Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to Hierarchical Database Model
Hierarchical Database Model, as the name suggests, is a database model in which the data is arranged in a hierarchical tree edifice. As it is arranged based on the hierarchy, every record of data tree should have at least one parent, except for the child records in the last level, and each parent should have one or more child records. The Data can be accessed by following through the classified structure, always initiated from the Root or the first parent. Hence this model is named as Hierarchical Database Model.
What is Hierarchical Database Model
It is a data model in which data is represented in the tree-like structure. In this model, data is stored in the form of records which are the collection of fields. The records are connected through links and the type of record tells which field is contained by the record. Each field can contain only one value.
It must have only one parent for each child node but parent nodes can have more than one child. Multiple parents are not allowed. This is the major difference between the hierarchical and network database model. The first node of the tree is called the root node. When data needs to be retrieved then the whole tree is traversed starting from the root node. This model represents one- to- many relationships.
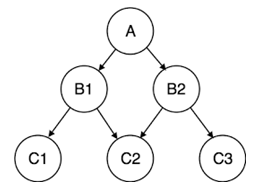
Let us see one example: Let us assume that we have a main directory which contains other subdirectories. Each subdirectory contains more files and directories. Each directory or file can be in one directory only i.e. it has only one parent.
Here A is the main directory i.e. the root node. B1 and B2 are their child or subdirectories. B1 and B2 also have two children C1, C2 and C2, C3 respectively. They may be directories or other files. This depicts one- to- many relationships.
Uses of Hierarchical Database Model
The uses of the database model are as explained here.
A Hierarchical database model was widely used during the Mainframe Computers Era. Today, it is used mainly for storing file systems and geographic information. It is used in applications where high performance is required such as telecommunications and banking. A hierarchical database is also used for Windows Registry in the Microsoft Windows operating system. It is useful where the following two conditions are met:
- The data should be in a hierarchical pattern i.e. parent-child relationship must be present.
- The data in a hierarchical pattern must be accessed through a single path only.
Advantages
Few advantages are listed below.
- Data can be retrieved easily due to the explicit links present between the table structures.
- Referential integrity is always maintained i.e. any changes made in the parent table are automatically updated in a child table.
- Promotes data sharing.
- It is conceptually simple due to the parent-child relationship.
- Database security is enforced.
- Efficient with 1: N relationships.
- A clear chain of command or authority.
- Increases specialization.
- High performance.
- Clear results.
Disadvantages
Below are some of the disadvantages given.
- If the parent table and child table are unrelated then adding a new entry in the child table is difficult because additional entry must be added in the parent table.
- Complex relationships are not supported.
- Redundancy which results in inaccurate information.
- Change in structure leads to change in all application programs.
- M: N relationship is not supported.
- No data manipulation or data definition language.
- Lack of standards.
- Poor flexibility
- Communication barriers
- Organizational Disunity.
- Rigid structure
Features
Some features are pointed out below:
- Many to many relationships: It only supports one – to – many relationships. Many to many relationships are not supported.
- Problem in Deletion: If a parent is deleted then the child automatically gets deleted.
- Hierarchy of data: Data is represented in a hierarchical tree-like structure.
- Parent-child relationship: Each child can have only one parent but a parent can have more than one children.
- Pointer: Pointers are used for linking records that tell which is a parent and which child record is.
- Disk input and output is minimized: Parent and child records are placed or stored close to each other on the storage device which minimizes the hard disk input and output.
- Fast navigation: As parent and child are stored close to each other so access time is reduced and navigation becomes faster.
- Predefined relationship: All relations between root, parent and child nodes are predefined in the database schema.
- Re-organization difficulty: Hierarchy prevents the re-organization of data.
- Redundancy: One to many relationships increases redundancy in the data which leads to the retrieval of inaccurate data.
Examples
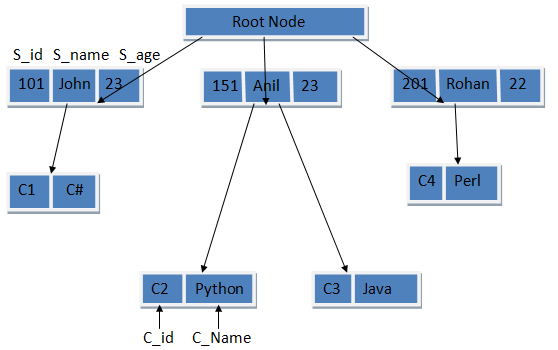
Let us take an example of college students who take different courses. A course can be assigned to an only single student but a student can take as many courses as they want therefore following one to many relationships.
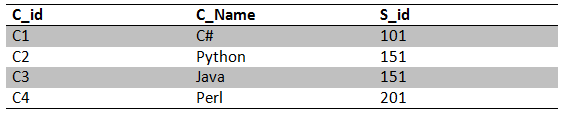
Now we can represent the above hierarchical model as relational tables as shown below:
Student Table:
Course Table:
In this manner, the hierarchical model can be represented in relational tables and vice versa can also be done.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the hierarchical database model in detail which depicts the parent-child relationship which makes it easy to represent data and understand the concept easily. It was mostly used in times of mainframe computers but still, it is used in many fields where high performance and easy concepts are the parameters. So the hierarchical model is efficient for one to many relationships and is widely used in recording file system data.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Hierarchical Database Model. Here we discussed the basic concepts, uses, features with advantages & disadvantages of the Hierarchical Database Model. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –