Updated March 17, 2023
Differences Between Array and ArrayList
Array and ArrayList are important data structures, which are used to store a number of elements and process those. But there are key differences are there between them. A good programmer must be aware of the comparisons between them to decide on what to use when and why effectively.
The array is a data structure where we can store elements of a given size of a similar type. For example, integer type array, string type array, etc. Therefore, a normal array in Java is a static data structure. An ArrayList is a dynamic data structure where items can be added and removed from the list. So if you are not sure about how many elements will be there in your array, this dynamic data structure will save you.
In this article, we will discuss the differences between Array and ArrayList in java.
Example to understand both Array and ArrayList
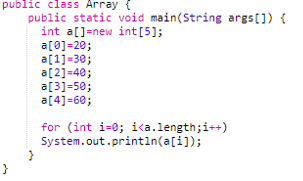
The array is a data structure where we can store elements of a given fixed size of a similar type.
Code Example:
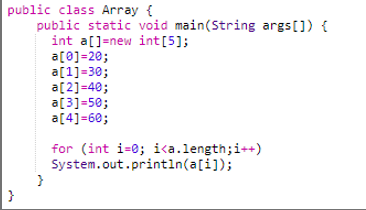
Let us create an array of five elements of int type. We will iterate through them using for loop.
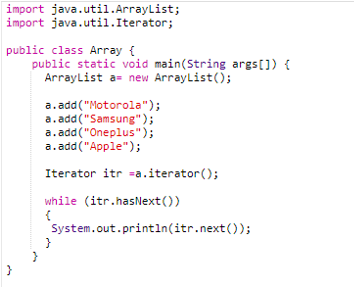
An ArrayList is a dynamic data structure where items can be added and removed from the list. So if you are not sure about how many elements will be there in your array, this dynamic data structure will save you.
Code Example:
Head to Head differences between Array and ArrayList (Infographics)
Given below are the top differences between Array vs ArrayList:
Key Differences between Array and ArrayList in Java
Below are the key differences between Array vs ArrayList:
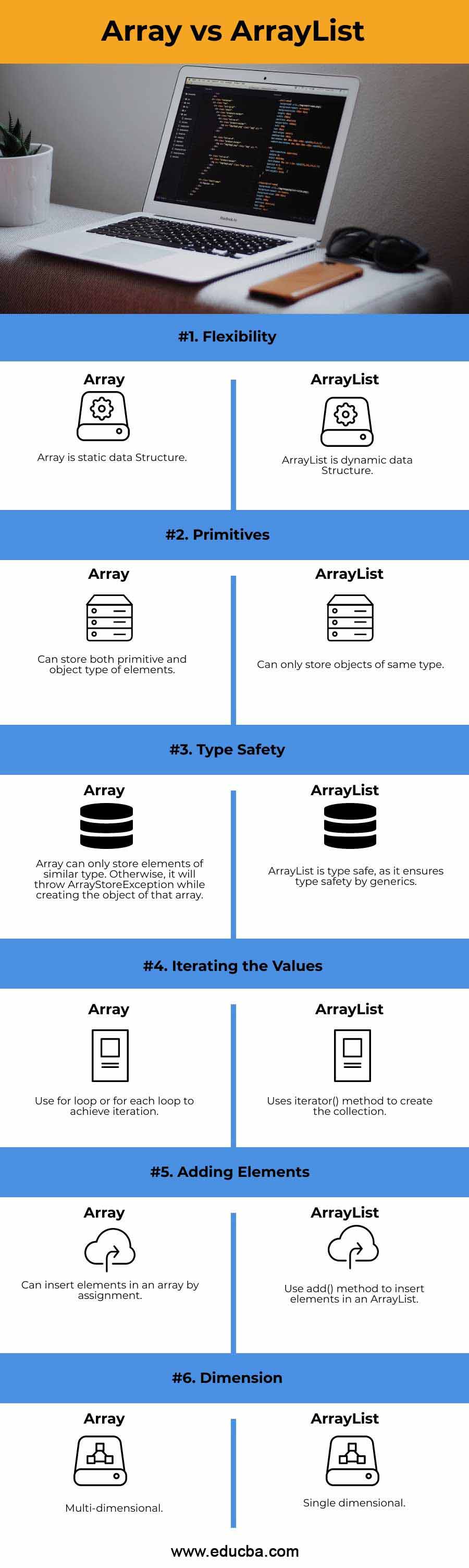
1. Flexibility
An array is a static data structure. Once you have defined the size of the array, you cannot change the value of its size. Therefore, a normal array in Java is a static data structure because the initial size of the array is fixed.
On the other hand, ArrayList is flexible in size. You can add or remove items from the list at your convenience. While removing items form ArrayList, we are assigning null to the index whose value is removed, and the whole index value is downgraded by one automatically. Similar goes for addition also.
2. Implementation
An array is a data structure where we can store elements of a given fixed size of a similar type. An ArrayList is a dynamic data structure where items can be added and removed from the list. Actually, ArrayList is implemented using an array in Java. It would help if you imported java.util.ArrayList package to use ArrayList() method to create ArrayList object.
Example code snippet of Array
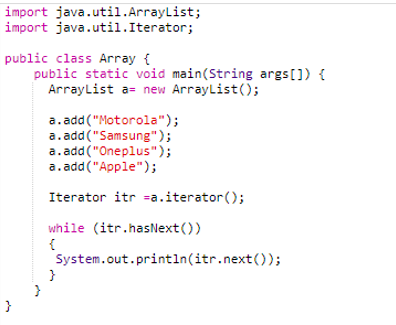
Example code Snippet of ArrayList
3. Performance
Although ArrayList is basically based on Array, we see performance differences between them. This is because of the storage type and functionality of the ArrayList. We see performance differences in terms of CPU time and memory utilization. Depending on the operations you are performing, the performance of Array and ArrayList will vary:
ArrayList requires more memory for storage purposes compared to an array. This is because storing similar objects require more memory than storing similar primitive type variables.
resize() operation: ArrayList uses automatic resize, where a temporary array is created to copy elements from the old array to a new array. This slows down the overall performance.
get() operation: For index-based access, both ArrayList and array have the same performance, as this requires constant time.
add() operation: Here, we see the key difference as adding a new element in ArrayList requires two operations internally: Copy and resize. Addition in ArrayList creates a new array in the background and copy elements from old to a new array.
4. Primitives
An array can store both primitive and object types of elements. On the other hand, an ArrayList cannot store primitive types; it can only store objects of the same type.
Then how can we store integer values in an ArrayList?
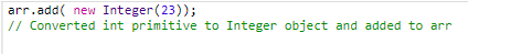
The answer is the autoboxing capability of JVM. Autoboxing internally converts primitive to its equivalent objects.
For example:
Hence, autoboxing internally performs the below things.
5. Type Safety
An array can only store elements of a similar type. If you want to store different types of elements in an array other than the specified ones, it will throw ArrayStoreException while creating that array’s object. This exception will be thrown at runtime, as the array is not type-safe; no compile-time checking is there for the array.
For example:
On the other hand, ArrayList is type-safe, as it ensures type safety by generics. Generics allows the compiler to check if there any mismatch in type during compilation.
6. Iterating the values
ArrayList uses the iterator() method to create the collection. Then using a while loop, we will traverse the elements one by one and print the values.
On the other hand, we can use for loop or for each loop to iterate through an array.
7. Length
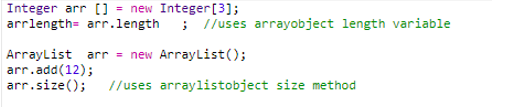
In many of the use cases, we might need to get the size of the whole array. In the case of Arraylist, this calculation is quite straight forward. We can get a length of ArrayList by using the size() method.
On the other hand, each array object has the length variable, which returns the length of the array.
For example:
8. Adding elements
Adding or insertion is possible in ArrayList as it is a dynamic data structure. We can use add() method to insert elements in an ArrayList after its creation.
On the other hand, the size of the array is fixed. However, we can insert elements in an array by assignment. We cannot dynamically add new elements beyond the size of an array.
For example:
9. Dimension
ArrayList is single-dimensional. Whereas, the array can be multi-dimensional.
For example:
Array and ArrayList – Comparison table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Array vs ArrayList
| Basis of Comparison | Array | ArrayList |
| Flexibility | The array is a static data Structure | ArrayList is a dynamic data Structure |
| Primitives | can store both primitive and object type of elements | can only store objects of the same type. |
| Type Safety | The array can only store elements of a similar type. Otherwise, it will throw ArrayStoreException while creating the object of that array. | ArrayList is type-safe, as it ensures type safety by generics. |
| Iterating the values | use for loop or for each loop to achieve iteration. | Uses iterator() method to create the collection |
| Adding elements | can insert elements in an array by assignment. | use add() method to insert elements in an ArrayList
|
| Dimension | multi-dimensional | single-dimensional |
Conclusion
That is all concerning the important distinction between an array and an ArrayList in Java. The foremost vital distinction you must keep in mind is that array is static, whereas ArrayList is dynamic in nature. Primarily based upon this distinction, you must use an array if you recognize the dimensions ahead; if you’re unsure, then simply use the ArrayList.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Array vs ArrayList. Here we discuss the key differences with infographics, examples and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –