Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Switch Case in PowerShell
Switch function in PowerShell is used to handle multiple If statements or in other terms it is replacement of multiple conditions If/Else If/Else. To check a single condition in Script or Function, you can use If/else statement but if you want to evaluate more IF statements then use Switch.
Switch is better compare to multiple If statements and easy to implement and simple use for coding. There are multiple conditions under each statement and when one of them satisfies then the action is performed.
Syntax:
Switch (<Value>)
{
<Condition1> {Action1}
<Condition2> {Action2}
}
Full Syntax:
Switch [-regex | -wildcard | -exact ] [ -casesensitive ] ( <value> ) {
"String" | Number | Variable | { expression } { statementlist }
default { statementlist }
}
OR
Switch [-regex | -wildcard | -exact ] [ -casesensitive ] -file [filename]{
"String" | Number | Variable | { expression } { statementlist }
default { statementlist }
}
Parameters of Switch Case in PowerShell
- Regex: It is also called Regular Expression. Performs the Regular expression check against the value of the condition. If you use Regex, WildCard and Exacts are ignored. Also, if the match clause is not a string then this parameter is ignored.
- Wildcard: Indicates that the condition is a wildcard string. If you use Wildcard, Regex, and Exacts are ignored. Also, if the match clause is not a string then this parameter is ignored.
- Exact: Performs the match against the exact string. If you use Exact, Wildcard and Regex are ignored and if the match clause is not a string then this parameter is ignored.
- CaseSensitive: This parameter will check the condition that matches exactly with the passed Value (case sensitive) if it doesn’t match then this parameter is ignored. It also needs a string value.
- File: Takes the file path as an input value rather than a string value. If multiple file parameters are passed, it takes only the last one. Each line of the file is read and evaluated against the condition and if the condition matches then it executes that value or displays a written message.
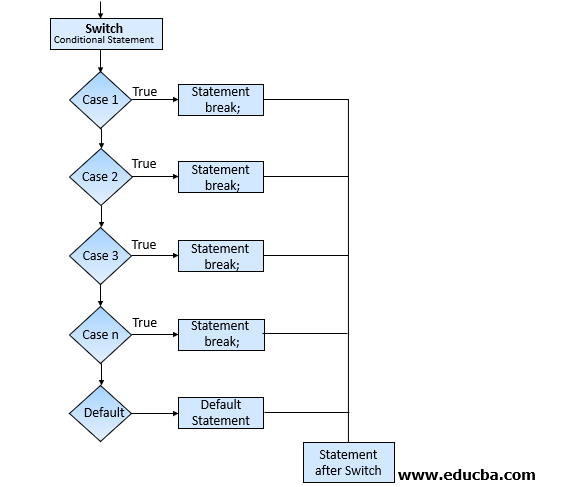
Flowchart
How does Switch Works in PowerShell?
As shown in above the diagram, whenever any value (string, Integer, float or other data types), array, wildcards, files, etc. is passed then it starts matching conditions one by one and when condition matches, the script executes that block. For multiple matching values, multiple scrips block will be executed and if no matching value found and if default condition is specified then it executes that block otherwise there is null output.
Examples of Switch Case in PowerShell
Let us see the given example:
Example# 1
1. Simple switch function with string, integer value passed.
Code:
switch (3) {
1 {"One"}
2 {"Two"}
3 {"Three"}
}
Output:
Code:
switch("data"){
"abc"{"Abc executed"}
"xyz"{"Xyz Executed"}
"data"{"Data Executed"}
}
Output:
Now, what if the parameter doesn’t match the expression. As an example given below, 5 doesn’t match with any of the Switch cases. In this case, the output will be null.
Code:
switch (5) {
1 {"One"}
2 {"Two"}
3 {"Three"}
}
To overcome the above problem, default needs to specify and default block executes when none of the parameter matches.
Code:
switch (5) {
1 {"One"}
2 {"Two"}
3 {"Three"}
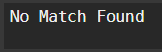
default{"No Match Found"}
}
Output:
Example# 2
Let us see the given example:
Difference between if / else if /else and Switch. From the below example, you can understand how it is easy to write a script with the Switch function.
Code:
$time = 3
if($time -eq 1){"It's 1 O'Clock"}
elseif ($time -eq 2) {"It's 2 O'Clock"}
elseif ($time -eq 3) {"It's 3 O'Clock"}
else {"No Match Found"}
$time = 3
switch ($time) {
1 {"It's 1 O'Clock"}
2 {"It's 2 O'Clock"}
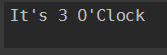
3 {"It's 3 O'Clock"}
default{"No Match found"}
}
Output:
Execution time for both the methods.
Code:
$time = 3
Measure-Command {
if($time -eq 1){"It's 1 O'Clock"}
elseif ($time -eq 2) {"It's 2 O'Clock"}
elseif ($time -eq 3) {"It's 3 O'Clock"}
else {"No Match Found"}
}
TotalMilliseconds :
Code:
$time = 3
Measure-Command {
switch ($time) {
1 {"It's 1 O'Clock"}
2 {"It's 2 O'Clock"}
3 {"It's 3 O'Clock"}
default{"No Match found"}
}
}
TotalMilliseconds:
Difference: 31.3154 milliseconds
This difference becomes vast when you write massive script or functions inside the switch.
1. Switch with Regex Parameter
If Regex is mentioned in switch, it evaluates the expression with passed value and if part of the condition matches then it executes that operation.
Consider the example below.
Code:
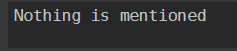
Switch ("Donkey"){
"Dog" {"Dog is Mentioned"}
"Cat" {"Cat is Mentioned"}
"Don" {"Donkey is Mentioned"}
"key" {"Donkey is mentioned again"}
default {"Nothing is mentioned"}
}
Output:
After adding Regex.
Code:
Switch -Regex ("Donkey"){
"Dog" {"Dog is Mentioned"}
"Cat" {"Cat is Mentioned"}
"Don" {"Donkey is Mentioned"}
"key" {"Donkey is mentioned again"}
default {"Nothing is mentioned"}
}
Output:
2. Switch with Wildcard Parameter
Wildcard works similar to Like parameter.
Code:
$msg = "Error, WMI connection failed"
Switch -Wildcard ($msg) {
"Error*" {"WMI Error"}
"Warning*" {"WMI Warning"}
"Successful*" {"WMI Connection Successful"}
}
Output:
3. Switch with Exact Parameter
Exact function is default in Switch. It doesn’t matter if you use it or not. But when you use two parameters at the same time then the last parameter takes precedence.
Code:
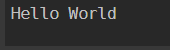
Switch -Regex -Exact ("Hello"){
"He" {"Hello World"}
"Hi" {"Hi World"}
Default {"No World"}
}
Output:
Code:
Switch -Exact -Regex ("Hello"){
"He" {"Hello World"}
"Hi" {"Hi World"}
Default {"No World"}
}
Output:
4. Switch with File Parameter
You can provide a file path directly to the Switch as a parameter. You can use File with a path to a file instead of giving it a variable expression.
Code:
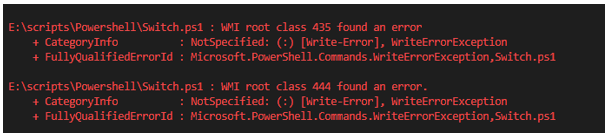
Switch -Wildcard -File C:\temp\switchtest.txt {
"*Warning*"{Write-Warning $PSItem}
"*Error*"{Write-Error $PSItem}
}
Output:
You can use $PSItem or $_ to work with current Items.
5. Switch with CaseSensitive parameter
When you use a Casesensitive parameter in a switch, then the condition has to match exactly by each character.
Code:
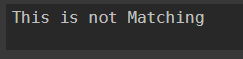
switch -CaseSensitive ("Hello") {
"HeLlo" {"This is different HeLlo"}
Default {"This is not Matching"}
}
Output:
6. Passing Array Value to switch function
Simple Array :
switch (10,12) {
9 { "Nine" }
10 { "Ten" }
11 {"Eleven"}
12 {"Twelve"}
Default {"None"}
}
Output:
Passing Array Object
Code:
$VMOps = @(
"VM_Delete"
"VM_Create"
)
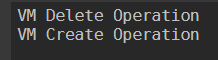
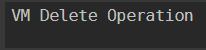
switch ($VMops) {
"VM_Delete" {"VM Delete Operation"}
"VM_Create" {"VM Create Operation"}
"VM_Shutdown" {"VM Shutdown Operation"}
}
Output:
7. Break condition
When you specify break condition, then Operation breaks in that loop and can’t continue further execution. This is pretty helpful when you don’t want to check further steps when condition satisfies and execution time becomes faster.
Code:
$VMOps = @(
"VM_Delete"
"VM_Create"
)
switch ($VMops) {
"VM_Delete" {
"VM Delete Operation"
break }
"VM_Create" {
"VM Create Operation"
break}
"VM_Shutdown" {
"VM Shutdown Operation"
break
}
}
Output:
If you notice, there is only one block executed and then it exits from the switch function.
8. Continue Condition
Continue parameter is used to skip the particular iteration. For example, if there are 3 items to match then it will execute first and when condition matches then it will skip other steps and move to the next step.
Code:
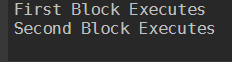
switch ('Hello') {
"hello" {'First Block Executes'
continue}
'HELLO' {'Second Block Executes'
continue }
'HeLLo' {'Third Block Exectues'
continue }
Default {'Nothing executed'}
}
Output:
As you can see there is only one argument passed (‘Hello’), it executes the first block only because the expression is matching and there is no other argument left to execute, the script will end.
- One more mixed example of break and continue with Switch.
Code:
switch ('Alpha','Beta','Delta') {
"Alpha" {'First Block Executes'
continue}
'Beta' {'Second Block Executes'
break }
'Delta' {'This will not Execute'}
}
Output:
Conclusion
All in all, Switch is far better than implementing multiple If conditions and provides more functionality and reduction in execution time.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Switch Case in PowerShell. Here we also discuss the syntax, parameters, and examples of switch case in Powershell. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more-
- What is Shell Scripting?
- PowerShell Commands
- PowerShell Operators
- Uses Of Powershell
- Guide to Array in PowerShell with Examples
- Examples of Regex in PowerShell
- Complete Guide to Function in Shell Scripting
- Learn the Echo in Shell Scripting
- Examples of Switch Case in Shell Scripting
- Python Switch Case | How to Implement?