Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Queue in Data Structure
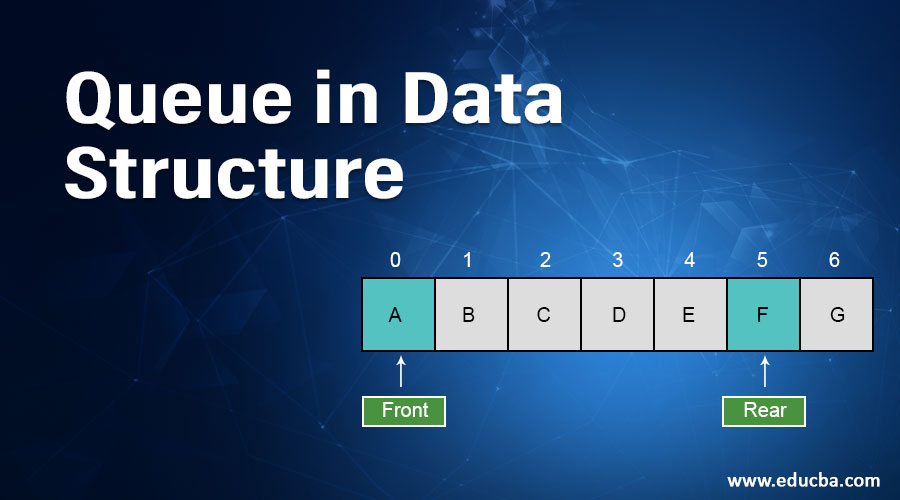
It is a type of linear data structure which follow the first in first out(FIFO) approach. This means the element that is inserted first will be removed first. The queue is said to have 2 ends, one from where the element is inserted is known as the REAR end, and the end where the element is deleted is known as FRONT. In the queue, one end (REAR) is always used to enqueue, and the other (FRONT) is used to dequeue. The queue data structure is similar to the queue at the bus stand where the passenger who comes first will board the bus first.
How to Create a Queue in Data Structure?
The queue can be created using below 2 data structures.:
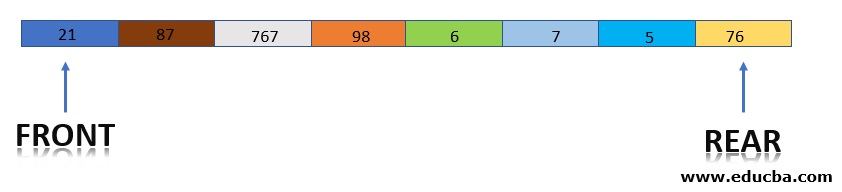
1. Using Array
In this representation, an array is declared with N number of elements capacity and 2 indices FRONT and REAR are maintained. In the case of insertion and deletion of elements in the queue, indices are updated accordingly.
Example: Let the Queue of 7 elements
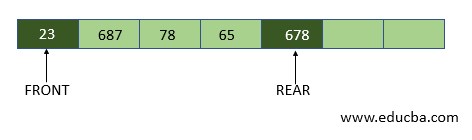
Here FRONT =0 and REAR =4. In case an element is inserted, REAR becomes REAR+1, i.e. 5 and element is inserted at Queue[5] position.
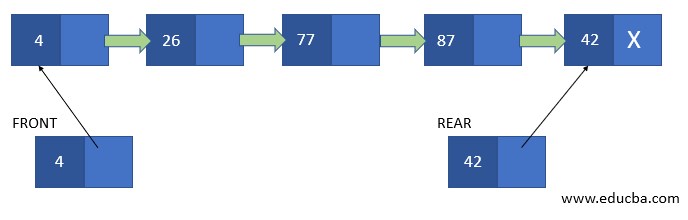
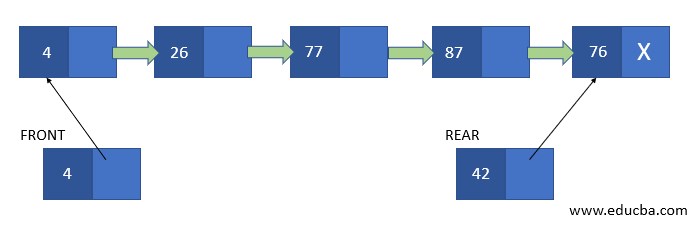
2. Using the Linked List
Sometimes the number of elements in the queue is not specified in the start; thus, a linked list represents a queue of elements. In this case, a structure is created having an integer key and a pointer as its elements. And 2 such structure variables are created to point the front and queue element of the array.
In case of inserting a new element in the queue REAR end of the queue is updated to point to the new location.
Structure of Linked List Node:
Struct QNode
{ int key;
QNode* next;
}
QNode *FRONT * REAR;
Here key consists of the elements present in the Queue and next represent the pointer to that element.
How to Insert an Element in a Queue?
Insertion in a queue occurs at the REAR end of the queue. This process is also known as enqueue.
Algorithm: Following is the algorithm for inserting an element in a queue.
- Check if a queue is full, FRONT = REAR+1. or (REAR= MAXSIZE of QUEUE and FRONT =0) then OVERFLOW exists thus exit.
- Else if FRONT =REAR =-1 then REAR=FRONT=0.
- Else REAR = REAR +1 and QUEUE[REAR] = Item.
Explanation: In the above algorithm, it is checked if the queue is full or not by checking If FRONT =REAR +1 or FRONT =0 and REAR = MAX. In this case, the Item can not be inserted into the Queue. Otherwise, if there is no element in the queue, both FRONT and REAR are incremented to 0 and the Item is inserted at the REAR end.
How to Delete an Element in a Queue?
Deletion in a queue occurs at the FRONT end. Thus in case FRONT < 0, indicates there is no element in the queue. Such a situation is known as underflow. To delete an element from a queue, one should also see FRONT of the queue has that value must contain that value. If not, then it needs to be updated after reading the value from the FRONT, it needs to be updated. There are 3 possible situations in case of a queue.
- FRONT == REAR !=0: This indicates there is only one element in the array. Thus after deletion is performed, FRONT will become 0.
- FRONT = MAX(Queue): Then FRONT will be equal =1, if deletion is performed.
- FRONT = FRONT +1.
Algorithm: Following is the algorithm for deletion in a queue.
- Check if FRONT < 0, if there is an underflow situation in the queue, then exit.
- Item := Queue[FRONT].
- If FRONT = REAR then set FRONT =REAR=NULL. Else if FRONT = MAXSIZE(QUEUE) then set FRONT =0;
- SET FRONT=FRONT+1.
- Exit.
Explanation: First, the underflow situation is checked, then the variable Item is checked to become a front element of the queue. Now in case FRONT =REAR of the queue, both will become NULL after deletion of the element. Otherwise if FRONT = Max capacity of the queue then FRONT is updated as 0. Otherwise, FRONT is updated to FRONT+1.
Applications of Queue in a Data Structure
The queue is used in situations where we need a process to run in First in First Out order. It is beneficial to apply queue data structure in situations where data need not transfer synchronously.
Breadth-First Search: This is one of the traversal method used to traverse the nodes of a tree. Here a queue is maintained of the adjacent nodes of the current node that needs to be traversed before going to the next level of depth.
Single Shared Resources: The queue is used to maintain the order in which a single resource needs to be provided to various requesting processes. Operating systems also use a queue for maintaining the processes that need to be pulled for execution from its waiting states such as priority queues.
MM1 Queue: This is a queuing model that is being used to model various real-world situations. Following are ways to categorize its usage:
- A single Server is available.
- A non-empty queue has an exponential distribution of its service time with rate mu per minute.
- A queue has an inter-arrival time also has an exponential distribution of lambda per minute.
Conclusion
The queue data structure is a linear type of data structure that is used to store the elements. In this data structure elements are stored in the FIFO technique. A queue data structure used an array or linked list during its implementation. Insertion in queue occurs at the REAR end, and deletion from queue occurs at the FRONT end. This type of data structure is used for serving various requests by a single shared resource.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Queue in Data Structure. Here we discuss how to create a queue in a data structure along with insert, delete an element in a queue and its application, etc. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-