Current Assets = Cash and Cash Equivalent + Account Receivable + Inventory + Prepaid Expenses + Marketable Securities + Other Liquid Assets
Current Assets = $8,000 + $2,500 + $7,800 + $1,800 + $2,000 + $4,000
= $ 26,100
So, after the calculation, the resultant current assets for Retail King is $26,100
Real-world Examples
#1 Starbucks Corporation
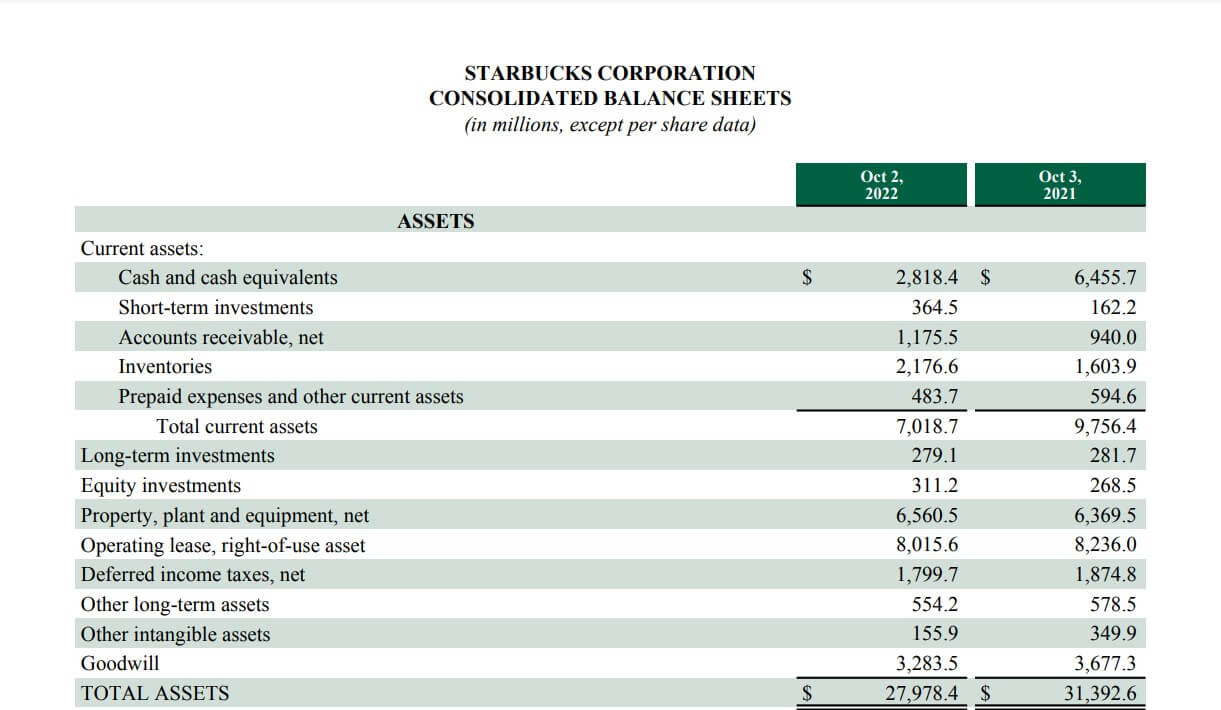
Let’s take the example of the famous coffee chain; Starbucks and calculate its liquid assets by analyzing its balance sheet.
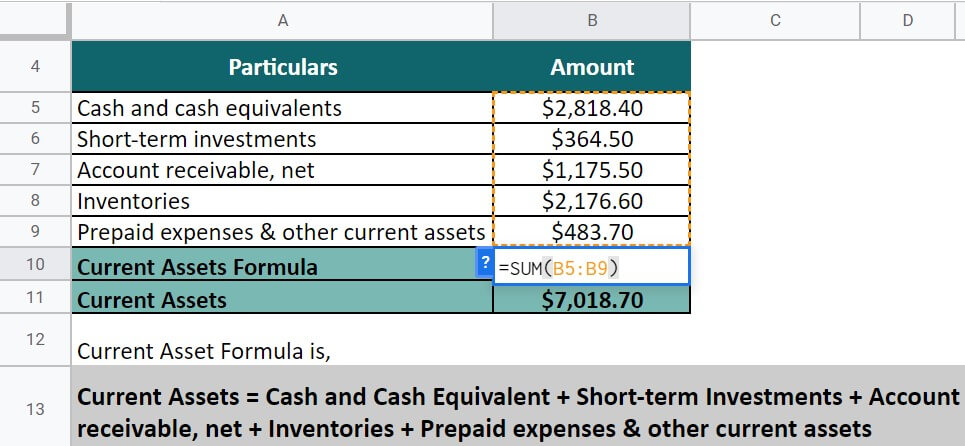
(Annual Report of Starbucks Corporation for FY22)
Given,
Solution:
We have to implement the below formula to calculate the liquid assets
Current Assets = Cash and Cash Equivalent + Short-term Investments + Inventories + Account receivables, net + Inventories + Prepaid expenses & other short-term assets
Current Assets = $2,818.40+ $364.50 + $1,175.50 + $2,176.60 + $483.70
= $7,018.70
So, after the calculation, the short-term assets of Starbucks are $7,018.70.
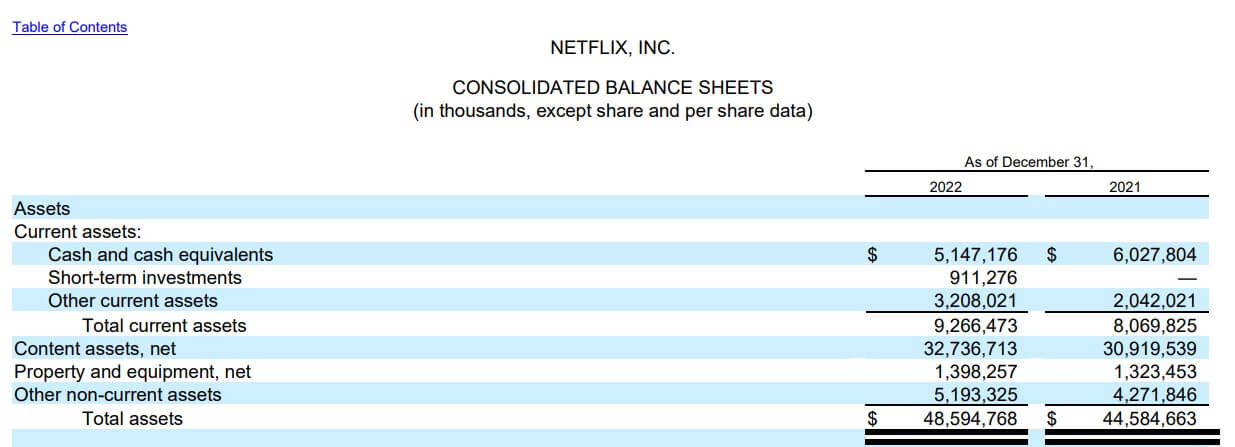
#2 Netflix Inc.
Netflix Inc. has provided the below information on its balance sheet. Calculate the current assets for the company using the given data:
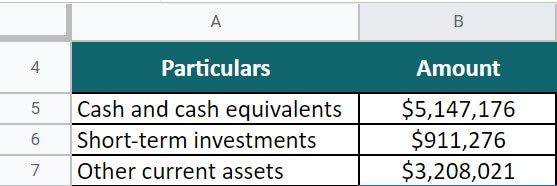
- Cash and cash equivalents = $5,147,176
- Short-term investments = $911,276
- Other current assets = $3,208,021
(Annual Report of Netflix Inc for FY22)
Given,
Solution:
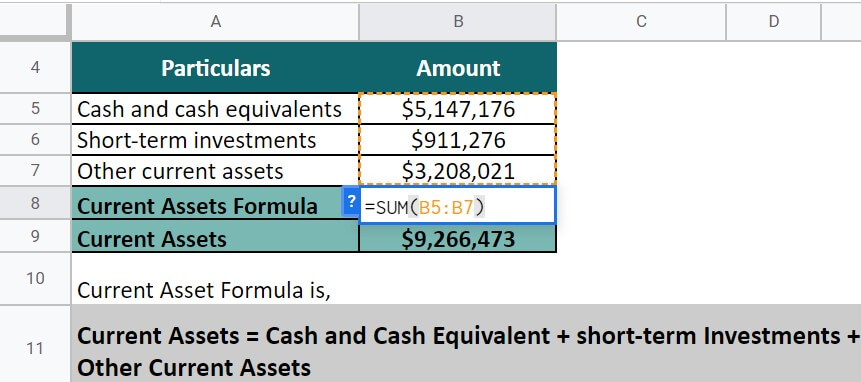
Current Assets = Cash and Cash Equivalent + Short-term Investments +Other Liquid Assets
Current Assets = $5,147,176 + $911,276 + $3,208,021
= $9,266,473
Thus, Netflix Inc. records liquid assets worth $9,266,473.
Examples of Each Type of Current Assets
|
Types |
Examples |
| Cash and cash equivalents | Petty cash, bank deposits, money market funds |
| Accounts receivable | Invoices awaiting payment from customers |
| Inventory | Raw materials, finished goods, work in progress |
| Marketable securities | Treasury bills, commercial papers, government bonds |
| Prepaid expenses | Rent paid in advance, insurance premiums |
| Accrued income | Interest income, dividends |
| Other liquid assets | Advances to suppliers, deposits paid, tax refunds due |
Current Assets vs Non-Current Assets
|
Current Assets |
Non-Current Assets |
| These are Short-term investments | These are Long-term investments |
| These can be liquidated or spent in one fiscal year. | These aren’t so easy to liquidate, and their expected life is at least more than one year. |
| The companies use these for immediate needs | The companies use these for their future needs |
| These can be easily convertible into cash | These are not easily convertible into cash |
| These refer to payments or money. | These are the kind of resources that help in making a profit for the company. |
| They sit at the top of the balance sheet of the company | They sit at the bottom of the balance sheet of the company |
| Depreciation does not apply to short-term assets | Depreciation does apply to non-liquid assets |
Conclusion
The current asset is any asset expected to be sold, realized, or consumed within a short period or converted into cash in hand or any liquid. This act is the blood of any organization which maintains its day-to-day business operations. Determining and maintaining adequate asset levels is crucial for business entities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are fixed assets current assets?
Answer: No, we can’t classify fixed assets as current assets. Current A company uses its liquid assets in day-to-day operations, and they use it within one year. On the contrary, fixed assets are those used in the production process and have a useful life lasting longer than one year. This category of non-liquid assets may include land, buildings, machinery, and vehicles.
Q2. Are intangible assets current assets?
Answer: We don’t list intangible assets as current assets but rather as non-current or long-term assets. These assets are investments that will benefit the company over time, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks.
Q3. What is the current asset’s liquidity order?
Answer: The current assets liquidity order is how businesses list such assets in order of their liquidity. Generally, the most liquid assets are listed first, and the least liquid assets are listed last. This order gives businesses a clear picture of how quickly they can convert their liquid assets into cash. Commonly, this order consists of accounts receivables, prepaid expenses, cash flows, temporary investments, and inventories.
Q4. What is the current assets turnover ratio formula?
Answer: The current assets turnover ratio is a key metric in understanding a company’s efficiency in generating sales and revenue. This ratio is calculated by taking a company’s net sales and dividing it by its average total assets. The formula is:
Current assets turnover ratio = Company’s net sales / Average total assets.
A higher ratio indicates that a company uses its assets more efficiently to generate sales and revenue, while a lower ratio indicates that it could use its assets more effectively.
Q5. What is the difference between current assets and current liabilities?
Answer: The essential difference between liquid assets and liabilities is converting time into cash. Current assets can be converted into cash within one fiscal year or an operating cycle, whereas current liabilities are obligations a company must pay within one year.
Examples include inventory, cash, and accounts receivables. Current liabilities include wages payable, accounts payable, and principal payments. In short, they are short-term resources that can be cash convertible, while current liabilities are short-term obligations that a company must pay within a year.
Recommended Articles
It is a guide to Current assets. Here we also discuss the introduction to liquid assets, their types, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –