Updated June 12, 2023
Difference Between HBase vs Cassandra
HBase is a database that uses Hadoop distributed file system for its storage. HBase is an integral part of HDFS and runs on top of the Hadoop Cluster. HBase is not a traditional relational database; it requires a different data modeling approach. Cassandra works on the data replication model to avoid data loss if any node is unavailable. Cassandra is a distributed database means a client can access data from any cluster and node.
Cassandra
Facebook started it because it’s always on the application requirement. Cassandra was started in 2005 and made available to the public in 2008. Cassandra was developed for always-on applications such as social networks like Facebook & Twitter.
Cassandra works on “always-on” architecture and has an Active-Active node model, so there is no SPoF (Single point of failure). CQL (Cassandra Query Language) is Cassandra’s query language but has syntax the same as SQL. It supports all major OS like Linux, Unix, OSX, and Windows.
Always On:
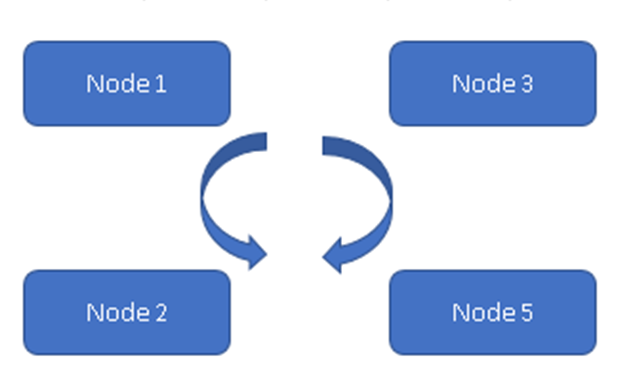
Cassandra is a database with a distribution model; all the nodes are the same within the cluster. Data is replicated on configurable nodes, so in case of failure of some no. of nodes will not result in the loss of the data.
(Always on Model)
In Figure 1, All four nodes are in sync with each other & replicating the data within the cluster. All are working on Active-Active Model so in case of any node failure will not result in data loss. A Client can read the data from the rest of the available Node/Nodes.
HBase
HBase is a NoSQL-based Database designed to process queries in large tables with billions of rows and millions of columns running across a commodity/normal hardware cluster. It provides real-time query capabilities with the speed of a “key/value store.”
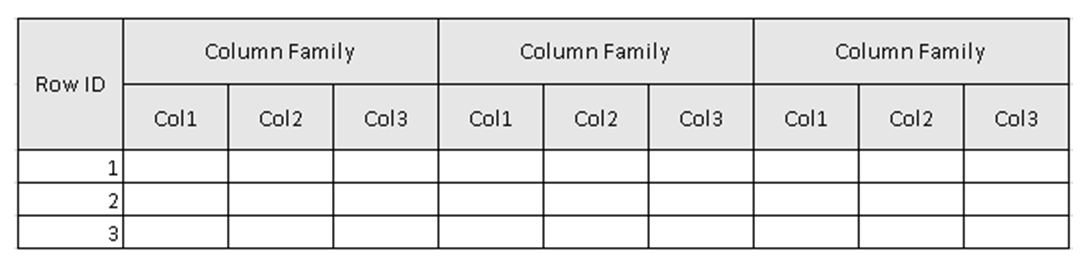
HBase is based/works on a four-dimensional data model.
- Row ID/Row Key
- Column Family
- Key-value pairs
(Figure 2, Example schema of the table in HBase.)
In Figure 2, the Table is the collection of Column Family & Column Family is the collection of Columns. Columns are the collection of Key-value pairs.
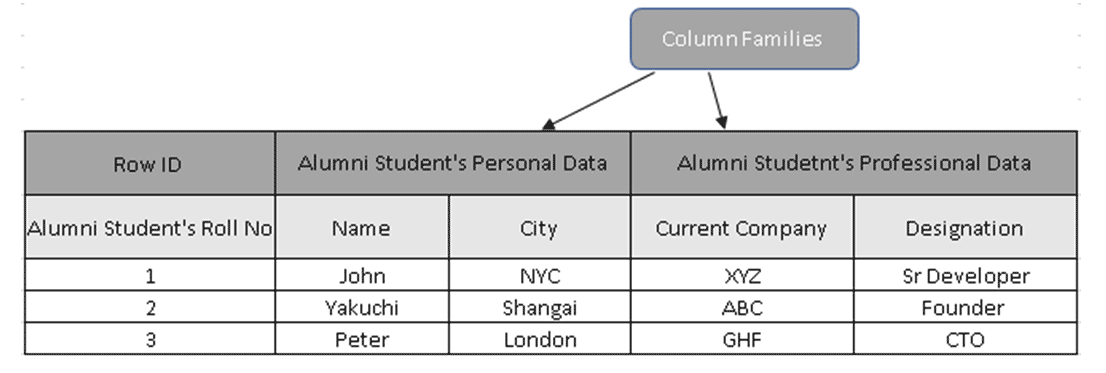
(Figure 3, Sample Table in HBase)
In Figure 3, Column families collect Alumni students’ data, and Row IDs (Row Keys) contain the Student’s Roll No.
Row Keys hold the unique value against the Column Family data. Using the Row Key, one can extract the entire details, reasons why Column-oriented databases are much faster than traditional databases.
Apache HBase can be used for random read/write access, providing failure support. It also supports replication & work on the distribution database model.
Head-to-Head Comparison of HBase vs Cassandra (Infographics)
Below is the top 9 difference between HBase and Cassandra:
Key Differences Between HBase vs Cassandra
Below are the lists of points that describe the key differences between HBase and Cassandra:
- Cassandra uses GOSSIP Protocol for internal node communication, while HBase is based on Zookeeper. Cassandra’s other side has integrated GOSSIP Protocol’s services. Zookeeper is an entirely separate distribution application.
- In Cassandra architecture, All the nodes work as Active Node while the HBase architect follows the Master-Slave Node model. The Active-Active Node model has no SPoF (Single Point of Failure). In HBase, If the Master node goes down entire cluster will not be accessible.
- HBase supports the Binary tree searching model, while Cassandra doesn’t support the B-Tree model. Without B-Tree, you can’t search User’s Column Family for everyone with an Anniversary in April, while you can search for everyone who lives in Beijing with an Anniversary in April.
- HBase supports C, C++, Java, Python, and Scala scripting languages, while Cassandra also supports JavaScript & Ruby.
- HBase has a feature called coprocessors, while Cassandra does not currently have this feature. Coprocessors provide a library and run-time environment for executing user code within the HBase region server and master processes.
- HBase is designed to support Data warehouses, while Cassandra will be perfect for All time running applications like Web and Mobile Applications.
- The HBase query language is a custom language that needs to be learned, while Cassandra uses its own developed CQL (Cassandra Query Language), SQL-Like language.
- Managing Cassandra is much easier than HBase. In Cassandra, one needs to run a single Java process per node, while in HBase, a fully operational HDFS, several HBase processes, and a Zookeeper system are required.
- HBase does end-to-end checksums and automatic rebalancing, while Cassandra doesn’t support the rebalancing of the cluster overall.
- Based on the “CAP Theorem,” Cassandra works on AP Model while HBase is CP Model.
CAP Theorem:
This theorem is used for distributed systems. C stands for Consistency, A means Availability & P is Partition Tolerance.
CAP theorem is explained below:
- C (Consistency): Consistency means that if someone has written a value to a database, others can immediately read the same value.
- A (Availability): Availability means if some nodes are unavailable in your cluster (Nodes Went down/not live in the cluster because of some issue) will not impact the whole cluster, and Distributed system/Database will be available to access the data. The cluster will be accessible for all kinds of tasks.
- P (Partition Tolerance): Partition Tolerance means if One Data Center goes down still, that should not affect the data on the nodes, and all the data should be accessible at any time. This means, Partition tolerance allows better data replication to other Data Centers within the cluster environment.
HBase vs Cassandra Comparison Table
Following is the comparison table between HBase vs Cassandra.
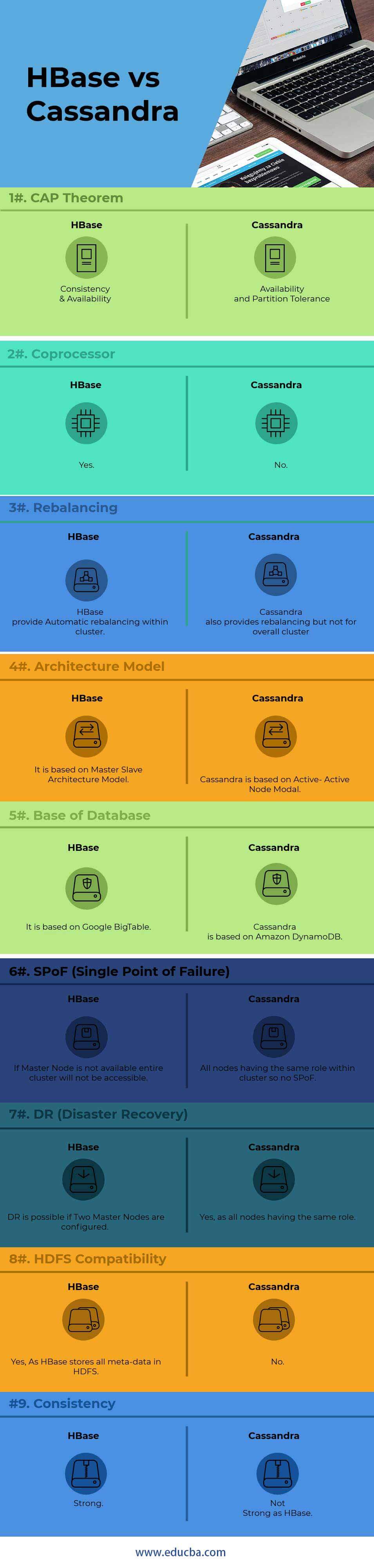
| Points | HBase | Cassandra |
| CAP Theorem | Consistency & Availability | Availability and Partition Tolerance |
| Coprocessor | Yes | No |
| Rebalancing | HBase provides Automatic rebalancing within a cluster. | Cassandra also provides rebalancing but not for overall cluster |
| Architecture Model | It is based on Master-Slave Architecture Model | Cassandra is based on Active-Active Node Modal |
| Base of Database | It is based on Google BigTable | Cassandra is based on Amazon DynamoDB |
| SPoF (Single Point of Failure) | If Master Node is not available, the entire cluster will not be accessible | All nodes have the same role within-cluster, so no SPoF |
| DR (Disaster Recovery) | DR is possible if Two Master Nodes are configured | Yes, as all nodes have the same role |
| HDFS Compatibility | Yes, As HBase stores all meta-data in HDFS | No |
| Consistency | Strong | Not Strong as HBase |
Conclusion
Facebook & other social networking sites would prefer HBase (earlier, both were using Cassandra, refer to Facebook post) because of its availability other side banking domain sector looks for security for every financial transaction, so that they would select Cassandra over HBase. Cassandra’s Key characteristics involve High Availability, Minimal administration, and No SPoF (Single Point of Failure). Another side HBase is suitable for faster reading and writing the data with linear scalability. Companies like Verizon, Bloomberg, and Bank of America utilize HBase, while major social networking sites like Twitter and Facebook use Cassandra. We can’t conclude which is best; HBase vs Cassandra both have advantages and disadvantages. We can observe the actual performance of both HBase and Cassandra databases in the production environment.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to HBase vs Cassandra. Here we have discussed HBase vs Cassandra head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –