Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Trees in Data Structure
Before understanding the Types of Trees in Data Structure, first, we will study the trees in Data Structure. Tree in the computer field is also referred to as the real-world tree however the difference between the real world and the computing field tree is that it is visualized as upside down and root on top of it and branch from root to tree leaves. Among various real-world applications, the tree data structure is used to demonstrate relationships between different nodes with the parent-child hierarchy. It is also called a hierarchic data structure because of this. It is most popular for simplifying and speeding up searching and sorting. It is regarded as one of the strongest and most advanced data structures. A tree is a representation of the non-linear data structure. A tree can be shown using different user-defined or primitive types of data. We can use arrays, and classes connected lists or other kinds of data structures to implement the tree. It is a group of interrelated nodes. Nodes are attached to the edges to demonstrate the relationship.
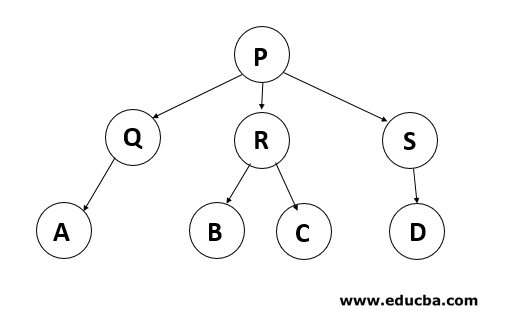
Relations in a Tree: In the above-given diagram, P is the root of the tree also P is Parent of Q, R and S. Q is the child of P. Hence Q, R and S are siblings. At the same time, P is grand-parent of A, B, C, D, and E.
What are Trees?
A tree is a Hierarchical data structure that naturally hierarchically stores the information. The Tree data structure is one of the most efficient and mature. The nodes connected by the edges are represented.
Properties of Tree: Every tree has a specific root node. A root node can cross each tree node. It is called root, as the tree was the only root. Every child has only one parent, but the parent can have many children.
Types of Trees in Data Structure
Below are the types of trees in a data structure:
1. General Tree
If no constraint is placed on the tree’s hierarchy, a tree is called a general tree. Every node may have infinite numbers of children in General Tree. The tree is the super-set of all other trees.
2. Binary Tree
The binary tree is the kind of tree in which most two children can be found for each parent. The kids are known as the left kid and right kid. This is more popular than most other trees. When certain constraints and characteristics are applied in a Binary tree, a number of others such as AVL tree, BST (Binary Search Tree), RBT tree, etc. are also used. When we move forward, we will explain all these styles in detail.
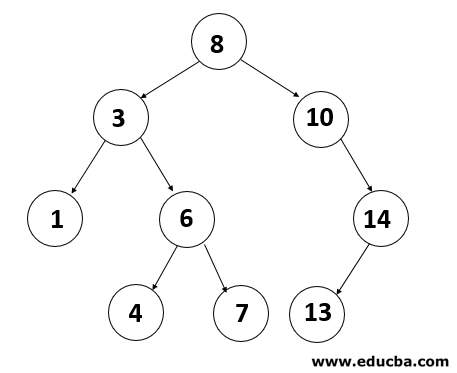
3. Binary Search Tree
Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree extension with several optional restrictions. The left child value of a node should in BST be less than or equal to the parent value, and the right child value should always be greater than or equal to the parent’s value. This Binary Search Tree property makes it ideal for search operations since we can accurately determine at each node whether the value is in the left or right sub-tree. This is why the Search Tree is named.
4. AVL Tree
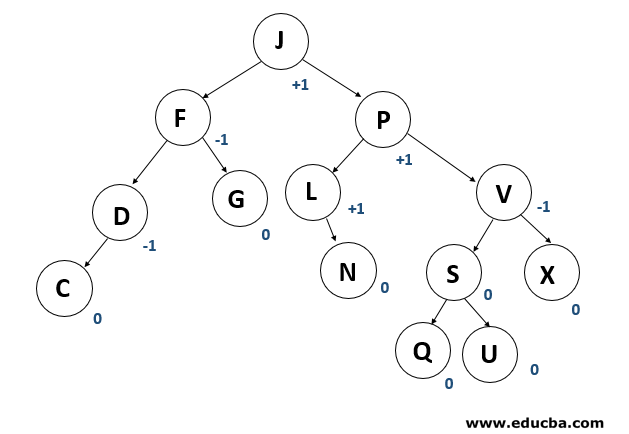
AVL tree is a binary search tree self-balancing. On behalf of the inventors Adelson-Velshi and Landis, the name AVL is given. This was the first tree that balanced dynamically. A balancing factor is allocated for each node in the AVL tree, based on whether the tree is balanced or not. The height of the node kids is at most 1. AVL vine. In the AVL tree, the correct balance factor is 1, 0 and -1. If the tree has a new node, it will be rotated to ensure that it is balanced. It will then be rotated. Common operations such as viewing, insertion, and removal take O(log n) time in the AVL tree. It is mostly applied when working with Lookups operations.
5. Red-Black Tree
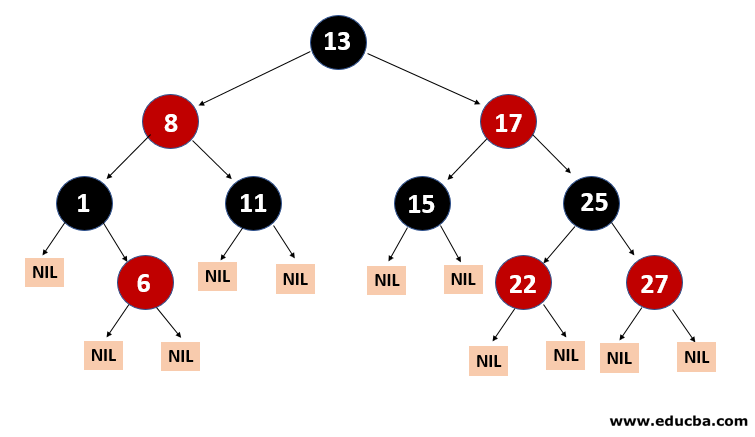
Another kind of auto-balancing tree is red-black. According to the red-black tree’s properties, the red-black name is given because the Red-black tree has either red or Black painted on each node. It maintains the balance of the forest. Even though this tree is not fully balanced, the searching operation only takes O (log n) time. When the new nodes are added in Red-Black Tree, nodes will be rotated to maintain the Red-Black Tree’s properties.
6. N-ary Tree
The maximum number of children in this type of tree with a node is N. A binary tree is a two-year tree, as at most 2 children in every binary tree node. A complete N-ary tree is a tree where kids of a node either are 0 or N.
Advantages of Tree
Now we will understand the Advantages of Tree:
- The tree reflects the data structural connections.
- The tree is used for hierarchy.
- It offers an efficient search and insertion procedure.
- The trees are flexible. This allows subtrees to be relocated with minimal effort.
Conclusion
Here in this article, we have seen what a tree structure is, different types of trees in a data structure, and its benefits. I hope you got an idea of some of the common trees in the structure of the data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Trees in Data Structure. Here we discuss the basic concept with 6 types of Trees in Data Structure along with advantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –