Updated March 31, 2023
Introduction to DBMS Constraints
Constraints are very important parts of the dbms, which allows us to impose rules of the data type of data. The main purpose of using constraints is to maintain and provide the integrality while deleting, inserting or updating from the database tables. We have many types of constraints available in dbms, which ensures that we don’t have to handle manually in the code; the dbms constraints will automatically handle it. A few of the types of constraints in dbms are integrality constraints, referential constraints, domain constraints, entity constraints etc.
Relational Model Concepts
The relational model is used to represent a table which consists of rows and columns. Each row in the tables is known as the tuple, and each column of the table is associated with a name which is called as the attribute of the table. These column names are used to identify the type of value stored inside it. Relational model concepts consist of few terminologies.
- Domain: It is used to represent the type of value that attribute will hold for a column. That means if the attribute is ‘name’, then it will contain the character, not numeric values inside it. So this decides the domain for the specific attribute.
- Relational instance: This can be represented by the set of tuples or rows from the table. All these tuples or rows should be unique and should not contain duplicates.
- Attribute: This concept of the relational model is used to represent the name of the column in a table. An attribute must define the type of an attribute as well. So it is used to represent the column of the table uniquely.
- Relational key: Relational key can be used to identified the record of the table uniquely. In relational key, every row in that table can have one or more attributes.
- Relational schema: This concept is used to define our relation model’s name, attribute or column, etc.
Example:
| Student_id | First_name | Last_name |
City |
| 1 | Abc | Xyz | Mumbai |
| 2 | Pq | Ask | Pune |
Operations in Relational Model
These operations are required to perform anything on the relational model; we have four basic operations that can be used to get the record from the table. By using this, we can easily modify the structure of the model in dbms.
1. SELECT
This is used to get any record from the table or model. We can either select all the records from the table or apply a filter based on the condition we want.
Syntax:
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE your_condition if any;This is the basic syntax for using the SELECT statement in a relational model. Let’s see the basic select query to fetch data.
Example:
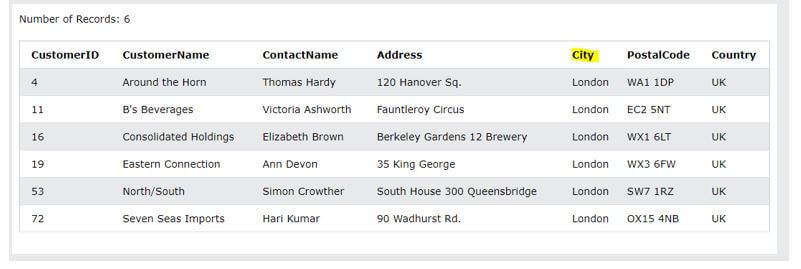
Code:
SELECT * FROM Customers where city = ‘London’;Output:
2. DELETE
This statement can be used to delete the record from the table; also, we can specify the condition with it using the ‘where’ clause.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE your_condition;This is the basic syntax for using the DELETE statement in a relational model; let’s see at the basic select query to fetch data.
Example:
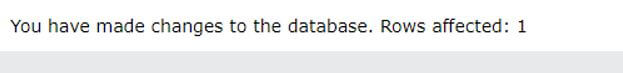
Code:
DELETE FROM Customers where city = 'Berlin';Output:
3. INSERT
This is used to insert new records into the table. It will always create a new row inside the table.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, so on..) VALUES (value1, value2, so on..);Example:
Code:
INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerName, ContactName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country) VALUES ('New Cus', 'Hello', 'some house', 'Mumbai', '400078', 'India');Output:
4. UPDATE
This statement is used to update the records inside the table, which is already existing.
Syntax:
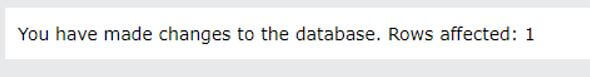
UPDATE Customers
SET ContactName = 'amit verma', City= 'Mumbai'
WHERE CustomerID = 2;Output:
Examples of DBMS Constraints
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1 – Key constraints
This is used to identify the record in the table uniquely, so that means we cannot duplicate the column with key constraints applied.
| Id (Key Constraints) | First_Name | Last_Name |
| 1 | Amit | Verma |
| 2 | Sumit | Sharma |
| 1 | Anita | Verma |
Not allowed because Id already present at the table.
Example #2 – Domain constraints
This is used to define the value that an attribute can take. Here age can only be numeric; we cannot insert a string to it.
| Id (Key constraints) | Name | Age (Numeric) |
| 1 | Amit Verma | 20 |
| 2 | Sumit Sharma | 30 |
| 1 | Anita Verma | ABC |
Not allowed because Age is a numeric attribute.
Example #3 – Entity integrity constraints
This is used to indicate the rule on the primary key filed, which cannot contain the null key because we used this to identified the record.
| Id (Primary Key) | Name | Age (Numeric) |
| 1 | Amit Verma | 20 |
| 2 | Sumit Sharma | 30 |
| Anita Verma | ABC |
Example #4 – Referential constraints
Related with the foreign key, every foreign key value must be present in the primary key table.
| Id (Primary Key) | Name | Age (Numeric) |
| 1 | Amit Verma | 20 |
| 2 | Sumit Sharma | 30 |
| 3 | Anita Verma | ABC |
| Id(Foreign Key) | City |
| 1 | Mumbai |
| 2 | Pune |
| 5 | Delhi |
Not allowed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using DBMS Constraints
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- It helps us to achieve the data integrity.
- Need not to handle separately in code by applying checks.
- Throw exception if anything invalid we try to add.
Disadvantages:
- Increase complexity
- Database failure
- Huge size, cost
- Performance
Conclusion
By using it, we can take care of our data in the table, all the points seen in the article, which helps us understand when to use this. Easy to use, readable, and maintainable by the developers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “DBMS Constraints” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.