Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction to Tkinter Combobox
The Tkinter Combobox is a UI widget available in the Tkinter library, serving the purpose of selecting values from a dropdown list. It combines the functionality of an Entry widget and a dropdown widget. The dropdown entries are replaceable, and if the user does not select a value, the default value is automatically displayed on the screen. The Tkinter module utilizes standard library functions, making it the primary choice for GUI-based widgets. The Combobox select option arrow automatically scrolls down when the user searches for a particular value in the field.
Syntax:
The Tkinter module, following the Tk interface, is recognized as the most powerful GUI-based widget. Also, it has the most advanced library methods in Python. It has more global plans; hence Combobox() is also one of the widgets and globalized methods. It allows direct utilization of specific functions and behaviors within the application. It has its own syntax and default parameters.
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
variable name=Tk()
ttk.Label(window, text=””, …)
variable name=ttk.Combobox(variable name, width=, text= )
variable name.mainloop()The above code is the basic syntax of the Combobox Tkinter library. We have called the UI items like labels, textbox, etc; based on the requirement, and we will proceed with further steps to enhance the application.
How Combobox Works in Tkinter?
The Tkinter module has a different set of widgets in the library. This package has a set of built-in functions that have been used for covering the UI parts of the web application. It has the most interactive and advanced library. The UI widget has buttons, views, a scroll box, a list box, a combo box, etc. Once we click the button, it operates and works the backend areas code that the user-defined logic can cover. If the user is not choosing any values, it takes the default value based on the front and backend code logic.
If the user selects any values of the combo list box again, the value will be replaceable if the user needs it. The Combobox has different parameters that will be passed, and attributes like font family, size, weight, colors, etc. These types of attributes are passed to the Combobox(). Also, Tkinter has a default font. It could be more specified with the tuple side of options. The Tkinter combo box used an event binding feature while we used the Combobox callback function binding, and these data binding will be called using the combo box virtual events. The user will use these events while selecting the values in the drop-down list box. The combo box has another option called <comboboxSelected> option. It executes the predefined function before executing the pop-down list of values in the apps.
Also, the Combobox has two different forms before the normal state 1. read-only and 2. disabled. The read-only state used in the text field area is mostly non-editable, and the user will choose only the values in the drop-down list box.
Examples
Lets us discuss the examples of Tkinter Combobox.
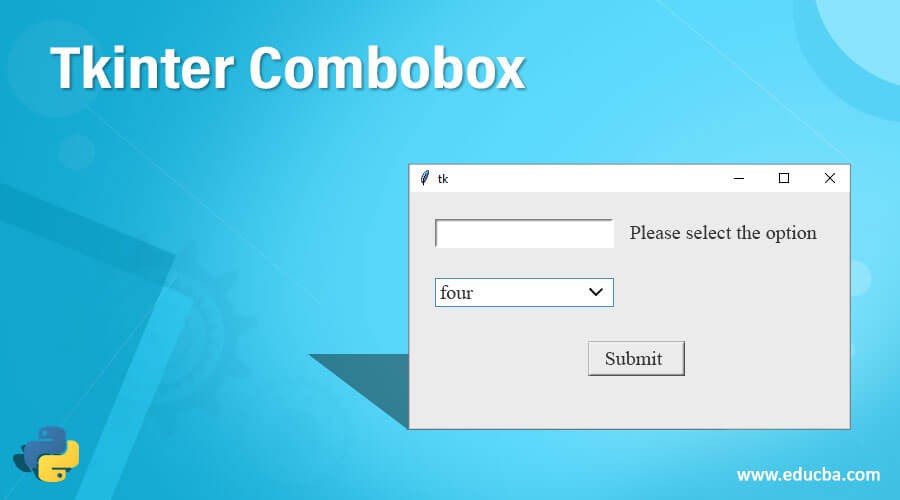
Example 1
from tkinter import *
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
user = Tk()
uname = Label(user,text = "uname").grid(row =1, column = 1)
un= Entry(user).grid(row = 0, column = 0)
passw = Label(user,text = "pass").grid(row = 1, column = 1)
ps = Entry(user).grid(row = 1, column = 1)
result = Button(user, text = "submit").grid(row = 3, column = 3)
comb = tk.Label(user,
text = "Please select the option")
comb.grid(column=2, row=1)
example = ttk.Combobox(user,
values=[
"first",
"second",
"third",
"four"])
print(dict(example))
example.grid(column=2, row=2)
example.current(3)
user.mainloop() Output:
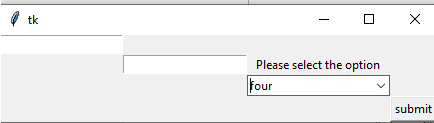
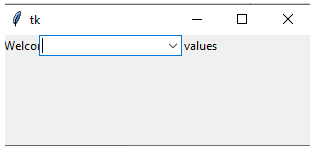
Example 2
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
def demo(events):
print("Please select the new events from the list")
first = tk.Tk()
first.geometry('310x110')
def month():
example["values"] = ["first",
"second",
"third",
"four"
]
lists = tk.Label(first,
text = "Welcome User please select list of values")
lists.grid(column=5, row=5)
example = ttk.Combobox(first,
values=[
"first",
"second",
"third",
"four"],
postcommand=month)
example.grid(column=5, row=5)
first.mainloop()Output:
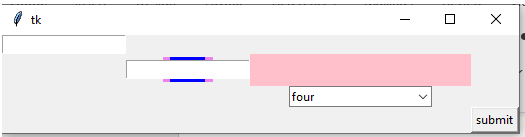
Example 3
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import *
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
user = Tk()
uname = Label(user,text = "uname", background = 'violet', foreground ="violet",
font = ("Times New Roman", 13)).grid(row =1, column = 1)
un= Entry(user).grid(row = 0, column = 0)
passw = Label(user,text = "pass", background = 'blue', foreground ="blue",
font = ("Times New Roman", 13)).grid(row = 1, column = 1)
ps = Entry(user).grid(row = 1, column = 1)
result = Button(user, text = "submit").grid(row = 3, column = 3)
comb = tk.Label(user,
text = "Please select the option",background = 'pink', foreground ="pink",
font = ("Times New Roman", 17))
comb.grid(column=2, row=1)
example = ttk.Combobox(user,
values=[
"first",
"second",
"third",
"four"])
print(dict(example))
example.grid(column=2, row=2)
example.current(3)
user.mainloop()Output:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the above concepts and examples for the combo box are the basics and usages of the Python application. The variation in the output depends on the user’s requirements, particularly the selection of widgets and combo box options. It’s one of the user-friendly widgets of the Tkinter library in Python.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tkinter Combobox. Here we discuss the definition and working of Tkinter Combobox along with examples and code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –