Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to AVL Tree in Data Structure
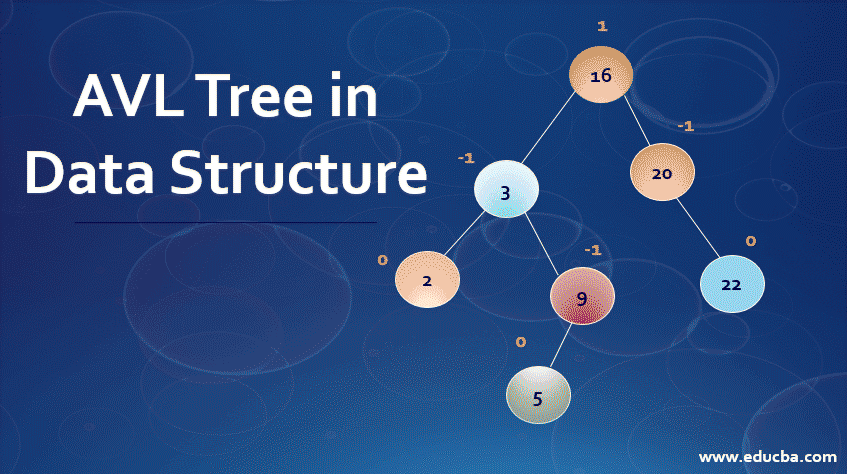
AVL tree stands for Adelson, Velskii & Landis Tree, and it can be explained as an extension of the binary search tree data structure. Though it’s similar to a binary search tree, there is one highlight of a difference that is the height of the tree value should be <=1, and unlike the binary search tree, AVL has the elements in both sides of the tree to be balanced. The formula to represent the balancing factor is ‘Balance Factor = height (left – subtree) − height (right – subtree)’. The AVL tree structuring is implemented with the three basic data structure operations, namely search, insert and delete.
E.g., Consider the following trees.
In the above example, the height of right sub-tree = 2 and left =3 thus BF= 2 that is <=1 thus tree is said to be balanced.
Why do we need an AVL tree in DS?
While working with Binary Search Tree, we come across a scenario where are the elements are in sorted order. In such cases, all the array elements are arranged on one side of the root, which leads to an increase in the time complexity of searching an element in an array and complexity becomes- O(n), i.e. worst-case complexity of the tree. To resolve such issues and decrease the searching time, AVL trees were invented by Adelson, Velski & Landis.
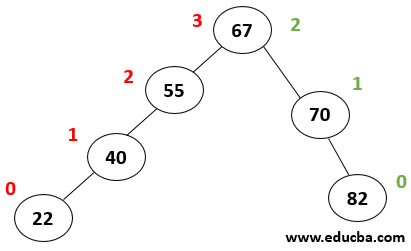
Example:
In the above figure, Height of left subtree = 3 was as
Height of right subtree = 0
Thus Balance Factor = 3-0 = 3 . Thus searching for an element in such a tree has O(n) of complexity which is similar to linear search. To avoid that complex search AVL tree was introduced where every node in the tree needs to maintain
balance factor <=1, otherwise various rotation techniques are to be performed to balance such tree.
Struct AVLNode
{
int data;
struct AVLNode *left, *right;
int ball factor;
};
Types of Rotations
When the tree’s balance factor does not satisfy <=1 condition, then rotations need to be performed on them to turn it into a balanced tree.
There are 4 types of rotations:
1. Left Rotation: If the addition of a node to the tree’s right makes it imbalance then, in that case, Left Rotation needs to be performed.
2. Right Rotation: If the addition of a node to the left of the tree makes the node imbalance then Right Rotation needs to be performed. In other words, When the number of nodes increases on the left side, then there emerges a need to shift the elements to the right side to balance it thus it is said to be Right Rotation.
3. Left-Right Rotation: This type of rotation is a combination of the above 2 rotations explained. This type of rotation occurs when one element is added to the right subtree of a left tree.
In such a case first, perform left rotation on the subtree followed by a right rotation of the left tree.
4. Right-Left Rotation: This type of rotation is also composed of a sequence of above 2 rotations. This type of rotation is needed when an element is added to the left of the right subtree, and the tree becomes imbalanced. In such a case, we first perform right rotation on the right subtree and then left rotation on the right tree.
Operations on AVL tree in DS
Below 3 operations that can be performed on the AVL tree:-
1. Search
This operation is similar to performing a search in Binary Search Tree. Steps followed are as below:
- Read the element provided by the user say x.
- Compare the root element, if it is the same, then exit otherwise go to the next step.
- If x<root element: go to left child, and compare again.
Else go to the right child and compare again.
Follow processes B and C until you find the element and exit.
This process has O(log n) complexity.
Example:
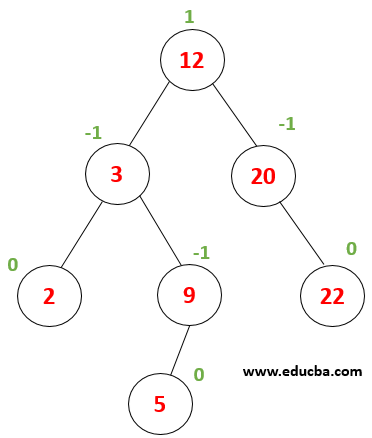 |
Consider this Tree, where we need to perform a search for node value 9. First- let x=9, root value (12) > x then, the value must be in the root element’s left subtree. |
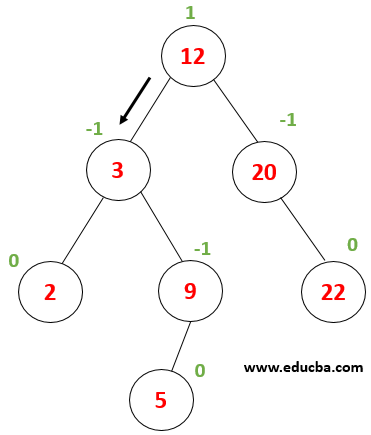 |
Now x is compared with node value 3 x> 3 thus we must proceed towards the right subtree. |
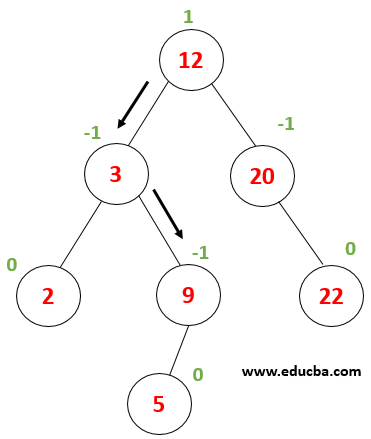 |
Now x is compared with node (9) , where 9 == 9 returns true. Thus, element searching completes in the tree. |
2. Insertion
While inserting an element in the AVL tree, we need to find the location particular element that needs to be inserted. Then the element is attached the same as an insertion in BST, but after that, it is checked if the tree is still balanced or not, i.e. balance factor of a node is <=1. And particular rotations are performed as required.
Complexity is O(log n).
Example: Consider the below tree,
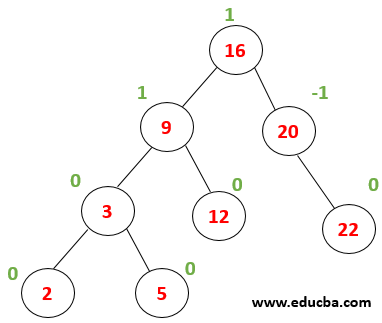 |
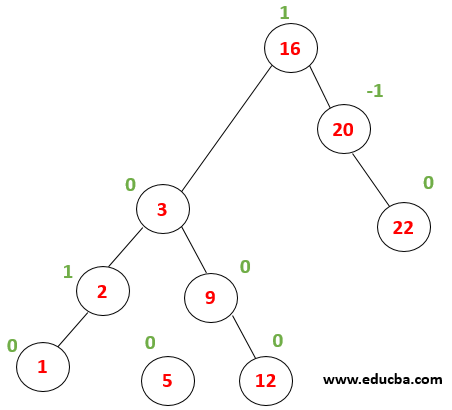
Every node has a balance factor as 0,-1 or 1 thus tree is balanced. Now lets what happens when a node with value 1 is inserted. The first tree is traversed to find the location where it needs to be inserted… 1<2 thus is written as a left child of the node(2). |
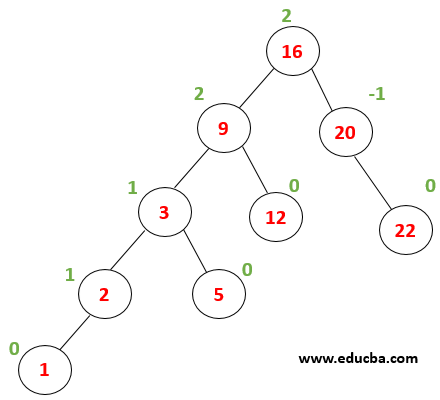 |
After insertion, the node (9) becomes unbalance with a balance factor = 2. Now it is subjected to undergo right rotation. |
 |
A tree becomes balance after Right rotation, and thus Insertion operation is completed successfully. |
3. Deletion
Deleting an element in the AVL tree also comprises searching an element in the tree and then deleting it. The search operation is the same as BST, and after finding the element to be deleted element is removed from the tree and elements are adjusted to make it BST again. After these elements are checked to have a balance factor of 0,-1 or 1, suitable rotations are performed to make it balanced.
Complexity if O(log n).
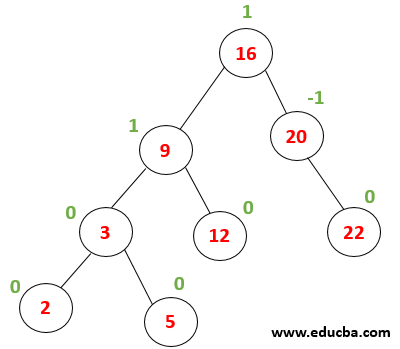 |
Consider the given tree, whose all have a balance factor of 0,-1 or 1. Now let us delete a node with value 16. The first tree is traversed to find the node with value 16 same as a searching algorithm. |
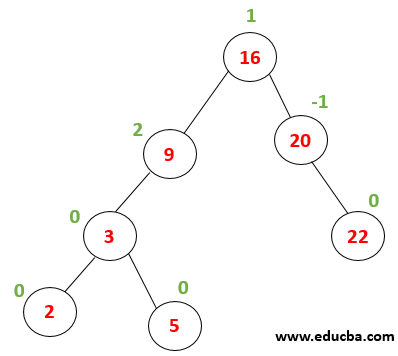 |
Node 16 will be replaced with the inorder predecessor of this node that is the largest element from left subtree, i.e. 12 The tree has become unbalanced thus LL – rotation needs to be performed. |
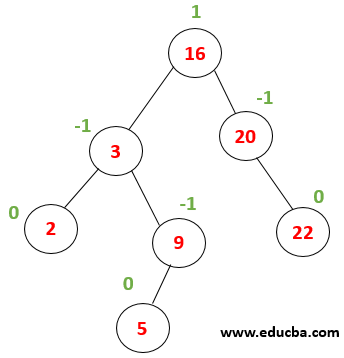 |
Now each node has become balanced. |
Conclusion – AVL Tree in Data Structure
AVL tree is a descendant of Binary Search Tree but overcomes its drawback of increasing complexity if the elements are sorted. It monitors the balance factor of the tree to be 0 or 1 or -1. In case it tree becomes unbalanced corresponding rotation techniques are performed to balance the tree.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to AVL Tree in Data Structure. Here we discuss the Introduction, Operations on AVL tree in DS and Types of Rotations. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more–