Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Bubble Sort in Data Structure
Bubble Sort in Data Structure is one of the easiest sorting algorithm being used. The idea behind this algorithm is to repeatedly compare the elements one by one and swap the adjacent elements to bring them in the correct sorted order. Thus if there are n number of elements in the array, then each element will undergo n-1 comparisons. This way, after comparing one element with other elements in the array, an element is placed at its place in the sorted list just like a bubble rises up and move. Thus this algorithm is known as Bubble Sort. Several comparisons are more; thus, its complexity is more.
Algorithm for Bubble Sort in Data Structure
Bubble Sort is most often used to provide an insight into the sorting algorithms due to its simplicity. It is a stable as well as an in-place algorithm as it does not require extra storage area. Below is the pseudocode for this algorithm to sort the elements of an array arr in ascending order.
Code:
BubbleSort (arr):
BubbleSort (arr):
n =len(arr)
For i=0 to n-1 Repeat step 3
For j=1 to n-1:
If arr[i] > arr[j]: // Compare which one is greater
swap(arr[i],arr[j])
Explanation: In the above pseudocode, n refers to the number of elements in the array. Then the loop is run from the first element of the array to the last element for comparing every element to the next element of the array, if it is greater then they are swapped otherwise loop is incremented. This way, the first element is placed at its right place.
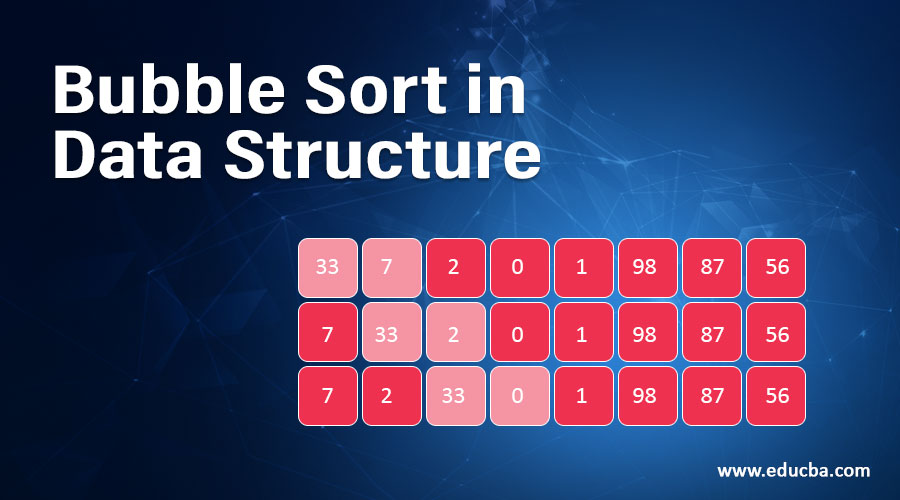
Example: Lets consider an array arr = [33,7,2,0,1,98,87,56]
First Pass:
I. 33,7,2,0,1,98,87,56
II. 7,33,2,0,1,98,87,56
III. 7,2,33,0,1,98,87,56
IV. 7,2,0,33,1,98,87,56
V. 7,2,0,1,33,98,87,56
VI. 7,2,0,1,33,98,87,56
VII. 7,2,0,1,33,87,98,56
VIII. 7,2,0,1,33,87,56,98
Second Pass:
I. 7,2,0,1,33, 87,56,98
II. 2,7,0,1,33, 87,56,98
III. 2,0,7,1,33, 87,56,98
IV. 2,0,1,7,33, 87,56,98
V. 2,0,1,7,33, 87,56,98
VI. 2,0,1,7,33, 87,56,98
VII. 2,0,1,7,33,56,87,98
VIII. 2,0,1,7,33, 56,87,98
Third Pass:
I. 2,0,1,7,33, 56,87,98
II.0,2,1,7,33,56,87,98
III. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
IV. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
V. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
VI. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
VII. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
VIII. 0,1,2,7,33,56,87,98
A similar process is repeated until the loop ends. But we can see we already have got the sorted array. This limitation can be corrected using a flag that sees if any element is swapped in one pass, in case no element has been swapped indicates every element has been placed in the right position.
Code:
BubbleSort (arr):
n =len(arr)
swapped = true
For i=0 to n-1 Repeat 3 and 4 step:
For j=1 to n-1:
If arr[i] > arr[j]:
Swap(arr[i],arr[j])
else swapped =false
if(swapped == false)
break;
Program to Implement Bubble Sort in Data Structure
Bubble Sort algorithm is mostly used in computer graphics as it can detect minimal errors such as a swap of 2 elements in almost sorted arrays. It is also capable of fixing the error in linear time complexity. Its one of the famous implementation can be seen in polygon filling algorithm where sorting of bounding lines of polygon occurs using their x coordinate, and order changes occur at every intersection of the lines with incrementing y coordinate.
Program #1 – Bubble Sort Program
Below is the example of an implementation of the bubble Sorting algorithm in python:
Code:
def bubbleSort(myarr):
n = len(myarr)
for i in range(0,n-1):
for j in range(0, n-1):
if myarr[j] > myarr[j+1]:
myarr[j], myarr[j+1] = myarr[j+1], myarr[j]
myarr = [33,7,2,0,1,98,87,56]
bubbleSort(myarr)
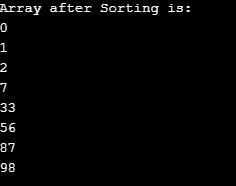
print ("Array after Sorting is:")
for i in range(len(myarr)):
print ("%d" %myarr[i])
Output:
In the above program, one can also iterate the inner loop from 0 to n-i+1 as, after each pass, one element from the last comes to its sorted order location. Thus with each pass, the number of elements to be sorted reduces by 1.
Still, in the above program, one can also optimize to reduce the number of loops by checking if elements have become sorted with every pass.
Example #2 – Optimized Bubble Sort Program
Code:
def bubbleSort(myarr):
n = len(myarr)
for i in range(n):
swapped = False
for j in range(0, n-1):
if myarr[j] > myarr[j+1]:
myarr[j], myarr[j+1] = myarr[j+1], myarr[j]
swapped = True
if swapped == False:
break
myarr = [33,7,2,0,1,98,87,56]
bubbleSort(myarr)
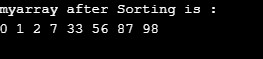
print ("myarray after Sorting is :")
for i in range(len(myarr)):
print ("%d" %myarr[i],end=" ")
Output:
The complexity of Bubble Sort
- Worst Case Complexity: O(n*n). This type of case occurs when elements of the array are sorted in reverse order. Thus each element of the array is visited twice.
- Average Case Complexity: This case is similar to Worst case complexity as in this case array is half sorted. Thus loops are run through half the array. Thus complexity is O(n2).
- Best Case Time Complexity: O(n). When elements of the array are already sorted, then complexity includes the time to loop through all elements once. Thus it takes linear time in the Best case.
- Auxiliary Space: O(1) – As Bubble Sort requires no extra space for storing intermediate results; thus, almost no auxiliary space is required.
The disadvantage of Bubble Sort
The main disadvantage of Bubble sort can be seen while dealing with an array containing a huge number of elements. As worst-case complexity of this algorithm is O(n2), thus a lot more time is taken to sort them. Thus it is more suitable for teaching sorting algorithms instead of real-life applications.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that bubble sort is an effortless way of sorting the elements of an array, thus having more time complexity. It is a stable and in-place algorithm which is most used for introducing the concept of sorting algorithms. It is also used in computer graphics because of its feature to detect the minute errors and fix them in linear time.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bubble Sort in Data Structure. Here we discuss the algorithm, complexity, and program to implement bubble sort in data structures with its disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –