Introduction to DBMS Types
DBMS (Database management systems) come in various types, each created to meet particular data administration and storage requirements. Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) use structured tables with established relationships, which provide strong SQL querying capabilities. On the other hand, NoSQL databases stray from the rigorous RDBMS structure and are appropriate for managing unstructured or semi-structured data. Graph databases are perfect for situations like social networks and recommendation systems because they are excellent at expressing complex relationships.
Rather than storing data in rows, columnar databases optimize storage for analytical tasks. In-memory databases use fast memory storage to enable quick data access. Specialized time-series databases handle timestamped data points, which is essential for applications like the Internet of Things and financial trading. Databases built using NewSQL combine scalability and ACID compliance. Object-Oriented DBMS supports complex data structures in software applications. Each DBMS type has particular advantages, allowing it to meet various data management needs.
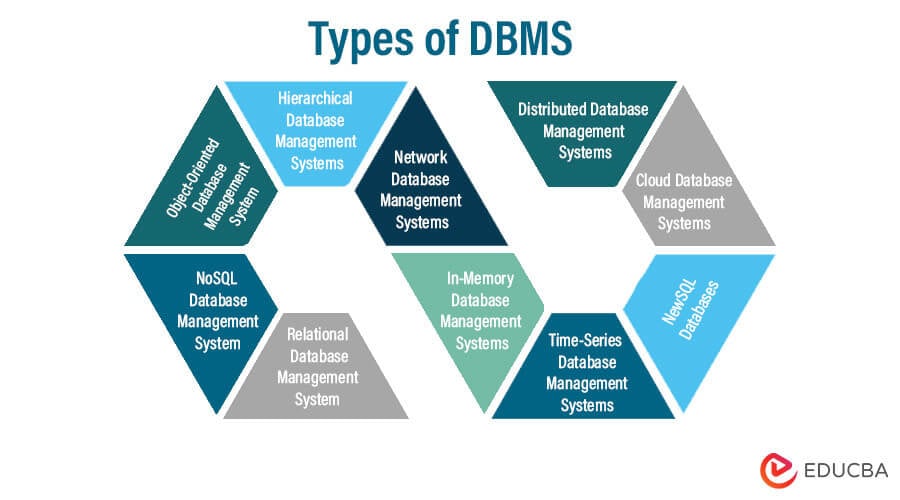
Table of Contents
- Introduction to DBMS Types
- Types of DBMS (Database Management System)
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)
- NoSQL Database Management System
- Object-Oriented Database Management System (OODBMS)
- Hierarchical Database Management Systems
- Network Database Management Systems
- In-Memory Database Management Systems
- Time-Series Database Management Systems
- NewSQL Databases
- Cloud Database Management Systems
- Distributed Database Management Systems
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Types of DBMS (Database Management System)
Let’s discuss various types of DBMS (Database Management Systems) one by one:
1. Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)
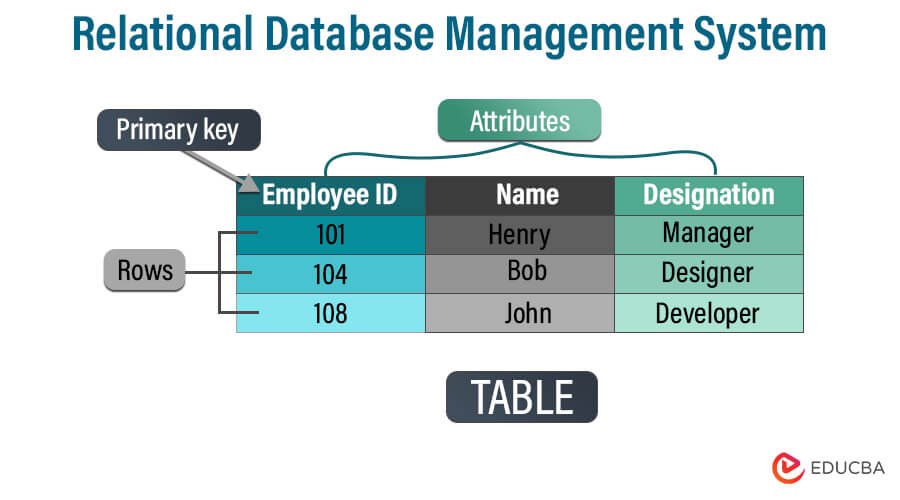
Using tables with rows and columns, a relational database management system (RDBMS) uses tables to organize and store data in an organized way. We build linkages between tables based on shared data elements to facilitate effective data retrieval and manipulation. The relational model, first by E.F. Codd in the 1970s, is the foundation for RDBMS.
Characteristics
- Tabular Structure: RDBMS arranges data in tables (relations), where each row corresponds to a record and each column to a data attribute.
- Data Integrity: RDBMS applies data integrity rules using constraints (such as primary and foreign keys) to maintain accurate and consistent data.
- SQL-based: RDBMS manipulates and retrieves data using Structured Query Language (SQL).
- Data Relationships: It enables data normalization by supporting the creation of linkages between tables using keys.
- ACID Transactions: Through ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) features of transactions, RDBMS ensures data consistency.
Components
- Tables: The primary data storage units for storing data in rows and columns.
- Attributes: We call the columns in a table representing particular data pieces attributes.
- Rows: Individual records that comprise a table’s rows, each with values for a particular attribute.
- Keys: Special identifiers that link tables together (for example, primary and foreign keys).
- Indexes: Data structures that make getting data for particular columns easier.
- Constraints: Unique constraints, main key constraints, and foreign key constraints are examples of constraints that uphold data integrity.
Advantages
- Data Integrity: Constraints enforce data quality and consistency.
- Data Relationships: Supports intricate connections between data elements using data relationships.
- Query Capability: Enables users to utilize SQL to run effective queries.
- Security: Provides mechanisms for data security and role-based access control.
- ACID Transactions: ACID ensures reliable data transactions.
Disadvantages
- Complex Schema: Designing and keeping up a relational database schema can be challenging.
- Performance: Complex joins and large-scale data retrieval may have an impact.
- Scalability: Horizontal scaling involves complicated installations, and vertical scaling has restrictions.
- Lack of Flexibility: Modifying the schema might be challenging and impact already-running applications.
- Joins and Performance: Performance constraints might be caused by excessive join usage.
2. NoSQL Database Management System
A database management system known as NoSQL (Not Only SQL) databases offers adaptable and scalable solutions for managing sizable and varied datasets. Unlike conventional relational databases, NoSQL databases overcome the drawbacks of strict table-based schemas, making them suitable for various data types, topologies, and scalability requirements. Developers designed them to handle the vast amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data modern applications generate.
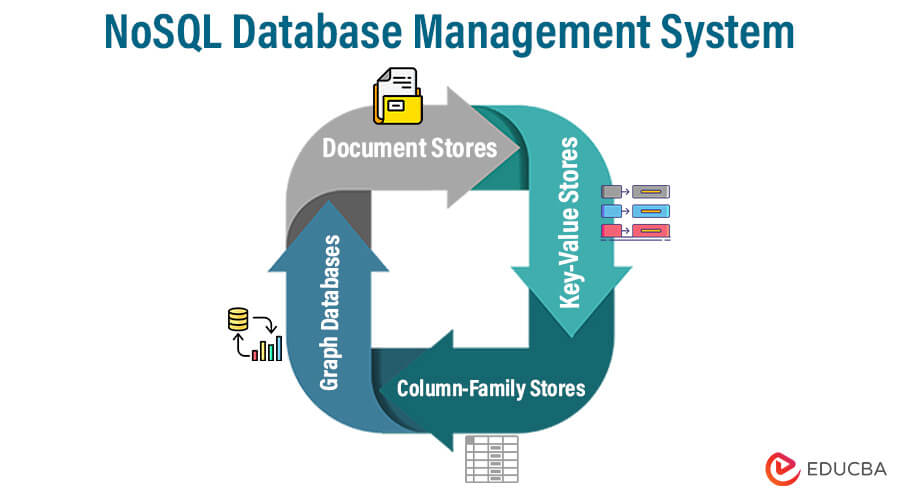
Types
- Document Stores: Document-oriented databases store data as documents similar to JSON, which can have a flexible format and don’t need a set schema. These databases can handle unstructured or semi-structured data. MongoDB and Couchbase are two examples.
- Key-Value Stores: Key-value stores are effective for high-speed data retrieval since they require a single key to get values. They are appropriate for real-time and caching applications. Examples include Amazon DynamoDB and Redis.
- Column-Family Stores: Column-family stores organize data into column families rather than rows and columns, enabling them to quickly store and retrieve sparse data. They are appropriate for applications involving vast amounts of data and analysis. HBase and Apache Cassandra are two examples.
- Graph Databases: Graph databases describe and query complicated networks, strongly emphasizing links between data elements. They perform particularly well in applications involving social networks, ranking algorithms, and knowledge graphs. Neo4j and Amazon Neptune are two examples.
Characteristics
- Schema Flexibility: Flexible and dynamic schema designs are possible with NoSQL databases. NoSQL databases can accommodate various data types and structures without rigid schema restrictions, unlike RDBMS, where tables and columns set data structures. This adaptability is especially helpful when managing changing or unstructured data.
- Scalability: NoSQL databases achieve horizontal scalability, enabling them to distribute data across multiple servers and nodes. Consequently, they excel at handling substantial traffic loads and vast amounts of data. They are simple to scale up or down to meet rising demand.
- Data Model Variety: Various NoSQL database types offer different data models, including key-value, document, column-family, and graph. Developers can choose the most suitable data model for their application’s needs since each model caters to a particular use case.
- Performance Emphasis: Many NoSQL databases commonly emphasize performance, especially in terms of read and write operations. Designers create them for specific queries, allowing faster data retrieval and modification.
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance: Numerous NoSQL databases have built-in functionality for high availability and fault tolerance. To guarantee continuous access to data despite hardware or network problems, they support systems for data replication, distribution, and automatic failover.
Components
- Data Model: Different types of NoSQL databases, such as key-value, document, column-family, or graph, enable different data models. The database’s data model specifies the organization, storage, and querying of data.
- Storage Engine: The storage engine controls data and retrieval from the underlying storage system. Tailoring it to the database’s particular data model and query patterns.
- Query Language or API: NoSQL databases frequently have proprietary query languages or APIs suited to the data model. Developers can efficiently connect with and obtain data from the database using these query capabilities.
- Indexing Mechanism: Indexes enhance query performance by enabling the database to find data that meets specific criteria. To enhance data retrieval, many NoSQL databases employ various indexing techniques.
- Replication and Sharding: To guarantee high availability and fault tolerance, replication involves making duplicate copies of data across several nodes. To scale, sharding entails partitioning data over several nodes to divide the strain.
Advantages
- Scalability: NoSQL databases can handle enormous volumes of data and heavy traffic loads by scaling horizontally.
- Flexible Schema: They can incorporate various data structures without rigid, pre-established schemas.
- Performance: NoSQL databases frequently offer fast data retrieval and processing because of their optimized data models.
- High Availability: Several NoSQL databases include built-in replication and clustering for high availability and fault tolerance.
- Data Variety: They suit modern applications because they can handle various types of data.
Disadvantages
- Lack of ACID Transactions: To gain scalability, NoSQL databases may forego some ACID features, which might pose problems for data integrity.
- Learning Curve: For each form of NoSQL database, developers may need to master different data models and query languages.
- Challenges with Consistency: Keeping high consistency across distributed nodes can occasionally be difficult.
- Data Fragmentation: Data can become disorganized or fragmented without a rigid framework.
- Limited Tooling: NoSQL databases may have fewer tools and frameworks available than relational databases that have reached maturity.
3. Object-Oriented Database Management System (OODBMS)
A database management system known as an Object-Oriented Database Management System (OODBMS) combines database management features with notions from object-oriented programming. An OODBMS stores data as objects with characteristics and methods, unlike conventional relational databases, which store data as tables, rows, and columns. This architecture closely adheres to object-oriented programming principles and enables a more natural representation of real-world items and their interactions.
Object-Oriented Concepts in Databases
- Objects: These are instances of classes that represent real-world entities and have methods to manipulate the data and attributes.
- Classes: Classes serve as blueprints for producing instances and specify the composition and behavior of things. They contain information and procedures.
- Inheritance: Inheritance allows new classes (subclasses) to inherit traits from older classes (superclasses), fostering hierarchy and code reuse.
- Encapsulation: By preventing direct manipulation, objects limit access and ensure data integrity by encapsulating data and operations.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphism enables dynamic behavior and flexibility by treating objects of various classes as instances of a single superclass.
Features
- Complex Data Modelling: OODBMS better models relationships, nested objects, and complex data structures than relational databases.
- Persistence: To bridge the gap between application objects and data storage, objects may be kept in the database.
- Query Language: Object-oriented query languages are frequently provided by OODBMS, allowing for expressive and understandable querying based on the structure of objects.
- Data Integrity: By requiring controlled access to data, encapsulation and object-oriented principles protect data integrity.
- Concurrency Control: OODBMS controls concurrent access to objects to guarantee data consistency in multi-user scenarios.
Advantages
- Natural Representation: An OODBMS organically represents data structures, which fits well with object-oriented programming.
- Complex Relationships: Compared to relational databases, OODBMS manages complex data relationships more naturally.
- Flexible Schema: Supporting agile development by making it simpler to handle changes to data structures.
- Efficiency in Development: A direct object-oriented model for database mapping eliminates the need for complex data transformations.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Compared to conventional relational databases, OODBMS can be more difficult to design, build, and maintain. Integrating object-oriented ideas into data management requires a thorough understanding of object-oriented programming and database concepts.
- Learning Curve: Database administrators and developers may need to learn object-oriented programming and database management techniques. This learning curve may impede progress and raise the likelihood of mistakes.
- Performance Overhead: Due to the added complexity of handling objects, inheritance, and encapsulation, OODBMS can occasionally result in performance overhead. Compared to relational databases’ well-proven query optimization methods, some query operations might be less optimized.
- Limited Standardisation: Compared to relational databases, OODBMS implementations and query languages are less standardized. Switching between multiple OODBMS solutions might be difficult because of this lack of standardization, which can result in vendor-specific techniques.
- Performance Variability: Depending on the individual use case and how objects and relationships are modeled, OODBMS performance can vary more. Models with poor design could produce less-than-ideal results.
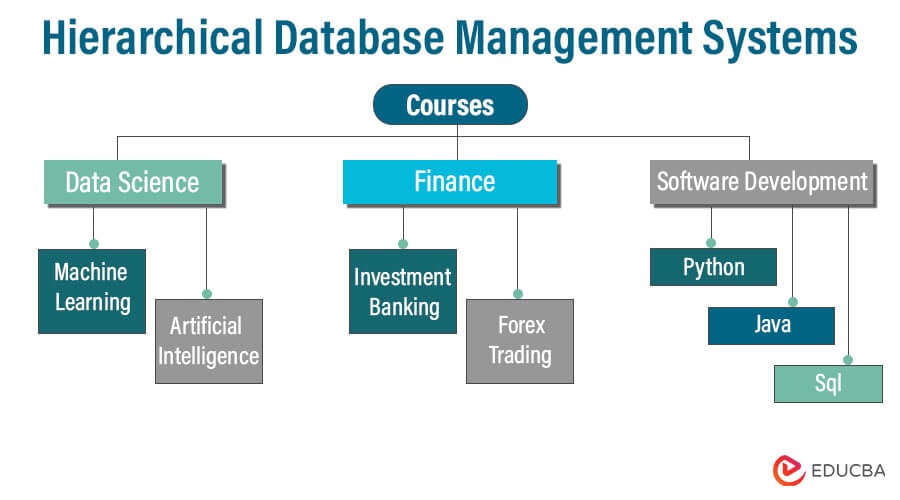
4. Hierarchical Database Management Systems
A database management system that stores and arranges data in a hierarchical structure is known as a hierarchical database management system (HDBMS). The data organization in this structure resembles a tree; parent-child relationships are used to store the data. Each parent node in a hierarchical model can have several child nodes, but each can only have one parent. In the early days of computing, this model, one of the earliest database models, saw widespread use.
Characteristics
- Tree Structure: Arrange data in a top-down tree structure, where each node (except for the root) has a single parent and potentially many children.
- Relationships between Parents and Children: The records are related one to many. Although a parent record may have several children, each kid record only has one parent.
- Navigation: Data retrieval requires navigating the hierarchical structure from the root to the targeted node. Hierarchical query languages or specialized navigational commands are often used for this navigation.
- Performance: When it comes to obtaining data through predetermined paths, hierarchical databases are effective. However, they risk losing effectiveness when faced with challenging or unpredictable queries.
- Data Redundancy: Because data is kept structured and each piece of data only appears once, data redundancy is minimized.
Components
- Root Node: As the first node in the hierarchy, the root node serves as the beginning point for data access. It has no parent node, but multiple child nodes are possible. A hierarchical database’s root node serves as a representation of the complete database.
- Parent Nodes: Parent nodes are linked to one or more child nodes. Although a parent node may have several child nodes, each child node is only connected to one parent node.
- Child Nodes: Nodes that connect to a parent node are called child nodes. A single parent node directly connects to each child node. They form a hierarchical structure because child nodes can become parents to their own set of child nodes.
- Segments: A segment is a logical data storage unit in a hierarchical database. Segments are arranged hierarchically to create the database’s general structure, which can hold a group of records.
- Records: Records are the basic data storage units in a hierarchical database. Typically, each record has fields for storing particular pieces of data. Records are segmented and arranged according to their hierarchical relationships.
- Fields: Individual data items that make up a record are called fields. Each field is associated with a particular attribute or data describing the record. Actual data values are stored in fields, including names, addresses, dates, etc.
Advantages
- Effective Retrieval: Hierarchical databases are effective when data access patterns are well-defined since they are optimized for retrieving data in a particular path.
- Simpleness: The hierarchical paradigm is uncomplicated and simple to comprehend. It corresponds nicely to several real-life situations where information logically follows a parent-child relationship.
- Data Integrity: Since the data can be organized and handled more readily, the rigorous parent-child relationships help protect data integrity.
Disadvantages
- Limited Data Relationships: Parent-child relationships are the only ones that hierarchical databases are intended to support. Due to this restriction, it is difficult to depict more intricate data linkages that don’t easily fit into a tree-like structure. Hierarchies can’t accurately model many real-world circumstances since they entail more complex relationships.
- Complexity of the Query: Retrieving data not on a predetermined path can be difficult and call for several inquiries or specialized navigation commands. Queries involving several hierarchy levels can become complex and challenging to formulate.
- Data Independence: Modifying a hierarchical database’s structure without disrupting any existing applications that depend on the present hierarchy can be extremely difficult. It frequently takes a lot of work to add or change data relationships, and doing so could interfere with current functionality.
- Scalability: Hierarchical databases may become less scalable as the database expands regarding the number of records or the intricacy of the relationships. Increasing the hierarchy’s tiers or nodes might make administration more complex.
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Strict parent-child connections can, in some circumstances, support data integrity, but they can also provide difficulties. For instance, handling the orphaned offspring nodes might be challenging if a parent node is destroyed.
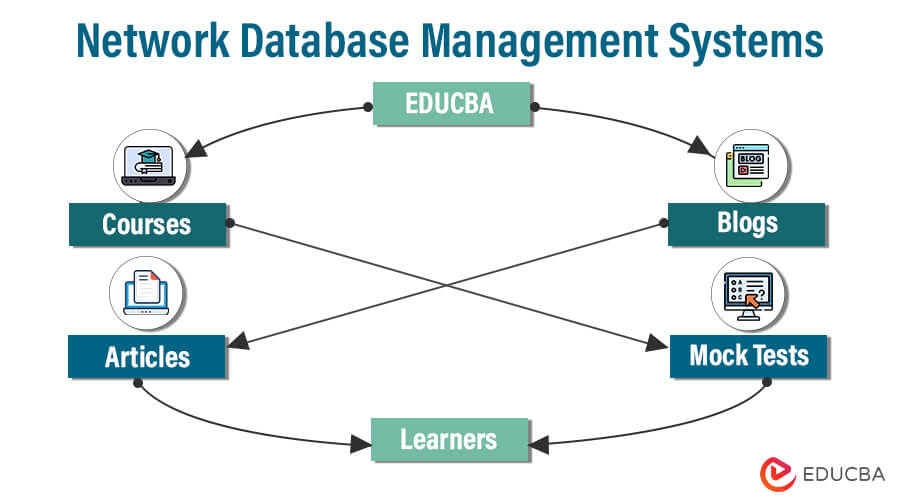
5. Network Database Management Systems
By enabling entries to have many parent and child relationships, Network Database Management Systems (NDBMS), a particular database management system class, expands the hierarchical model. This framework resembles a linked network or graph of data. The network model aims to improve the representation of complicated data interactions and to overcome some of the shortcomings of the hierarchical model.
Network Data Model
The foundation of the network data model is the idea of sets, in which records are grouped into sets, and each record can be a member of numerous sets. Set membership is used to construct connections between records.
The network data model’s essential elements are as follows:
- Sets: Sets are groups of documents with logical connections. Records in a set are instances of the entity types represented by the sets they are a part of.
- Member Records: Records that are part of a set are known as member records. Each member record contains attributes comparable to fields in other database models in that they store data values.
- Owner and Member Relationship: Records from one set may be owners of records from another set, establishing owner-member relationships. These connections enable the network-like connection of records.
- Pointers: To construct connections between owner and member records, pointers are employed. Pointers offer the linkages between records in various sets required for network traversal.
Advantages
- Complex Relationships: Network databases are ideal for modeling complicated data linkages that cannot be sufficiently captured in a hierarchical structure. It is easier to capture real-world relationships when records have numerous parents.
- Flexible Queries: The network approach provides more flexible querying than hierarchical databases. Users can retrieve data by navigating the network structure and following different connections and paths.
- Data Integrity: By accurately representing the links between data pieces in real life, the network model can assist in maintaining data integrity by establishing and managing complex interconnections.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Regarding schema design and query formulation, the network model introduces a higher level of complexity. It can be difficult to navigate the network structure and comprehend the relationships.
- Maintenance Obstacles: Because of the data’s interconnected nature, changing a network database’s schema or structure can be difficult and needs changes in several places.
- Lack of Standardisation: Unlike other models, such as SQL for relational databases, the network model does not include standardized query languages.
- Limited Adoption: Despite addressing some of the shortcomings of the hierarchical model, the relational model, which provided a more standardized and adaptable method of managing data, was more widely adopted.
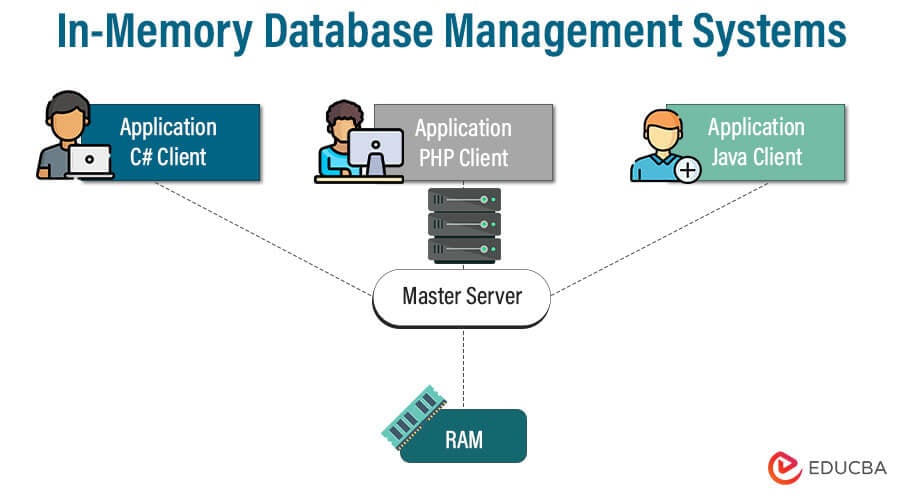
6. In-Memory Database Management Systems
Database management systems known as in-memory database management systems (IMDBMS) store and manage data primarily in a computer’s main memory (RAM) instead of conventional disc storage. This method greatly accelerates data retrieval and processing using memory’s quicker access times. Due to their capacity to enable high-performance data processing for various applications, IMDBMS have grown in prominence in recent years.
Characteristics
- Data Management and Storage in Main Memory: The primary feature of IMDBMS is that they primarily store and manage data in the computer’s main memory (RAM). This makes it possible to retrieve and process data quickly, improving performance noticeably.
- Ultra-Fast Data Access: Data retrieval and manipulation in IMDBMS occur at breakneck speeds due to the main memory’s nearly instantaneous access times, which do away with the latency associated with disk-based storage.
- Real-Time and Near-Real-Time Processing: Because IMDBMS can give extremely low latency, they are well suited for real-time and near-real-time processing applications that call for immediate insights, decisions, and replies.
- Optimized for Analytical Workloads: IMDBMS are exceptional in handling intricate analytical queries involving aggregations, joins, and calculations. Analytical operations that require a lot of data can benefit from in-memory storage’s quickness.
- Performance that is Predictable and Consistent: IMDBMS are suited for applications where performance predictability is important because they provide predictable and consistent response times for queries and transactions.
Advantages
- Faster Data Access: Unlike disk-based databases, data retrieval requires disc I/O operations, and getting data from memory is much faster.
- Reduced Latency: IMDBMS is the best choice for applications needing real-time processing because data access takes less time.
- Improved Performance: IMDBMS can significantly enhance read-intensive and complex query workload performance, increasing the overall effectiveness of applications.
- Complicated Analytical Queries: Because these processes considerably benefit from faster memory access, IMDBMS excels at complicated analytical queries that entail aggregations, joins, and calculations.
Disadvantages
- Memory Constraints: The dependence on available memory is the main restriction of IMDBMS. Large datasets might not fit entirely in memory, which could cause data eviction or result in poorer performance from data paging between memory and disc.
- Cost: Memory is more expensive than disc storage in terms of price. Larger datasets may require scaling up memory, which could increase hardware expenses.
- Data Resilience: Traditional disk-based databases provide data resilience since data is preserved even during a power outage. In-memory databases need procedures like regular snapshots or replication to ensure data persistence, which can add complexity and overhead.
- Warm-Up Period: Data must be loaded into memory before a system starts or restarts. Performance may be temporarily impacted during this warm-up phase until all the data has loaded.
- Restart Overhead: If the system shuts down or restarts, data must be reloaded into memory, which may prolong the time it takes for performance to return to normal.
7. Time-Series Database Management Systems
Database systems known as time-series database management systems (TSDBMS) were developed to store, handle, and retrieve time-series data effectively. Because time-series data comprises observations captured at regular intervals, it is ideal for applications where understanding how data evolves is crucial for analysis and decision-making.
Characteristics
- Timestamps: Each data point has a timestamp that identifies when the observation was made.
- Sequential: Data points are arranged chronologically, with either regular or erratic gaps in time between them.
- Streaming Data: Time-series data, including sensor readings, market data, server logs, and more, is frequently created in or very close to real-time.
- Data volatility: Periodic and non-periodic trends and potential abnormalities or events that call for close monitoring can all be seen in time-series data.
Advantages
- Effective Data Storage: Time-series databases reduce storage needs by optimizing storage for sequential and time-based data.
- Fast Data Retrieval: These databases make it possible to quickly analyze data by efficiently retrieving it depending on time intervals.
- Real-time Analytics: Time-series databases make it possible to analyze data in and close to real-time, giving insights as events happen.
- Scalability: Many time-series databases are built to handle growing data quantities and rapid data ingestion rates by scaling horizontally.
Disadvantages
- Data Volume and Scalability: The sheer amount of time-series data can be intimidating as it grows. Over time, large dataset management and analysis can burden system resources and affect performance.
- Data Quality and Noise: Outliers and missing values can affect time-series data. When working with sensor data or data generated by the Internet of Things, it cannot be easy to ensure data quality and accuracy.
- Complexity of Queries: Although many time-series databases come with built-in aggregations and optimizations for time-based queries, complex questions that incorporate many data sources, time intervals, and different sorts of analysis can be difficult to construct and carry out effectively.
- Data Retention and Purging: Keeping track of data retention rules can be difficult. Planning is necessary to decide when and how to delete old material without erasing important historical context.
- Data Variability: Data irregularities, missing data, and fluctuating data rates are all possible with time-series data. Data processing and analysis might become more challenging when dealing with data structure and period changes.
- Initial Data Loading: When implementing a time-series database, the initial historical data loading procedure can be time-consuming, especially when working with massive datasets.
8. NewSQL Databases
The relational database management system (RDBMS) class known as NewSQL combines the advantages of conventional relational databases with cutting-edge scalability and performance capabilities. While keeping familiarity with SQL and relational data formats, NewSQL databases seek to overcome the drawbacks of conventional relational databases.
Characteristics
- SQL Compatibility: SQL compatibility is maintained by NewSQL databases, enabling programmers and data specialists to use well-known SQL queries and language elements.
- ACID Compliance: Assuring high data consistency and integrity even in remote situations, NewSQL databases uphold the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) principles.
- Scalability: While keeping the advantages of relational data modeling, NewSQL databases are made to scale horizontally. They can manage heavy traffic loads and data quantities thanks to this.
- Sharding and Distribution: To accomplish scalability without compromising consistency, NewSQL databases use strategies including sharding, data segmentation, and distribution across nodes or clusters.
- Parallel Processing: To improve query performance and data processing, several NewSQL databases use parallel processing techniques.
Scaling and Performance
- Horizontal Scaling: NewSQL databases may split up data processing and queries among several nodes or clusters, enabling them to cope with high data volumes and multiple concurrent requests.
- Sharding: Data is divided into smaller pieces, or “shards,” with each shard resting on a different node. This makes data delivery and administration efficient.
- Shared-Nothing Architecture: NewSQL cluster nodes are frequently built to function independently and to connect only when necessary. This architecture improves scalability and fault tolerance.
- Parallel Query Execution: Multiple nodes can run queries concurrently in many NewSQL databases, improving query performance for complicated processes.
- In-Memory Processing: Some NewSQL databases use in-memory processing and storage to increase query response times.
Advantages
- ACID Compliance: Data integrity, consistency, and reliability are all guaranteed by the ACID compliance of NewSQL databases, even in distributed and highly scalable contexts.
- SQL Compatibility: Because NewSQL databases enable SQL queries and language structures, developers used to dealing with relational databases will find them easy to use.
- Scalability: NewSQL databases can potentially manage massive data volumes and heavy traffic loads by dividing data and processing across numerous nodes or clusters.
- Consistency: NewSQL databases provide robust consistency models that guarantee businesses’ data quality and integrity in distributed systems.
- Performance: Through parallel processing and indexing techniques, many NewSQL databases optimize query performance, making them suitable for complicated queries and real-time analytics.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Setting up and maintaining a distributed database system can be challenging and require specialized skills.
- Learning Curve: Even though NewSQL databases strive to preserve SQL compatibility, there may still be a learning curve for developers switching from conventional relational databases.
- Vendor Lock-In: Some NewSQL databases might offer exclusive features or query languages, which could lead to vendor lock-in and make switching to other systems difficult.
- Migration Difficulties: Data migration and application adjustments may be necessary when switching from conventional relational databases or other databases to NewSQL databases.
- Data Distribution Challenges: Sharding and data distribution schemes may make it more difficult to maintain data consistency and respond to cross-shard queries.
9. Cloud Database Management Systems
A class of database systems known as cloud database management systems (cloud DBMS) are hosted and controlled in cloud computing environments. These solutions enable users and organizations to store, manage, and retrieve data online using cloud resources rather than on-premises hardware.
Cloud-Based Database Services
- Database as a Service (DBaaS): Fully managed database services where the cloud provider handles database upkeep, scaling, backups, and upgrades. Users concentrate on the creation of data and applications rather than infrastructure management.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): A cloud platform that includes managed databases and provides a full environment for creating and deploying applications.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS, or infrastructure as a service, allows users to install and administer their preferred database software on virtual computers and infrastructure provided by cloud service providers.
Considerations for Choosing Cloud Databases
- Database Type: A range of database types, including relational, NoSQL, in-memory, and graph databases, are offered by various cloud service providers. Select the kind that best fits the demands of your application.
- Performance: Consider the database’s read and write operations, query complexity, and response times.
- Scalability: Consider the cloud database service’s scalability options, including auto-scaling, manual scaling, and the associated costs.
- Security: Examine the encryption, authentication, access controls, and compliance certifications the cloud provider offers.
- Data Location: Complying with data protection laws requires knowing the location of your data storage and processing.
Characteristics
- Scalability: Organizations and applications can easily adjust cloud-based DBMS solutions to meet their evolving needs. They can manage shifting workloads and automatically increase or decrease resources in response to changing demand. Without requiring manual intervention, its scalability guarantees top performance.
- Resource Sharing: Cloud databases use virtualization and multi-tenancy to distribute resources across many users and applications effectively. This resource sharing reduces costs and makes the most of the hardware infrastructure.
- On-Demand Self-Service: Using self-service interfaces offered by the cloud provider, users can provision, manage, and monitor their databases. Users can now manage their database resources independently of direct IT administration.
- Elasticity: Cloud DBMS can automatically alter resource allocation based on current demand. Due to this elasticity, apps can accommodate increasing user activity without experiencing slowdowns, even during traffic spikes.
Advantages
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go cloud databases enable businesses to avoid significant up-front capital costs. Only paying for the resources you use can result in cost savings, particularly for new and small organizations.
- Flexibility: There are many different database types, sizes, configurations, and performance options available with cloud databases. This flexibility allows Organizations to select the finest database solution for their unique requirements.
- Managed Services: Cloud providers provide managed database services for recurring duties, including backups, updates, security patching, and monitoring. This relieves internal IT teams of some of their administrative tasks so they can concentrate on their primary duties.
- Rapid Provisioning: The speed of provisioning and deploying cloud databases reduces the time needed for setting up or scaling existing ones. Businesses with fluctuating workloads might benefit significantly from this agility.
Disadvantages
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Storing sensitive data on the cloud can lead to data security and privacy concerns. Businesses must trust their cloud provider’s security precautions and ensure data protection laws are followed.
- Dependency on Internet Connection: Cloud databases need a steady internet connection to access and manage data. Poor connectivity or downtime might interfere with business operations. Tracing workloads might benefit significantly from this agility.
- Downtime and Outages: Service failures can still happen despite cloud providers’ best efforts to maintain high availability. These outages may impact application performance and data accessibility.
- Performance fluctuation: During periods of high utilization, shared resources in multi-tenant setups can cause performance fluctuation, impairing query performance and response times.
- Data Transfer Costs: Costs associated with data transfer: If your data transfer speeds are slow or you’re working with enormous datasets, moving significant amounts of data into and out of the cloud could be more expensive.
10. Distributed Database Management Systems
A distributed database management system (DDBMS) stores and manages data across multiple nodes or physical locations within a network. It stores data distributedly, offering advantages such as improved scalability, availability, and fault tolerance.
Types
- Homogeneous DDB: A homogeneous DDB has database management systems (DBMS) that are identical or have a similar model and user interface across all nodes. This indicates that the database software and data model are the same across all sites in the distributed system.
- Heterogeneous DDB: Different nodes in a heterogeneous DDB may employ various DBMS, data models, or interface types. As a result, the environment is more complex than it would be with homogeneous DDBs.
Distributed Database Concepts
- Data Fragmentation: Multiple nodes distribute smaller segments or fragments of information among themselves.
- Data replication: For increased availability and performance, copies of the data might be kept on various nodes.
- Data Transparency: Even though the database is scattered, it is still possible for users and applications to interact with it as if it were a single integrated system.
- Transaction Management: Distributed transaction management enables the consistency and integrity of data in a distributed setting.
Characteristics
- Transparency: DDBMS seeks to provide transparency to users and applications by abstracting the underlying distribution complexity. No matter where the data is physically located, users interact with the system as if it were a single, centralized database.
- Data sharing between Nodes: DDBMS mainly relies on network communication for data sharing. To reduce latency and increase performance, communication methods must be effective.
- Scalability: Adding additional nodes to the system enables the scaling of distributed databases horizontally. This allows the system to meet growing data processing and storage needs.
- Query Optimisation: To optimize query execution plans over distributed data, DDBMS needs advanced query optimization techniques. This calls for reducing network traffic and data transfer.
Advantages
- Scalability: Distributed databases enable horizontal scalability by distributing data across numerous nodes, which allows them to handle massive data volumes and expand workloads.
- Fault Tolerance: Distributed databases may withstand node failures without data loss or service interruptions, increasing system dependability.
- Performance Gains: Keeping data closer to its use points reduces network latency and enhances query performance.
- Local Autonomy: Nodes in a distributed system can function independently, enabling local management and optimization without centralized supervision.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Distributed database design, implementation, and management are challenging tasks that call for knowledge in data dissemination, consistency, and concurrency control.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining data consistency and integrity among distributed nodes can be difficult, mainly when there are changes or faults in the network.
- Concurrency Control: Managing concurrent transactions across distributed nodes requires careful coordination to guarantee data consistency and integrity.
- Data Duplication: Managing data distribution and retrieval can become difficult when data is distributed in pieces across nodes.
Conclusion – Types of DBMS
In data management, selecting the right Database Management System (DBMS) is akin to choosing the right tool for the right job. Relational DBMS excel in structured data handling, while NoSQL systems provide flexibility for unstructured or evolving data. NewSQL bridges the gap, offering scalability with SQL compatibility. Graph DBMS carve a niche for intricate data relationships. The choice hinges on data volume, structure, and application needs. Adapting to evolving trends ensures optimal data management and system performance as technology advances. The world of DBMS is a dynamic landscape, with options to suit every data-driven journey.
FAQs
Q1. When should I consider using a Time-Series DBMS?
Ans: For handling data containing timestamped entries, such as sensor readings, logs, or financial data, a time-series database management system is appropriate. Design it to handle sophisticated time-based queries and quick data intake.
Q2. How does a Distributed DBMS enhance scalability?
Ans: A Distributed Database Management System (DBMS) enhances scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes or servers. This enables it to manage larger workloads and user demands by adding additional nodes to the network. Scalability relies on parallel processing, load balancing, and enhanced fault tolerance, guaranteeing efficient and dependable data access and management as system demands expand.
Q3. What distinguishes an Object-Oriented DBMS (OODBMS)?
Ans: An Object-Oriented Database Management System (OODBMS) distinguishes itself by its ability to store and manage complex data structures as objects rather than traditional tabular data. It supports object-oriented programming concepts like inheritance and encapsulation, enabling seamless integration of application code and data and fostering flexibility and data modeling that mirrors real-world entities.
Q4. Which DBMS type is best for real-time analytics?
Ans: In-memory DBMSs like SAP HANA are ideal for real-time analytics due to their lightning-fast data access capabilities.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Types of DBMS” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.