Updated April 5, 2023
Introduction to NoSQL Database
NoSQL databases work with large sets of distributed data and are commonly used in real-time web applications. They have a simple design, offer fine control over availability, and enable simple horizontal scaling to clusters of machines. Due to their use of different data structures, the operations of NoSQL databases are generally faster than those of relational databases. However, the suitability of a database is determined by the type of problem it needs to solve.
The data structures of NoSQL databases are generally more flexible than the tables used in relational databases. Many NoSQL stores prioritize factors such as availability, partition tolerance, and speed over consistency. Although most NoSQL databases do not follow the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties of transactions, some databases such as Aerospike, Google Spanner, MarkLogic, OrientDB, and Symas LMDB have made these properties central to their designs.
What is NoSQL Database?
NoSQL Database is a database implementation method used for stacking, managing, and fetching the data from relational databases that are structured in any model but not in the typical tabular formatted relationship model. They are also known as “not only SQL,” “non-SQL,” or “non-relational databases,” as they support not only SQL programming languages, but also other types of programming languages. NoSQL databases are becoming increasingly popular for big data applications, as well as many other web-based applications.
Difference Between SQL Database and NoSQL Database
Given below are some of the differences between SQL database and NoSQL database:
| Sr. No | SQL Database | NoSQL Database |
| 1 | Same type with fewer variations. | Different types are available like document databases, key-value stores, graph databases, and wide-column stores. |
| 2 | Developed in the 1970s to handle data storage applications. | Developed in the 21st century to overcome the limitations of SQL databases such as multi-structured data, agile development sprints, and scalability. |
| 3 | Data stored in tabular format. | Data storage varies with database type. |
| 4 | Data types and structures are fixed beforehand. Then, the entire database needs to be altered to add a new data item. | Dynamic storage. Dissimilar data can be stored together, which is not the case with SQL databases. |
| 5 | Vertical scalability | Horizontal scalability |
| 6 | Open technologies and closed-source databases come into use as a development model. | Only open technologies come into use. |
| 7 | Supports multi-record ACID transactions. | Mostly does not support them. |
| 8 | Data manipulation is done using specific data manipulation language. | Data manipulation occurs through object-oriented APIs. |
| 9 | Strong consistency | Some products provide strong whereas others provide eventual consistency. |
| 10 | The velocity of data is moderate. | The velocity of data is very high. |
| 11 | Suitable for structured data. | Suitable for structured, semi-structured, as well as unstructured data. |
| 12 | Examples are MySQL, Oracle Database, Postgres. | Examples are MongoDB, HBase, Cassandra, Neo4j. |
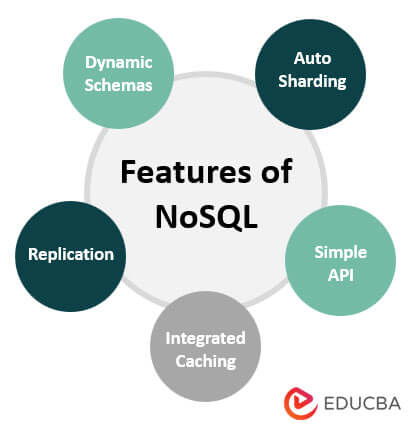
Features of NoSQL
Below are some of the important features of NoSQL:
1. Dynamic Schemas
NoSQL databases allow for the insertion of data without a predefined schema. As a result, one can make real-time application changes easily without worrying about service interruptions. This makes development faster, more reliable, and less time-consuming for the database administrator.
2. Auto-Sharding
Horizontal scaling is done in a NoSQL database, meaning servers are added instead of increasing the capacity of a single server. It provides an auto-sharding feature, which automatically spreads data across various servers. Applications do not need to be aware of the server pool composition, and data and queries are automatically balanced among the servers. If a server fails, it is quickly and transparently replaced without disrupting the application.
3. Replication
The database allows for automatic database replication to maintain availability in case of outages. Some sophisticated NoSQL databases provide automated recovery and are fully self-healing. To enable data localization and withstand regional failures, it can distribute the database across multiple geographic regions. NoSQL does not require a separate application to implement replication.
4. Integrated Caching
NoSQL databases have integrated caching capabilities, meaning they keep frequently used data in system memory and remove the need for a separate caching layer.
5. Simple API
NoSQL offers interfaces that are easy to use for storing and querying data. APIs allow for selection methods and low-level data manipulation. NoSQL does not use a standard-based query language.
Why Use NoSQL Database?
- Analytics: NoSQL databases are suitable for analytical queries, as the querying language used for atomic queries can also be used for analytical queries.
- Scalability: NoSQL databases are designed to scale easily. Data is divided and balanced among multiple nodes in a cluster, and by default, aggregate queries are divided. Hence, one prefers them for their scalability.
- Redundancy: NoSQL databases are designed with redundancy in mind. They are capable of handling hardware failures without affecting performance. The problem of hardware failure is dealt with during the development phase.
- Flexibility: NoSQL databases provide immense flexibility in data storage, leading to increased performance.
- Rapid Development: The database allows for easy modification of data storage and query methods. Batch processing and simple refactoring accomplish massive changes, making NoSQL databases ideal for rapid development.
Types of NoSQL Database
There are four primary types of NoSQL databases: key-value stores, document databases, wide-column stores, and graph stores.
- Key-Value Stores: These databases work on a simple data model that consists of a pair of unique keys and a value associated with it. These databases are highly efficient and scalable for caching in web applications and session management. They can work with RAM, disk drives, or solid-state drives.
- Document Databases: These databases store semi-structured data and their descriptions in document format. They do not require a master schema for creating and updating programs. Their usage has increased with the use of JavaScript and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation). They serve mobile application data handling and content management.
- Wide-column Stores: These databases organize data in columns instead of rows, which allows for faster querying of large datasets compared to other conventional databases. They have usage in catalogs, fraud detection, and recommendation engines.
- Graph Stores: These databases organize data as nodes and edges that show connections between nodes. They are useful for mapping relationships as per requirements, such as in customer relationships or reservation system management.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- High scalability
- High availability
- Big data capability
- Easy replication
- Fast performance
- High flexibility
Disadvantages:
- Narrow focus
- Open-source
- Management challenge
- GUI not available
- Large document size
Conclusion
NoSQL databases are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to handle large volumes of data efficiently and their flexibility in handling different types of data. With their scalability, redundancy, and rapid development capabilities, NoSQL databases are an excellent option for modern businesses looking to manage their data effectively.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: