Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Graph in Data Structure
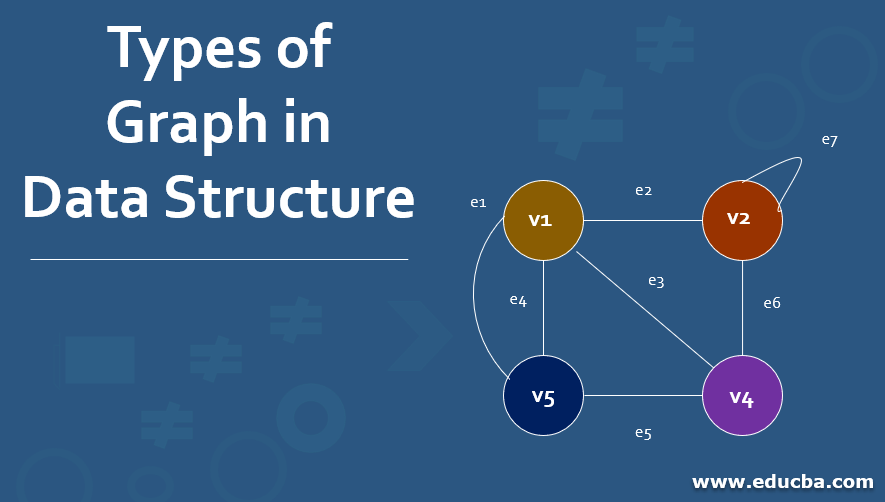
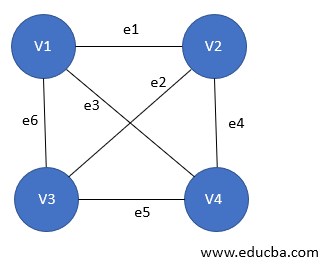
A graph(V, E) is a set of vertices V1, V2…Vn and set of edges E = E1, E2,….En. Here, each distinct edge can identify using the unordered pair of vertices (Vi, Vj). 2 vertices Vi and Vj are said to be adjacent if there is an edge whose endpoints are Vi and Vj. Thus E is said to be a connect of Vi and Vj. Let’s discuss various types of graph in the data structure below.
- Order of the graph = The number of vertices in the graph.
- Size of the graph = The number of edges in the graph.
- Degree of a vertex of a graph = Number of edges incident to the vertex.
Different Types of Graph in Data Structure
Following are the 17 different types of graph in the data structure explained below.
1. Finite Graph
A graph G= (V, E) in case the number of vertices and edges in the graph is finite in number.
2. Infinite Graph
A graph G=(V, E) is said to infinite if the number of edges and vertices in the graph is infinite in number.
3. Trivial Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to be trivial if there only exist single vertex in the graph without any edge.
4. Simple Graph
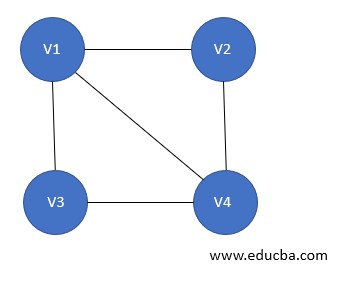
A graph G=(V, E) is said to be a simple graph if there is one and only one edge between each pair of vertices. Thus there is only edge connecting 2 vertices and can be used to show one to one relationships between 2 elements.
5. Multi Graph
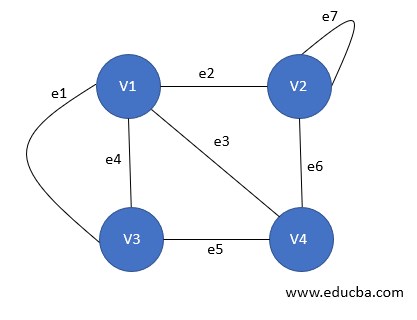
A graph g= (V, E) is said to be a multigraph if there are multiple edges between a pair of vertices in the graph. A Multigraph does not contain any self-loop. For example, A Road Map.
Two kinds of edges exist in such scenarios:
- Parallel Edges: Edges those are running parallel while going from a vertex Vi to Vj denoting parallel roads for going from one source to the same destination.
- Loop: This denotes an edge whose source and destination vertices are the same.
6. Null Graph
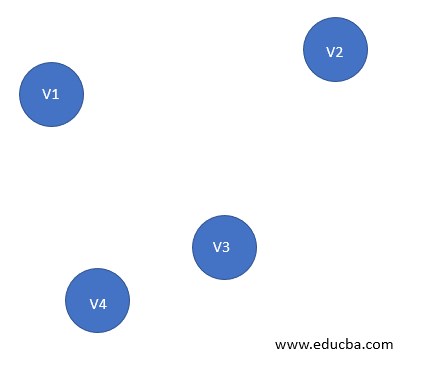
It is a modified version of a trivial graph. A graph G= (V, E) is said to a null graph if there are n number of vertices exist, but no Edge exists that connects then. This is the same as ordering food from a different city or farther places.
- Order of G = n
- Size of G = 0
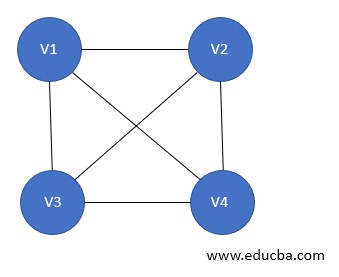
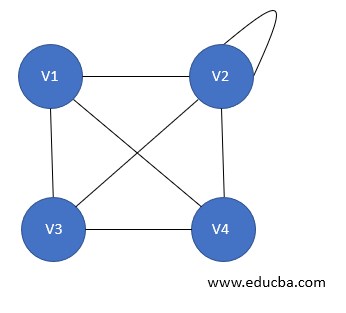
7. Complete Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to be a complete graph in case it is also a simple graph. With this n number of vertices must be attached to each of other vertices using the edges. It is also known as a full graph, and the degree of each vertex must be n-1.
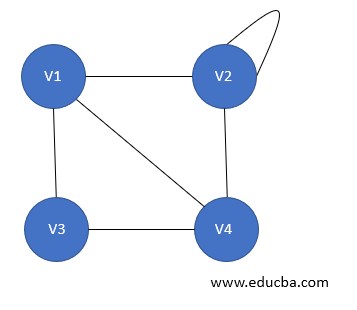
8. Pseudo Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to pseudo graph in case it contains a self-loop along with other edges.
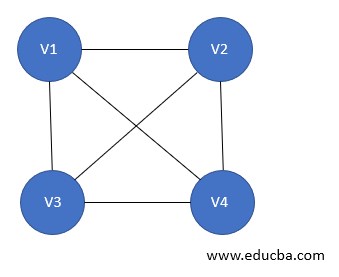
9. Regular Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to be a regular graph if it is a simple graph with each vertex of the graph having the same degree. Thus every complete graph is a regular graph.
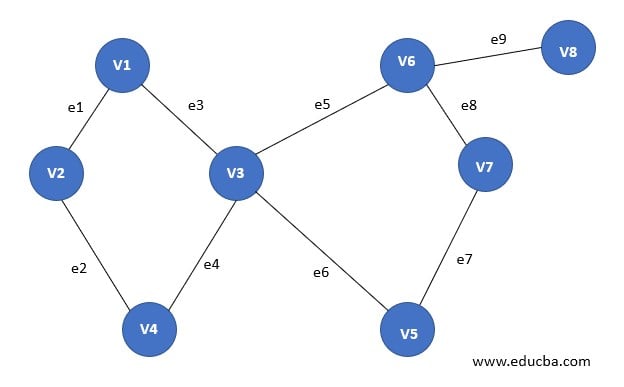
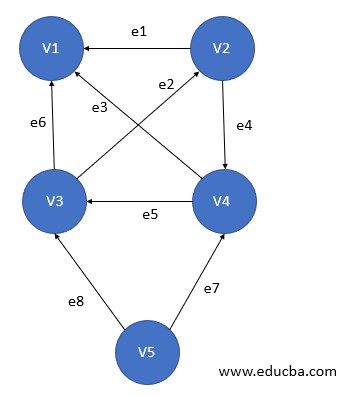
10. Bipartite Graph
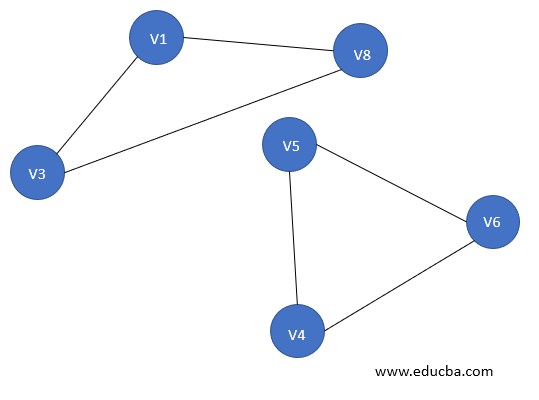
A bipartite graph is having a set of vertices that can be partitioned into 2 non-empty disjoint subsets such that every edge of that graph has its endpoints from each of these subsets, i.e. lets V1 and V2 are subsets then each edge e between x and y vertices exist such as x ∈ V1 and y ∈ V2. V1 and V2 must be mutually exclusive as well as disjoint.
Here in the figure:
V1(G)={V5, V4, V3}
V2(G)={V1, V2}
11. Labelled Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to be a labelled or weighted graph because each of the edges in the graph holds some value or weight that denotes traversal cost through that edge.
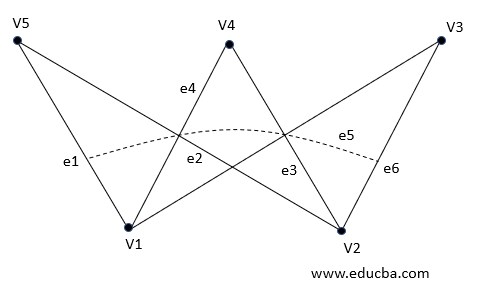
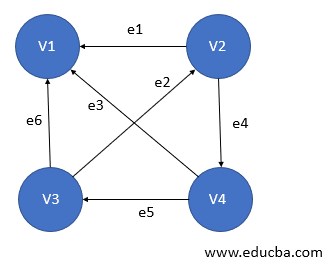
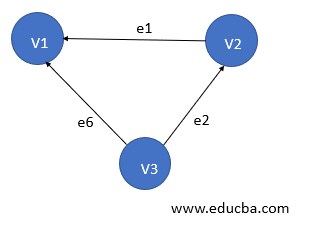
12. Digraph Graph
A graph is said to a digraph or directed graph in case the order of pair of vertices changes the meaning of the graph. i.e. in case, G=(V, E) is the graph and Vi, Vj is a par of vertices is different from Vj, Vi. This can be seen in road maps when one of the roads is unidirectional or one-way. To denote such kind of cases directed graph is used. For each edge e between (Vi, Vj), an arrow exists to denote its direction.
Here in the figure:
e1 = (V1, V2)
e2 = (V2, V3)
e4 = (V2, V4)
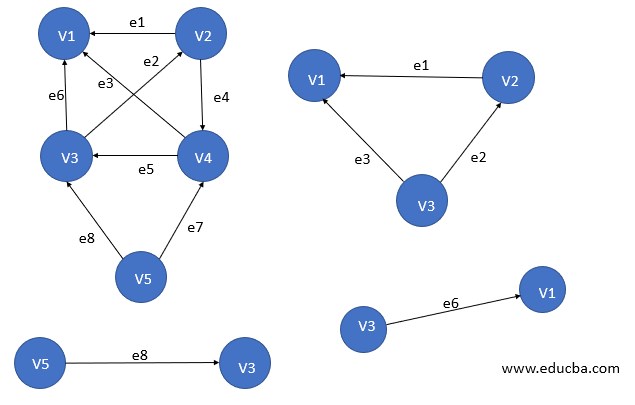
13. Subgraph
A graph G1 =(Vx, Ex) is said to be a subgraph of G=(V, E) if Vx ⊆ V and Ex ⊆ E.
There are 2 Types of Subgraph
- Vertex Disjoint Subgraph: A subgraph with no common vertex.
- Edge Disjoint Subgraph: A subgraph with no common edge.
14. Connected or Disconnected Graph
In case one can find a path from one vertex of the graph to any of the other vertex, then the graph is said to be a connected graph. Thus a null graph is said to a disconnected graph as there is no edge connecting the vertices.
(A) – Connected Graph
(B) – Disconnected Graph
15. Cyclic Graph
A graph G= (V, E) is said to be a cyclic graph when one can reach its own while traversal. i.e. if V1, V2, and V3 are vertices in the graph then, there always exist edges connecting (V1, V2) and (V2, V3) and (V3, V1).
16. Vertex Labeled Graph
The graph that holds some data in its vertices, such as it can help to determine the edges data like (key, value) pair mapping.
17. Directed Acyclic Graph
It’s also known as DAG, these are the graphs with directed edges, but they do not contain any cycle. Vertices also hold some data, and as it is directed; thus, edges are represented using an ordered pair of vertices.
Conclusion
Graphs are an important data structure used in many algorithms to improve an application’s efficiency. There are many types of graphs, and their usage depends on the requirement of the application. At every step, data is analyzed and how the application is required to work helps to determine the suitable graph for running an algorithm. This improves the efficiency of the system a lot.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Types of Graph in Data Structure. Here we discuss the basic concept with the top 17 types of a graph in the data structure. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-