Updated September 5, 2023
Definition of Table in Oracle
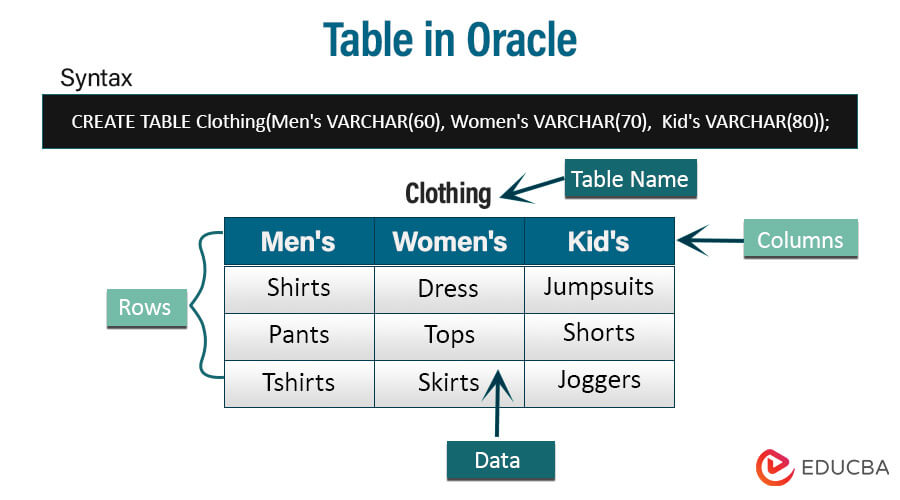
In Oracle, a database table is a structured collection of connected data divided into rows and columns.
Each column represents a unique record, and each row describes a specific attribute. Tables in a relational database management system provide an efficient means of storing, managing, and retrieving data.
Tables are the cornerstone of organized and structured data storage in Oracle databases. A table is a virtual container with rows and columns, much like a spreadsheet. This fundamental database construct is crucial for managing and manipulating data efficiently. This article delves into Oracle tables, exploring their definition, components, data types, creation, and more.
Table of Content
Components of a Table
The components of a database table include columns, rows, and cells, which collectively organize and store data in a structured manner:
- Columns (Fields): Each column in the saved data represents different aspects or properties. We assign a name and data type to each column, specifying the type of information it can hold, such as text, integers, dates, or binary data. For instance, a table containing employee information may include columns like “First Name,” “Last Name,” “Employee ID,” and “Salary.”
- Rows (Records): Rows in a table correspond to specific records or instances. Each row has a series of data values, each associated with a different column. These values constitute a comprehensive record. Using the employee information example again, each row may represent information about an individual employee, such as their first name, last name, employee ID, and salary.
- Cells (Data Values): Cells are the intersections of rows and columns that hold specific data values for a given attribute of a particular record. In the context of the employee table, a cell would hold a specific value, such as “Maria” for the “First Name” column in a specific employee’s record.
How to Create a Table in Oracle?
Now that we know what exactly a table in Oracle is, we will see how to create a table in the Oracle database.
Let us look into the syntax for creating a table in Oracle.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype [constraint],
column2 datatype [constraint],
...
);Parameters:
Let us now look into the parameters for the above syntax:
- CREATE TABLE: The SQL command is used to create a new table.
- table_name: The name of the table that you want to create. Replace this with the name of the table you want.
- column1, column2, …: You can define the table by specifying the names of the columns.
- data_type: The column’s data type. It defines the type of data that can be stored in the column.
- Constraints: Optional constraints that impose rules on the column’s data. NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY, UNIQUE, CHECK, and FOREIGN KEY are all common constraints.
Example:
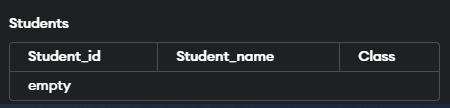
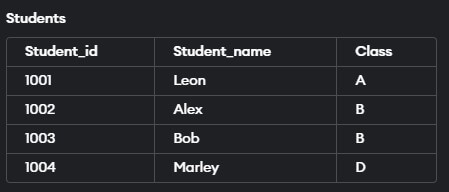
Now let us take an example to understand better. In this example, we will create a Student table with three columns named Student_id, Student_name, and Class.
Let us look at the query below:
CREATE TABLE Students (Student_id varchar(20) primary key,
Student_name varchar(10), Class varchar(10));Output:
Insert Data in Table
The insert statement adds a new row or rows in a table in the Oracle database. We generally use it after we have created a table in the database. One important point to remember is that while inserting records into a table, we must provide a value for every NOT NULL value. Let us look into the syntax of the INSERT statement in Oracle.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO
table_name (column1, column2,……….)
VALUES (expression1, expression2,……);Parameters:
- table_name: It refers to the name of the table in which we want to insert the data
- column: The column names in the table.
- Expression: The values/expression to be inserted in the respective columns.
Example:
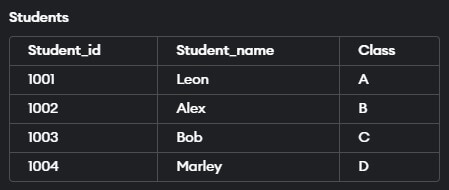
Now let us look at an example below to understand the INSERT statement better. In our example, we will insert values into the Students table we created a while ago. Let us look at the query below.
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, Student_name, Class)
VALUES ('1001', 'Leon', 'A');
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, Student_name, Class)
VALUES ('1002', 'Alex', 'B');
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, Student_name, Class)
VALUES ('1003', 'Bob', 'C');
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, Student_name, Class)
VALUES ('1004', 'Marley', 'D');If we look at the query, we are inserting values to all three columns created during the table creation.
The screenshot below represents the output of the same.
Edit Table in Oracle
To edit a table, follow these steps:
1. Update Column
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name
SET column = value
WHERE condition;Parameters:
- table_name= It refers to the name of the table.
- [where condition]: It refers to the condition that must be satisfied for the update to occur.
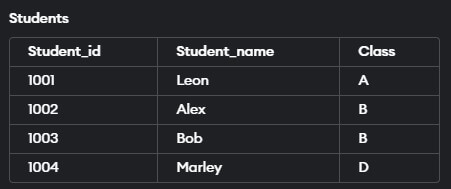
Example:
So, in this example, we will update the value of the ‘Class’ column of the ‘Students table’ where the Student’s name is ‘Bob’. Let us look at the query for the same.
UPDATE Students SET Class = 'B'
WHERE Student_NAME ='Bob';Output:
2. Adding Columns
The ALTER TABLE statement is used in Oracle to add columns to an existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD column_name data_type constraintParameters:
- table_name: The existing table’s name.
- column_name: The new column’s name.
- data_type: The new column’s data type.
- column_constraint (optional): Any constraint (e.g., NOT NULL, DEFAULT, etc.) applied to the new column.
Example:
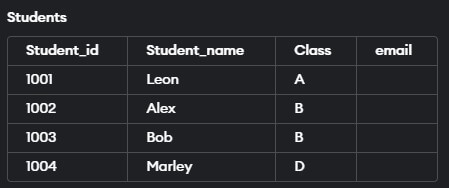
So, in this example, we will add an ’email’ column to the ‘Students table’. Let us look at the query for the same.
ALTER TABLE Students
ADD email VARCHAR(100);Output:
3. Dropping Columns
To delete a column from a table, use the ALTER TABLE statement and the DROP COLUMN clause.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP COLUMN column_name;Parameters:
- table_name: The table name from which you want to remove a column.
- column_name: The name of the column you want to drop.
Example:
So, in this example, we are dropping the ’email’ column from the ‘Students table’. Let’s have a look at the query.
ALTER TABLE Students
DROP COLUMN email;Output:
4. Retrieving Data
A fundamental operation in a database is retrieving data from a table. The SELECT statement is used to retrieve information from one or more tables. Here are some options and examples for retrieving data:
Syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;Parameters:
- column1, column2,..: The columns from which you want to retrieve data. To retrieve all columns, use *.
- table_name: The table name from which you want to retrieve data.
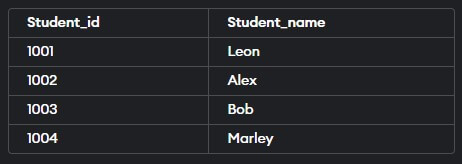
Example #1
Retrieve specific columns from the Students table.
Query:
SELECT Student_id, Student_name FROM Students;Output:
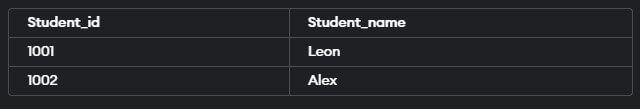
Example #2
Retrieve data with a condition using the “WHERE” clause.
Query:
SELECT Student_id, Student_name
FROM Students
WHERE Student_id < 1003;Output:
5. Renaming a Table
To modify the name of an existing table, use the RENAME command.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE old_table_name
RENAME TO new_table_name;Parameters:
- old_table_name: The table’s present name, which you want to rename.
- new_table_name: The new name you want to give the table.
Example:
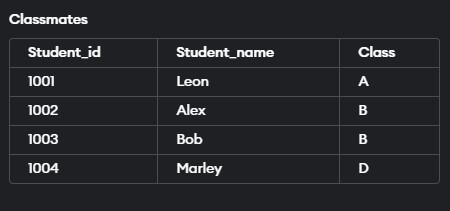
In this example, we will change the table name from ‘Students’ to ‘Classmates’. Let’s have a look at the query.
ALTER TABLE Students
RENAME TO Classmates;Output:
Delete Table in Oracle
We use the DELETE statement in the Oracle database to delete or remove records/records from a table.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE table_name;Parameters:
- table: The name of the table
- conditions: It refers to the conditions which must be met to get the record deleted.
Example:
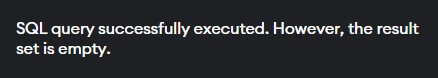
In this example, we will delete table’ Classmates’. Let us look at the query for the same.
DROP TABLE Classmates;The screenshot below shows the query output when run on SQL developer.
The output shows that the Classmates table satisfying the condition has been deleted.
Constraints
Constraints are rules or conditions applied to a database’s columns or tables to enforce data integrity and consistency. They prevent data from being inserted, modified, or deleted if the rules are not followed. Oracle provides a variety of limitations to assure the quality and accuracy of data. Here are some often-used constraints:
1. NOT NULL Constraint
Ensures that a column does not have any NULL values.
Example:
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR(80) NOT NULL,
birthdate DATE
);
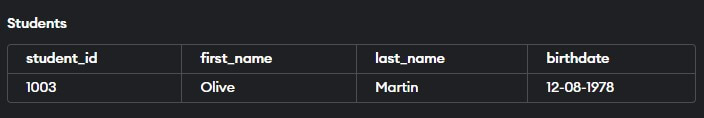
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate)
VALUES ('1003', 'Olive', 'Martin', '12-08-1978');
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate)
VALUES ('1002', 'Alex', '9-02-1971');Output:
The attempt to insert a row without providing a value for the last_name column in the second INSERT statement will result in an error due to the NOT NULL constraint.
Note: Error: 3 values for 4 columns
You will receive an error when you run the above query since we only provided 3 columns of Data instead of 4. Enter the last name for the second insert statement (Alex) to remove the error.
2. UNIQUE Constraint
Ensures that all column values are unique across the table.
Example:
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(60),
last_name VARCHAR(80),
email VARCHAR(150) UNIQUE
);
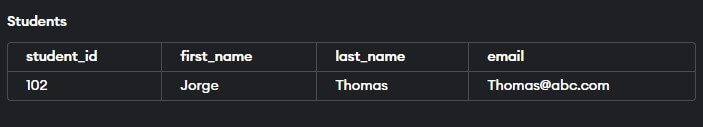
INSERT INTO students (student_id, first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES (102, 'Jorge', 'Thomas', '[email protected]');
INSERT INTO students (student_id, first_name, last_name, email)
VALUES (103, 'Rosie', 'Thomas', '[email protected]');Output:
The UNIQUE constraint prevents the second INSERT statement from inserting a row with a duplicate email address.
This Error will occur because of the repetition of emails. Use a separate email address for each statement to avoid the following error.
3. PRIMARY KEY Constraint
Identifies each table entry uniquely and enforces uniqueness and NOT NULL.
Example:
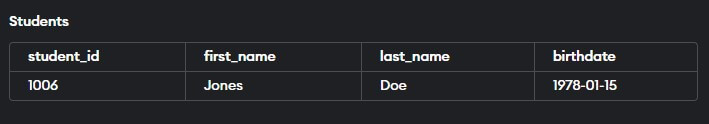
CREATE TABLE students (
student_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
birthdate DATE
);
INSERT INTO students (student_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate)
VALUES (1006, 'Jones', 'Doe', '1978-01-15');
INSERT INTO students (student_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate)
VALUES ('Alisa','Bailey','2009-05-20');
INSERT INTO students (student_id, first_name, last_name, birthdate)
VALUES (1006, 'Sophie', 'Walker', '1976-05-18');Output:
The PRIMARY KEY constraint prevents the second INSERT statement from inserting a row with a null student_id value.
Due to the PRIMARY KEY restriction, attempting to insert a row with a duplicate student_id value in the third INSERT statement would result in an error.
4. FOREIGN KEY Constraint
Establishes a link between tables by verifying that values in one column match values in the primary key of another table.
Example:
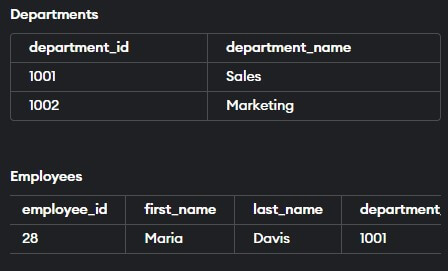
CREATE TABLE departments (
department_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
department_name VARCHAR(150)
);CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(80),
last_name VARCHAR(100),
department_id NUMBER,
CONSTRAINT fk_department FOREIGN KEY (department_id) REFERENCES departments(department_id)
);INSERT INTO departments (department_id, department_name)
VALUES (1001, 'Sales');
INSERT INTO departments (department_id, department_name)
VALUES (1002, 'Marketing');
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id)
VALUES (28, 'Maria', 'Davis', 1001);
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id)
VALUES (29, 'Rachelle', 'Smith', 1003);Output:
The attempt in the last INSERT statement to insert an employee with a department_id that does not exist in the department’s table will result in an error owing to the FOREIGN KEY constraint.
To avoid a FOREIGN KEY constraint Error, replace 1003 with 1002 in the department_id of the last insert statement.
5. CHECK Constraint
In Oracle, you can use the CHECK constraint to impose specific conditions or rules on the values stored in a column.
Example:
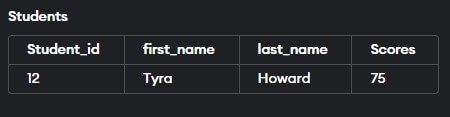
CREATE TABLE Students (
Student_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(60),
last_name VARCHAR(80),
Scores NUMBER(10, 2),
CONSTRAINT chk_positive_Scores CHECK (Scores > 35)
);
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, first_name, last_name, Scores)
VALUES (12, 'Tyra', 'Howard', 75);
INSERT INTO Students (Student_id, first_name, last_name, Scores)
VALUES (27, 'Camille', 'Perry', 34);Output:
The attempt to insert a row with a score less than 35 in the second INSERT statement will result in an error due to the CHECK constraint.
Note: Error: CHECK constraint failed: chk_positive_Scores
The error message “CHECK constraint failed” indicates that a row’s insertion or update violated the constraints defined by a CHECK constraint.
Types of Tables in Oracle
There are multiple sorts of tables in Oracle; here are some examples of common Oracle table types:
- Regular (Heap-Organized) Table: This represents the most common table type in Oracle, where data remains unsorted. Enter rows as they arrive, and let the database manage data storage and retrieval. This kind of table is appropriate for storing general-purpose data.
- Index-Organized Table (IOT): An IOT stores rows in a B-tree index structure based on the primary key. This design improves query performance for specific retrieval patterns, especially range queries or single-row lookups. It’s suitable for scenarios where quick access to rows based on the primary key is crucial.
- Partitioned Table: A partitioned table separates data into smaller, more manageable portions known as partitions depending on a defined partitioning key. Partitioning may improve performance by enabling more efficient data pruning during queries and maintenance procedures.
- Temporary Table: Use temporary tables to hold data that exists only for a session or transaction. They help store interim data during complex procedures or exchange data between query parts.
- External Table: An external table allows you to access data stored outside the database, such as in flat files. It lets you treat external data as part of the database, allowing you to load and query data without actually transferring it into the database.
- Clustered Table: A clustered table stores data in a cluster, a group of tables sharing the same storage blocks. Data in a clustered table is physically stored together based on the clustering key, which can increase query performance.
- Materialized View: A materialized view is a pre-computed table containing the query result. It increases query performance by storing aggregated or combined data, eliminating the need to compute the same results several times.
- Object Table: An object table holds object types, allowing you to create tables with object columns instead of traditional data types. This is beneficial for dealing with complex data structures and sustaining hierarchical relationships.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about Tables in the Oracle database. We discussed how to create a table and then insert, *edit and delete values in the table with the help of examples.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Table in Oracle” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.