Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Aliases
Oracle has Aliases for all the components associated with the database, like the columns and tables. Alias is a temporary name given to the column or the table in a query, for the user’s convenience in readability for minimizing the query length. When an alias is applied for a column or a table, the alias name is added to the select query in upper case typically, while placing ‘AS’ as an alias keyword between the actual name and the Alias name.
Types of Alias in Oracle
Here are two types of oracle Aliases which are explained below.
1. Column Alias
- Column Alias renames a column heading in a Query.
- The column Alias is specified in the SELECT list by declaring the Alias after the column name by using the space separator.
- Alias heading appears in UPPER casing by default.
- The Alias name should be declared in Double Quote if it is against the specification of naming conventions of Oracle (like Alias name consisting space etc.).
- The AS keyword can be used between the column name and the Alias name.
- An Alias name effectively renames the SELECT list item for the duration of that Query only.
- An Alias cannot be used, anywhere in the SELECT list for the operational purpose.
2. Table Alias
- Table Alias renames the original name of the table in a SQL statement.
- Table Aliases are very useful when working with self joins.
- Table Alias is applied for the current SQL statement only.
- It is an important source when implementing standards of MERGE statements, correlated Queries, and Analytical Functions.
Syntax of Oracle Alias
Here is the syntax of Alias which are given below with basic example:
SELECT Col_1 Column_1, Col_2 "Column 2", ..., Col_n Column_N
FROM TableName Table_Name WHERE condition(s);
Description: Here is the explanation of the above syntax given below.
- Col_1/2/n: The column(s) or calculation as per your requirement. Column_1, Column 2 and Column_N are the Column Alias name respectively.
- TableName: As per your requirement Table_Name is the ALAS name of TableName.
- WHERE: It’s optional, depends on your requirements.
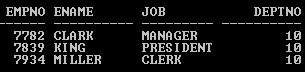
Example #1: Without Alias name,
Query:
SELECT Empno, Ename, Job, Deptno FROM Emp WHERE Deptno=10
Output:
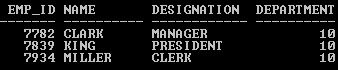
Example #2: With Alias name,
Query:
SELECT Empno Emp_id, Ename name, Job Designation, Deptno Department
FROM Emp WHERE Deptno=10;
Output:
Explanation: The above two examples (without and with Alias name) clearly shows that applying ALAS name is a good practice to hide the original name of columns and make it more readable.
Examples to Implement Oracle Aliases
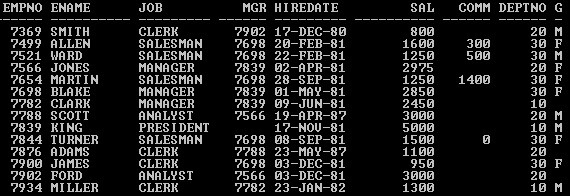
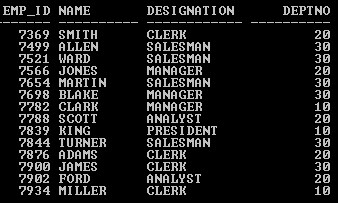
In this section, we’ll see the implementation of oracle Alias and its behavior. For that, we will use the below sample table (Emp) with 14 records to understand the oracle Alias behavior.
Query:
SELECT * from Emp;
Output:
1. AS Keyword Between Column Name and ALIAS
Query:
SELECT Empno AS emp_id, Ename AS name, job AS Designation, Deptno FROM Emp;
Output:
The AS keyword can be used for column Alias name but it’s optional in ORACLE. The AS keyword can be applied only for column(s) Alias name, not for Table(s) Alias name. We’ll get an error if we apply AS keyword for Table Alias name. Example below.
Query:
SELECT Empno AS emp_id, Ename AS name, job AS Designation, Deptno FROM Emp AS E;
Output:
2. ALIAS Name without Any Space
Query:
SELECT Empno emp_id, Ename name, job Designation, Deptno FROM Emp;
Output:
In this example, column Alias names don’t keep any space, so don’t need to enclose the ALAIS names with a double-quote.
3. ALIAS Name with Space
Query:
SQL> SELECT Empno Employee ID, Ename First Name, Job Designation, Deptno FROM Emp WHERE Job ='SALESMAN';
Output:
In this example, Output throws an Error because Alias names contain space. If Alias name contains space then Alias name must be enclosed with Double Quote (” “) to prevent the error.
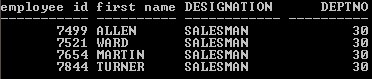
4. ALIAS Name Enclosed with Double Quote
Query:
SQL> SELECT Empno "employee id", Ename "first name", Job designation, Deptno FROM Emp WHERE Job ='SALESMAN';
Output:
In this example, there are two important points.
- Output is not throwing an error even if the Alias name contains space because it is enclosed with Double Quote.
- The SELECT statement supplied all column Alias names are in lower case only but the first two column ALIAS names (in output) are in lower case but the third one (DESIGNATION) is in upper case. WHY?
Because the ALAIS name doesn’t change the case if it is enclosed with Double Quote. In the above example, the first two ALAIS names are enclosed with Double Quote but the third one is not enclosed with, so by default third column name is in upper case but the first two are in lower case.
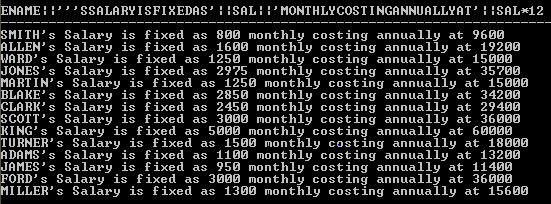
5. ALIAS Name Makes Column Name More Readable
Query:
SELECT Ename ||'''s Salary is fixed as '|| Sal ||' monthly costing annually at '|| Sal*12 FROM Emp;
Output:
In this example, it’s very difficult to understand the column name or column data because the column name tells about the column data and makes it easy to understand.
Query:
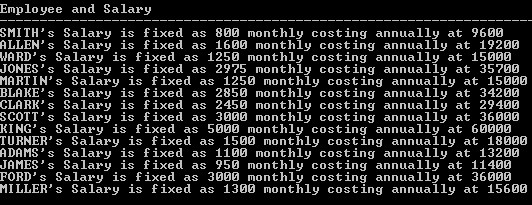
SELECT Ename ||'''s Salary is fixed as '|| Sal ||' monthly costing annually at '|| Sal*12 "Employee and Salary" FROM Emp;?
Output:
Here, column Alias name “Employee and Salary” makes it more readable and easier to understand.
6. ALIAS Name Behavior in WHERE Clause
Column Alias name cannot be used in the WHERE clause directly. It will throw an error, see the example below
Query:
SELECT Empno, Ename, Job Designation FROM Emp WHERE Designation = 'CLERK';
Output:
In this example, Designation is an Alias name of Job which is invalid in WHERE clause but the original column can be passed in WHERE clause. The column Alias name in WHERE clause can be used in two cases, given below with an example.
- Sub-Query
- Common Table Expression(CTE)
Query:
SELECT * FROM
(
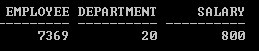
SELECT Empno AS employee, Deptno AS department, Sal AS salary
FROM Emp
)
WHERE employee = 7369;
Output:
Here Employee is an Alias name of Empno column which is getting used in WHERE clause.
7. Table ALAIS Name when Working with Self Join
Query:
SELECT Ename, Job FROM Emp, Emp;
Output:
The above SELECT statement is performing Self Join and output throwing an error because there are two tables with the same name that’s why getting an error. The table Alias name is the best way to avoid this ambiguous situation. Example below.
Query:
SELECT E1.Ename Employee, E2.Ename Manager FROM Emp E1, Emp E2 WHERE E1.MGR= E2.Empno;
Output:
In the above example, Table Alias name (E1 & E2) used to avoid the ambiguous situation and got the result without any error.
Points to Remember:
- Use Table Alias whenever performing joins, it makes easy and short the Query.
- ‘AS’ keyword can be used for column Alias, but not for Table Alias.
- AS keyword can be used in lower case as well.
- In Oracle, space can be used for column or table Alias name instead of AS keyword.
Conclusion
Oracle Alias is nothing but a temporary name of a column or table. To Hide original column(s) name or make column(s) of the result set more understandable or keep the query short, Oracle Alias (Column or Table) can be used.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Aliases. Here we discuss the syntax, types and different examples of Oracle Aliases along with the code implementation. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –