Updated June 30, 2023
Definition of Tkinter Calculator
Tkinter calculator is a simple Graphical User Interface calculator developed by using the module. Python offers many ways for developing various GUI applications. Tkinter module is one of the most useful and easiest ways for developing GUI applications because Tkinter works well in both Linux and Windows platforms. This article will show how to develop a simple GUI calculator using the Tkinter module.
Prerequisites for developing:
In order to create a simple Graphical User Interface calculator using Tkinter we need the following prerequisites.
- Tkinter
- Lamda
How to Create a Simple GUI Calculator?
In order to create a simple GUI do the following steps.
- Import the Tkinter module
- create the main user interface. (window for our calculator)
- Add the widgets to the user interface
- Apply the event trigger for the widgets
What can we do with Tkinter Calculator?
We can perform the following basic arithmetic operations.
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Division
- Multiplication
Steps to Create
Let us see how to create a GUI calculator step by step
-
Create the GUI Interface
# Python code for creating a GUI calculator.
# import tkinter package
from tkinter import *
# create a GUI user interface
if __name__ == "__main__":
giu_face = Tk()# set the background color for the GUI interface.
giu_face.configure(background="red")
# set the title for GUI interface
giu_face.title("Simple Calculator")# set the size of the GUI window interface.
giu_face.geometry("370x180")
giu_face.mainloop()
exp = ""-
Function to Update the exp in the Text Entry Box
def pres(number):
global exp
# string concatenation
exp = exp + str(number)
# using set method to update the expression
equation.set(exp)- Code for Calculating Ultimate Expression
def pres():
try:
global exp
- Using Eval Function to Calculate the Exp given and Convert the Result to String
# using eval function to calculate expression
total_value = str(eval(exp))
equation.set(total_value)
exp = ""
using except block to handle errors if generated
# using except block to handle generated errors
except:
equation.set(" error ")
exp = ""- Function for Clearing the Contents of the Calculator
def clearng():
global exp
exp = ""
equation.set("")
equation = StrVar()- Function for Creating the EntryBox for Typing the Text for Operation
exp_field = Ent(gui, text_variable=equation)- Using the Grid Method for Assigning the Widgets to their respective positions.
exp_field.grid(columnspan = 5)
equation.set('enter your value’)- Creating the Buttons for Typing the Numbers
# create the Buttons and position them inside the window.
bton1 = Button(giu_face, text =' 1 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(1), height = 1, width = 7)
bton1.grid(row = 2, column = 0, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton2 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 2 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(2), height = 1, width = 7)
bton2.grid(row = 2, column = 1, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton3 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 3 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(3), height = 1, width = 7)
bton3.grid(row = 2, column = 2, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton4 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 4 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(4), height = 1, width = 7)
bton4.grid(row = 3, column = 0, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton5 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 5 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(5), height = 1, width = 7)
bton5.grid(row = 3, column = 1, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton6 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 6 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(6), height = 1, width = 7)
bton6.grid(row = 3, column = 2, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton7 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 7 ', font="lucida 20 bold",,
command = lambda: input_val(7), height = 1, width = 7)
bton7.grid(row = 4, column = 0, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton8 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 8 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(8), height = 1, width = 7)
bton8.grid(row = 4, column = 1, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton9 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 9 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(9), height = 1, width = 7)
bton9.grid(row = 4, column = 2, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
bton10 = Button(giu_face, text = ' 0 ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val(0), height = 1, width = 7)
bton10.grid(row = 5, column = 0, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
plus = Button(giu_face, text=' + ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val("+"), height=1, width=7)
plus.grid(row = 2, column = 3, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
minus = Button(giu_face, text = ' - ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val("-"), height = 1, width = 7)
minus.grid(row = 3, column = 3, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
multiply = Button(giu_face, text = ' * ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val("*"), height = 1, width = 7)
multiply.grid(row = 4, column = 3, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
divide = Button(giu_face, text=' / ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val("/"), height = 1, width = 7)
divide.grid(row = 5, column = 3, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
equal = Button(giu_face, text=' = ', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = input_val, height = 1, width = 7)
equal.grid(row = 5, column = 2, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
clearng = Button(giu_face, text = 'clearng', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = clearng, height = 1, width = 7)
clearng.grid(row = 5, column = '1', ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
Decimal = Button(giu_face, text='.', font="lucida 20 bold",
command = lambda: input_val('.'), height = 1, width = 7)
Decimal.grid(row = 6, column = 0, ipady = 4 , ipadx = 2)
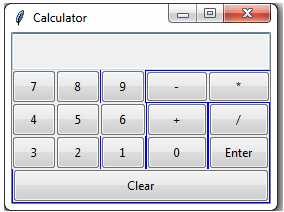
giu_face.mainloop()Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed how to create a simple GUI Tkinter calculator and perform simple arithmetic operations using various examples. The module is considered to be very important in Python since it is very easy to create many GUI applications. In Linux or Ubuntu machines, you need to download separately and install it. But in Windows OS, it is readily available in the Anaconda package. We hope this article helps. Thank you.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tkinter Calculator. Here we discuss the Definition of, How to Create a simple GUI Tkinter Calculator? with sample code for better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –