Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to INSERT in Oracle
INSERT statement in Oracle database is a statement which is used to write DML (Data Manipulation Language) statement/ queries to add one or more rows of data to an already created table in the database in two ways: conventional insert (oracle database reuses the free space available in the table without compromising referential integrity constraints) and direct-path insert (Oracle database directly inserts data into the data files bypassing the buffer cache and not reusing the free space of the table).
Syntax
The INSERT query has a pretty simple syntax as we will see below,
- Inserting a single record using the VALUES keyword.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name
(column1, column2, …… , column_n)
VALUES
(expression1, expression2, expression3, expression_n);
- Inserting multiple records using the SELECT keyword.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name
(column1, column2, …… , column_n)
SELECT expression_1, expression_2, ……. , expression_n
FROM source_table
[WHERE conditions];
Parameters of INSERT Statement in Oracle
Below are the different parameters of INSERT Statement in Oracle:
- table_name: The name of the table in which we want to insert the values.
- (column1, column2, …… , column_n): columns in which we want to insert values
- (expression1, expression2, expression3, expression_n): There are the values that we want to insert into the respective columns.
- source_table: This is the table from where we will extract data to insert into the current table.
- [where condition]: This condition is optional. It is used when we want to insert data based on some condition.
Examples to Implement INSERT Statement in Oracle
Following are the different examples to implement the insert statement in oracle:
Example #1 – INSERT using VALUES Keyword
This is the easiest way of using the INSERT command. In this case, we basically insert values by giving real values as per the columns. We can use it both ways by providing the columns in which we want to enter or without providing the columns. If we provide the columns then the values will be inserted as per the order of columns we provided. We will look into both ways with the help of examples.
Query:
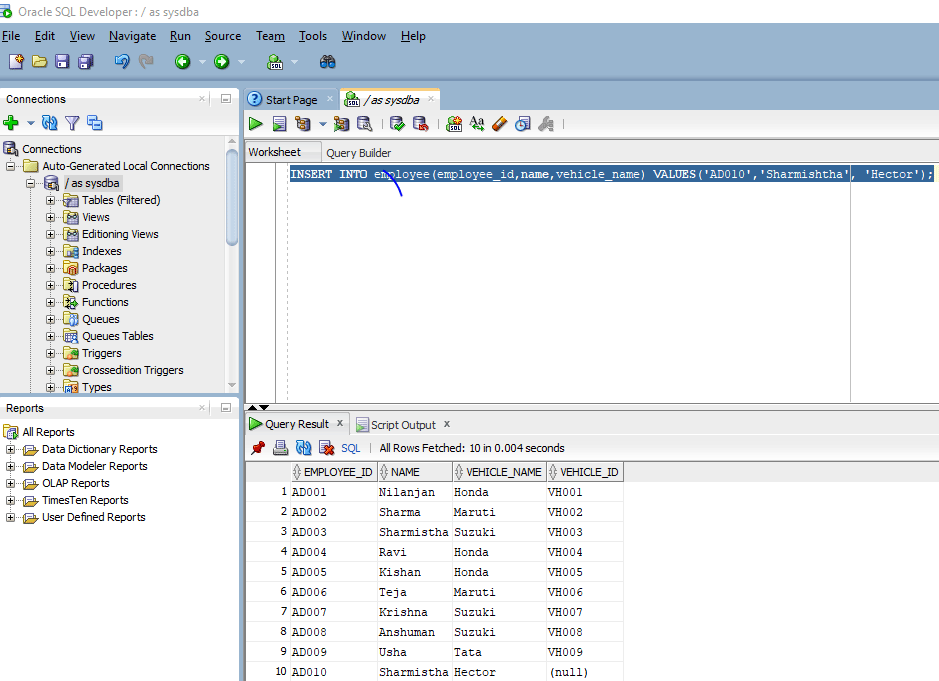
INSERT INTO employee (employee_id,name,vehicle_name) VALUES('AD010','Sharmishtha', 'Hector');
Now we have left one column here which is vehicle_id. So automatically null will be inserted in it.
The below image shows us the table data after data has been inserted.
As you can see the last column in the last record is null. Now we will not mention the columns just use the VALUES keyword with INSERT.
Query:
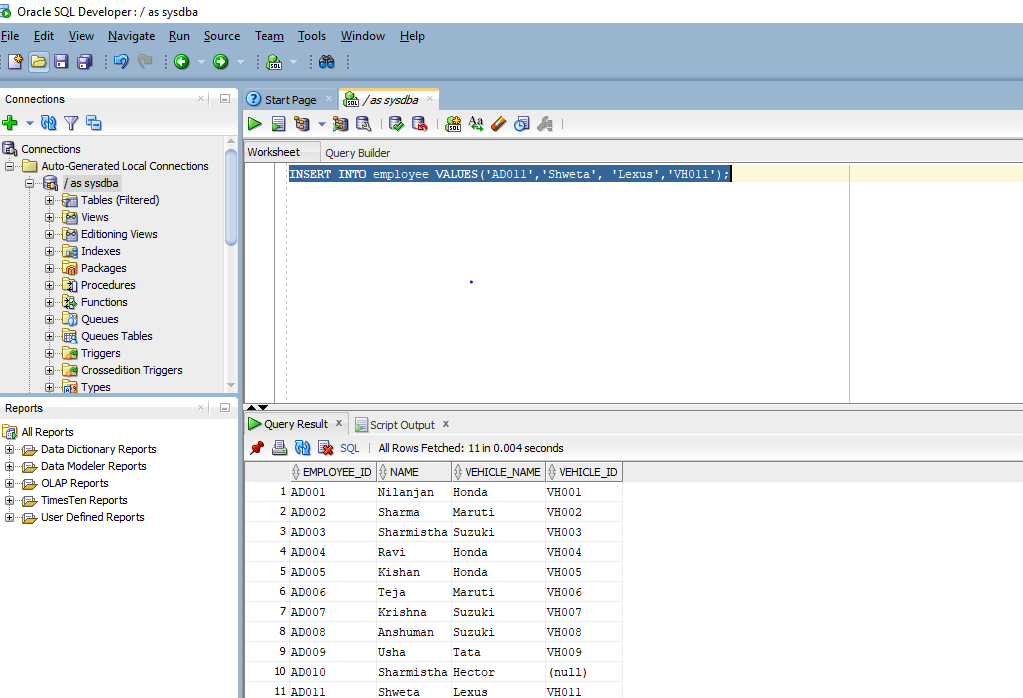
INSERT INTO employee VALUES('AD011','Shweta', 'Lexus','VH011');
As you can see we have not provided the columns. Let us look at the table values after executing the insert command.
As you can see the last record has been inserted into the table after the execution of the INSERT query.
Example #2 – INSERT using a SELECT keyword with the condition
This is very useful when we want to do multiple inserts in a table. In this, we use a SELECT statement to insert data to our table by extracting data from another table. We can also put conditions in the query if we want the data to get inserted based on some condition.
We will see some examples below which shows us how to use INSERT with SELECT.
Query:
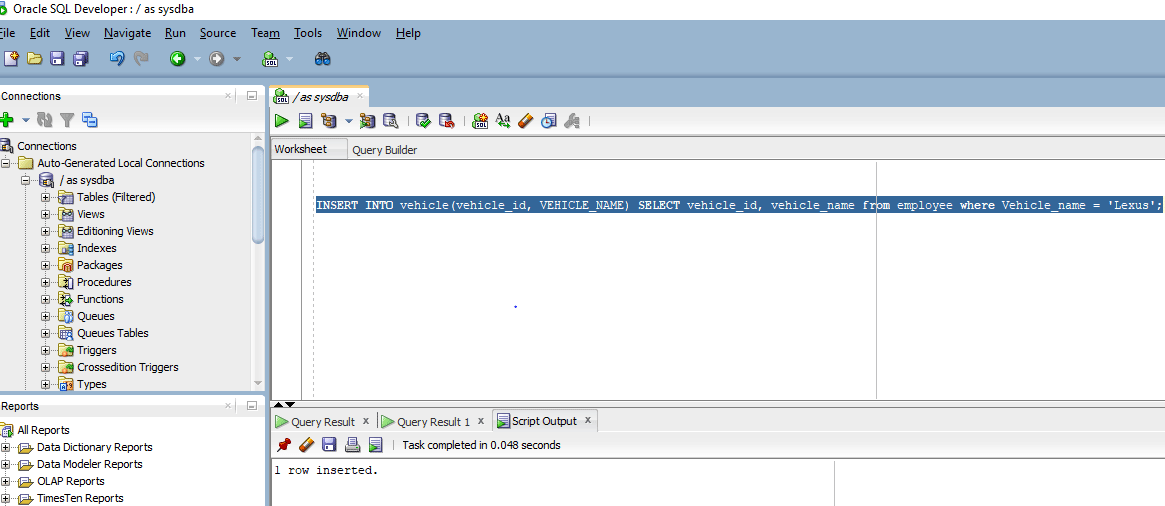
INSERT INTO vehicle(vehicle_id, VEHICLE_NAME) SELECT vehicle_id, vehicle_name from employee where Vehicle_name = 'Lexus';
In the above query, we are actually inserting in the table vehicle by extracting data from another table employee based on the condition that only those records which have value as Lexus in the column vehicle_name of table employees are eligible for getting extracted and then inserted in the vehicle table. So when we execute the above query all records which have vehicle_name as Lexus in table employee will get inserted in the table vehicle. In our case, we had only one such record so if you see the screenshot you will see that the console says “1 record inserted”.
Example #3 – Using INSERT ALL on a single table
This statement is used when we want to add multiple records into a single table by using a single INSERT statement. Instead of using INTO we are going to use ALL INTO with INSERT to achieve this. As an example suppose we have a table vehicle and we want to insert two records in it. If we use INSERT INTO then we have to write two insert queries but with INSERT ALL we only have to write one query. Let us look at the query for that
Query:
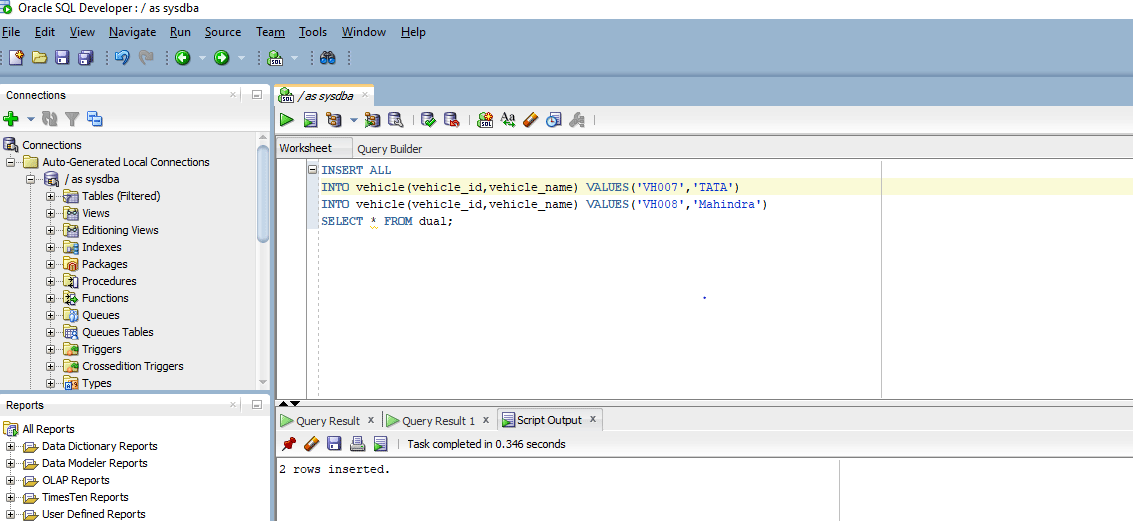
INSERT ALL
INTO vehicle(vehicle_id, vehicle_name) VALUES('VH007',TATA)
INTO vehicle(vehicle_id, vehicle_name) VALUES('VH008','Mahindra')
SELECT * FROM dual;
As you can see in the above query we are inserting two records by using a single INSERT statement. If we would have written the same query using INSERT INTO statement it would have been as written below,
INSERT INTO vehicle(vehicle_id,vehicle_name) VALUES('VH007',TATA)
INSERT INTO vehicle(vehicle_id,vehicle_name) VALUES('VH008','Mahindra')
Output:
As you can see on executing the query console provides an output that “2 rows inserted”.
Example #4 – Using INSERT ALL on multiple tables
We can also use INSERT ALL statement to insert data on multiple tables. The syntax will be the same and we just have to replace the table names and their corresponding columns and values. Suppose, for example, if we want to insert data in both employees as well as the vehicle table then the following query would do the job.
Query:
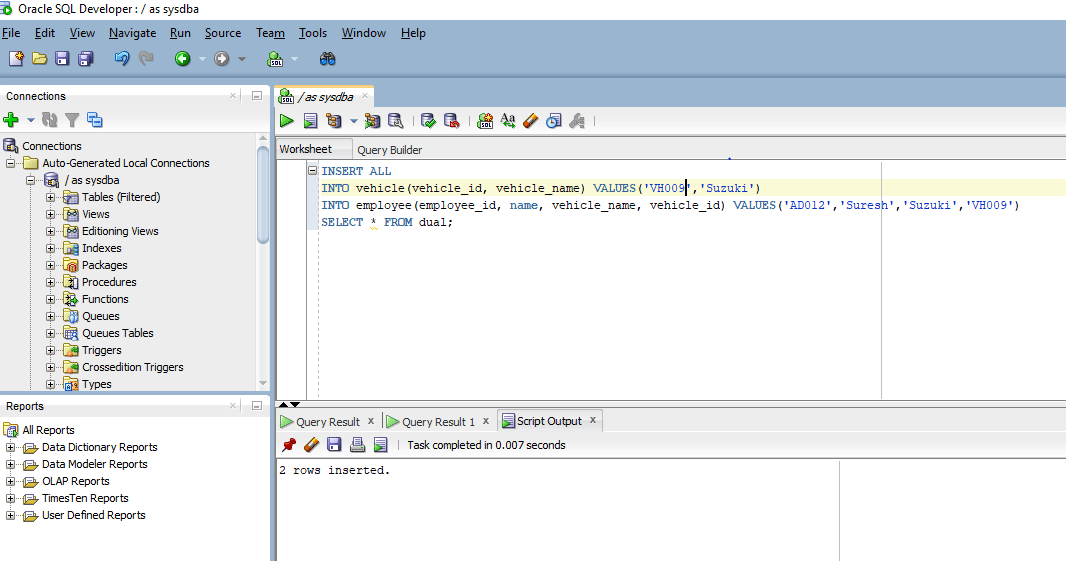
INSERT ALL
INTO vehicle(vehicle_id, vehicle_name) VALUES('VH009','Suzuki')
INTO employee(employee_id, name, vehicle_name, vehicle_id) VALUES('AD012','Suresh','Suzuki','VH009')
SELECT * FROM dual;
As you can see in the above query we have just changed the table name and accordingly their columns and values. If we would have written the same query using INSERT INTO statement it would have been as written below,
INSERT INTO vehicle(vehicle_id, vehicle_name) VALUES('VH009','Suzuki');
INSERT INTO employee(employee_id, name, vehicle_name, vehicle_id) VALUES('AD012','Suresh','Suzuki','VH009');
Output:
As you can see on executing the query console provides an output that “2 rows inserted”.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to INSERT in Oracle. In this article, we discuss what is INSERT statement, syntaxes and various ways in which we can use the INSERT statement along with their appropriate examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-