Cash and Cash Equivalents Meaning
Cash and Cash Equivalents are items on a company’s balance sheet that refer to the value of assets held in cash or easily converted to cash.
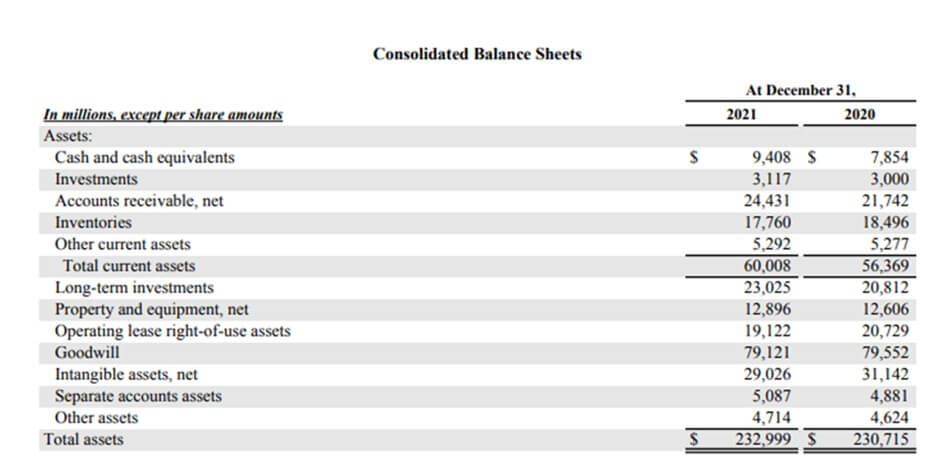
For example, CVS Health, an American healthcare company, shows $9,408 million as cash and cash equivalents in its balance sheet as of 31st December 2021. It is an increase from 2020’s report of $7,854 million. It signifies that the firm has high liquidity and is healthy.
(Image Source: CVS Health Annual Report 2021)
Key Highlights
- Cash and Cash Equivalent is readily accessible funds that can help pay for sudden expenses
- It includes physical currency and any funds that can easily convert into cash. It has short-term investments, such as money market funds and commercial paper
- A business’s amount on hand can be a good indicator of its financial health. Companies need to maintain liquidity and meet their financial obligations
- Businesses should carefully monitor their assets, as they can be susceptible to theft and fraud.
Explanation
Cash and cash equivalents refer to the value of a company’s assets like short-term bonds, treasury bills, commercial papers, etc. Marketable securities and money market holdings are equivalent to cash because they are highly liquid and do not have material deviations in value. Bank accounts and marketable securities are cash equivalents, just like debt securities.
It is generally for those assets whose maturity is less than three months or 90 days. When a business records it on its balance sheet, it is the total money it has on hand. All businesses must identify it in their annual report.
A business with a large amount of cash is in a better position to weather unexpected expenses or take advantage of opportunities as they arise. It is generally efficient enough to meet its short-term obligations. They offer liquidity to the company.
Cash and Cash Equivalents On the Balance Sheet (Financial Statement)
It is generally available in a company’s balance sheet under the current asset section with the same name as cash and cash equivalent, and only the overall value is present.
A note provides the breakup of the overall sum at the end of the financial statement. The cash and cash equivalent will generally bear a number beside its total, which describes the serial number in the notes section to understand the breakup of the cash and cash equivalent.
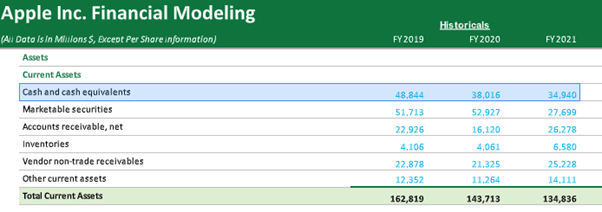
(Image Source: Apple Inc Annual Report 2021)
Real Company Examples
Example #1-Apple Inc.
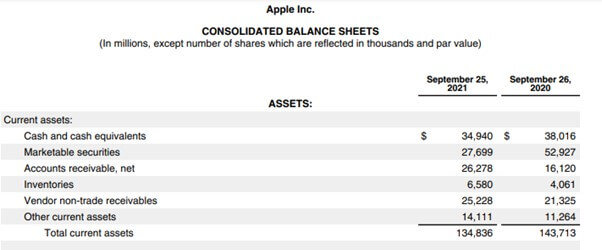
(Image Source: Apple Inc Annual Report 2021)
According to the 2021 financial statement by Apple Inc, its total cash and cash equivalents are $34,940 million.
- Cash= $34940 million
- Total assets=$351002 million
- Cash as % of Total Assets= 9.95%
- Total Sales= $297392 million
- Cash as % of Total Sales= 11.74%
The cash-to-total asset ratio of the company is 9.95% which is not very significant. Similarly, the cash-to-sales ratio is 11.74 %, which indicates that most sales are in credit. The company is not thinking of any heavy investment in the future as its cash reserves are unlimited compared to the total assets.
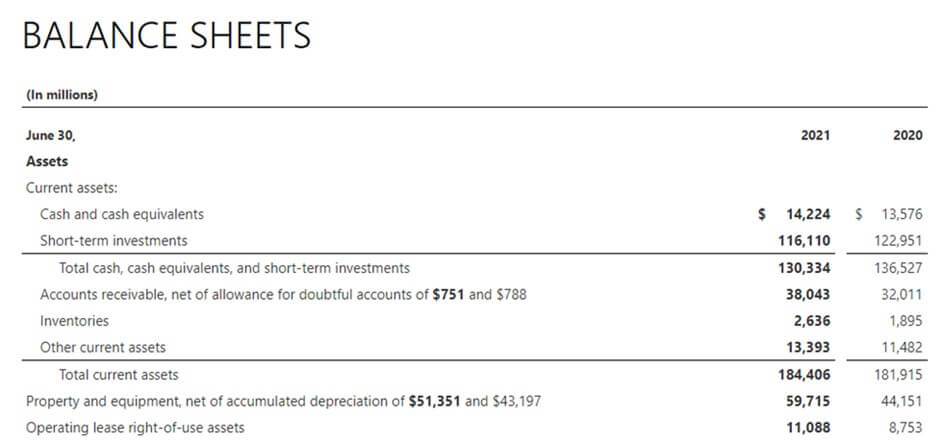
Example #2-Microsoft Corporation
(Image Source: Microsoft Annual Report 2021)
The financial statement of Microsoft shows that the value of assets has increased in the financial year 2021 for the company.
- Cash= $14224 million
- Total sales in 2021= $168088 million
- Cash % of Total Sales (2021) = 8.46%
- Total sales in 2020= $143015 million
- Cash % of Total Sales (2020) = 9.94%
The cash-to-sales ratio for 2021 has decreased to 8.46% compared to 9.94% in 2020. According to the acquisition strategy, we can assume that the company is not thinking of any new acquisitions in the future as they have not increased their cash reserves over 12 months.
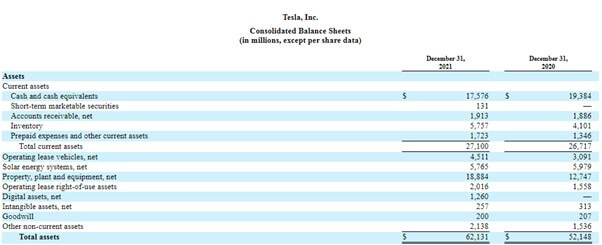
Example #3-Tesla Inc.
(Image Source: Tesla Annual Report 2021)
The above extract from the financial statement of Tesla Inc. shows a cash and cash equivalent of $17,576.
- Cash= $18144 million
- Total assets= $62131 billion
- Cash as % of Total Assets= 29.20%
- Total Sales=$53823 million
- Cash as % of Total Sales= 33.71%
Cash as a percentage of total assets is 29%. The company might be thinking of business acquisitions in the future as cash reserves are significantly higher according to industry standards. If the company is not thinking of an acquisition, it should invest in short-term or long-term investments to earn interest income.
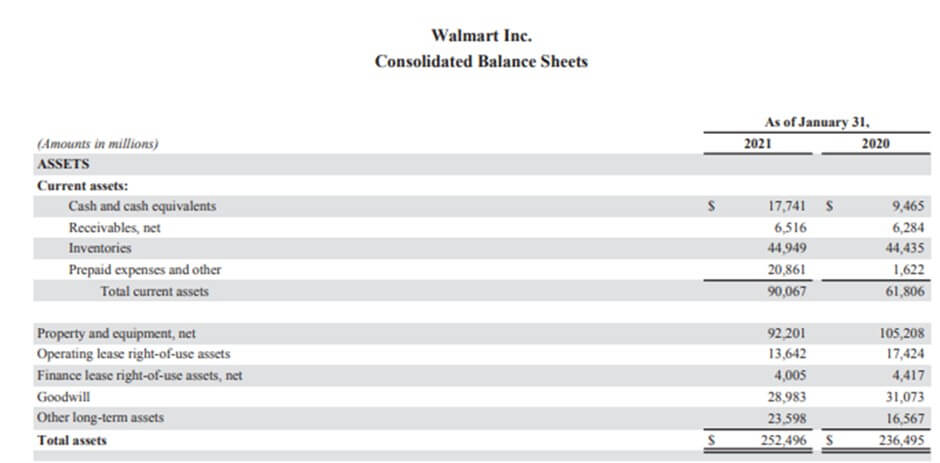
Example #4- Walmart
(Image Source: Walmart Annual Report 2021)
The value of cash and cash equivalent balance with Walmart Inc. was $17,741 for the financial year 2021.
- Cash= $252496 million
- Total sales in 2021= $559151 million
- Cash % of Total Sales (2021) = 45.15%
- Total sales in 2020= $523964 million
- Cash % of Total Sales (2020) = 48.19%
In both financial years, the percentage cash of total sales is significantly higher compared to industry standards. The company should invest in short-term or long-term investments for a certain proportion of it. They might lose an opportunity to earn interest income on extra cash Reserves.
Formula
The formula is,
- It includes assets such as paper money, accounts, deposits, receipts, government bills, and more
- It excludes government securities, loans, inventories, AR accounts, etc.
How to calculate it? – Excel Examples
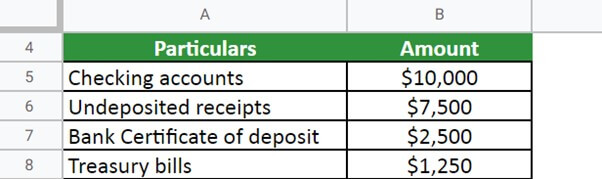
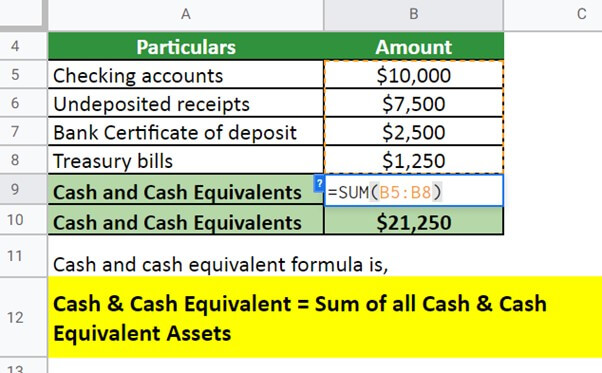
Example #1:
XYZ Ltd has the following items on its balance sheet for the financial year 2021,
- Checking accounts = $10,000
- Undeposited receipts = $7,500
- Bank Certificate of deposit = $2,500
- Treasury bills = $1,250
- Prepaid expenses = $10,000
- Inventory = $3,250
Calculate cash & cash equivalents.
Given,
As inventory and prepaid expenses do not count in cash & cash equivalents, we have,
Solution:
Totalling all the values,
The value of cash and cash equivalent for XYZ Ltd is $21,250.
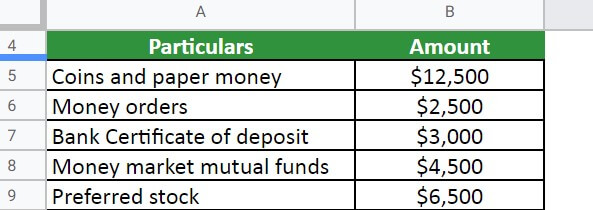
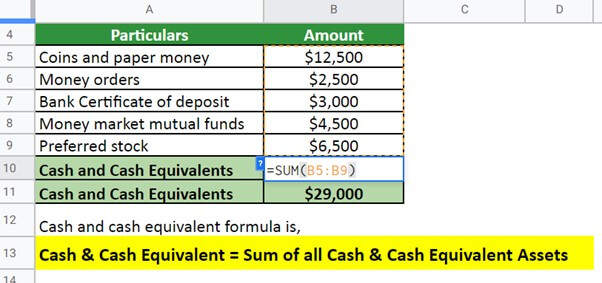
Example #2:
ABC Ltd wants to consider the following to calculate cash and cash equivalent,
- Coins and paper money = $12,500
- Money orders = $2,500
- Bank Certificate of deposit = $3,000
- Money market mutual funds = $4,500
- Preferred stock = $6,500
Given,
Solution:
Implementing the formula,
ABC’s cash and cash equivalent is $29,000.
Types
Bank Account:
- Cash stored in the bank account is the best example for this discussion because it is one of the company’s most liquid assets and can help it repay its short-term obligations.
- It is money in the form of currency, coins, and notes.
- A demand deposit plays a role here. It is an account from which one can withdraw funds at any point in time without informing the business.
Foreign Currency:
- Companies that have a lot of forex transactions may face certain exchange risks.
- It is better to convert the currency to the reporting currency for financial reporting.
- It also includes the gains made in the conversion mode. Still, any losses caused in the conversion mode are reported as “accumulated other comprehensive income.”
Cash Equivalents:
- These investments can be easily converted to cash and must be short-term, usually with a maturity period of not more than three months or 90 days.
- They must have high liquidity and can easily sell in the market.
- The buyers of such an asset class must be easy to access.
Certificate of deposit:
- A certificate of deposit can be a cash equivalent, provided the maturity date is less than 90 days.
- Preferred equity shares can also be considered an example of a cash equivalent.
- Treasury bills, commercial papers, and short-term bonds are examples of it.
What does Cash & Cash Equivalents Include?
- Coins and paper money: Coins and paper money are easy to use and don’t require a bank account, but they can be lost or stolen more quickly than other forms of cash.
- Checking accounts: They’re more secure than coins and paper money, but you’ll need a bank account to use them.
- Money orders: Money orders are similar to checks, and they do not need a bank account to work.
- Undeposited receipts: Undeposited receipts are also cash equivalent that does not require a bank account. However, they’re less common than other forms of cash.
- Bank Certificate of deposit: Certificates with a maturity period of fewer than 90 days are an example of cash and cash equivalent.
- Commercial papers: Commercial papers issued by corporations are also considered cash equivalents.
- Treasury bills: It is a government backup security with a high level of liquidity.
- Money market mutual funds: Money market mutual funds are a type of investment fund that invests in short-term debt instruments, such as government bonds, corporate bonds, and commercial paper.
- Preferred stock: Preferred stockholders typically have priority over common stockholders when it comes to receiving dividends. They also have the right to receive their investment back before common stockholders.
What Does Cash & Cash Equivalents Not Include?
- Securities or other investments: They are not cash equivalents as they are not as liquid as cash
- Accounts receivable: As the company is yet to receive this amount, they cannot consider it cash
- Credit cards and Loans: These are debt instruments that the company cannot count for cash equivalents
- Prepaid expenses: As the companies have already made these payments, they cannot include them in the cash
- Inventory: It is not cash equivalent because it is a physical asset that can fluctuate in value.
Difference Between Cash & Cash Equivalents
|
Cash |
Cash Equivalents |
| It is a currency that is physically in your possession | An investment that can quickly convert into cash |
| It includes cash, receipts, bank accounts, etc | Includes money market funds, short-term commercial paper, and Treasury bills. |
| It is subject to theft and loss, so it is not as safe as cash equivalents. | These are less risky than other investments since they are short-term and highly liquid. |
Cash & Cash Equivalents IFRS
Under IFRS, cash includes physical cash on hand, demand deposits, and short-term investments readily convertible to known amounts of money and subject to an insignificant risk of change in value.
To be classified as a cash equivalent under IFRS, an investment must be:
- Readily convertible to known amounts of cash
- Subject to an insignificant risk of change in value.
Examples of investments that typically meet these criteria are short-term, highly liquid investments such as commercial paper and Treasury bills. The requirements for classification intend to ensure that only genuinely short-term and low-risk assets are in this category.
Advantages and Disadvantages
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It offers the highest level of liquidity available to the management of the company | The company may misuse the excess balance |
| It can help repay short-term obligations and other operating expenses | Too much cash may resemble that company is not paying dividends to its shareholders |
| A company with a healthy balance is perceived to perform well and manage its resources | Retaining cash & cash equivalents doesn’t fetch a reasonable interest rate which means that the investment is reaping a loss |
| This component significantly influences the company’s valuation during mergers and acquisitions. | In business handling, a lot of cash in foreign exchange may eventually lead to an exchange loss while converting it to the reporting currency. |
Final Thoughts
Cash & cash equivalents are essential components of a balance sheet and resemble a company’s financial health. It helps pay off short-term obligations very quickly without any need for borrowing. It is also essential for the shareholders as it can pay them dividends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the definition of cash & cash equivalents in accounting?
Answer: In accounting, it refers to the short-term investments that a company has made that are readily convertible to cash. It could include investments in money market funds, short-term bonds, and commercial paper.
Q2. How to audit cash & cash equivalents?
Answer: When auditing cash & cash equivalents, there are key things to remember. First, always obtain an unqualified opinion on the financial statements. Second, focus on risk areas such as receivables and payables. Finally, make sure to test for compliance with internal controls.
Q3. What are restricted cash & cash equivalents?
Answer: These are funds that a company sets aside for a specific purpose. They do not use it for general corporate expenses. The most common type of restricted cash is held in escrow to secure a loan or lease agreement. Other types of restricted cash may include money set aside to pay taxes, insurance premiums, or employee bonuses.
Q4. How do the changes in the exchange rate affect cash & cash equivalents?
Answer: When a country’s currency Exchange rate changes, the value of cash & cash equivalents also changes. For example, if the US dollar weakens against the euro, then a US company with money in euros will see the value of its cash increase when translated back into US dollars.
Conversely, if the US dollar strengthens against the euro, the value of cash held in euros will decrease when translated back into US dollars. The change in the exchange rate can also have an indirect effect on it.
Q5. What are the uses of cash & cash equivalents for a business?
Answer: Businesses primarily use cash to purchase assets or make investments. It signifies that the company has enough money to meet its short-term obligations, like payroll, rent, and utilities. It is generally a buffer against unexpected expenses. For instance, if a company has future bills, it saves money in cash equivalents.
Cash And Cash Equivalents Video
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Cash and Cash Equivalents. Here we also discuss the definition and types and their advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –