Introduction to Array in PowerShell
The array is a type of data structure that can be used to store a collection of items, the collection of items can be either of the same datatype or different. The elements in an array can be accessed using the index. The index of the array usually starts at 0, so to access the first element you must use the index [0]. Typically, only two operations can be on an array, i.e. adding an element to the array or removing an element. In this article, we are going to learn about the Array in PowerShell.
Defining an Array in PowerShell
An array can be defined in any of the following ways,
The @ () is one of the ways of defining an array.
Example:
$Subject = @(‘History’,’Geo’,’Maths’)
- An array can be created as a comma-separated list as well.
$test=’testone’,’testtwo’,’testthree’
- An array can be created for a specific datatype element as follows,
[int[]] $numbersarray = 1,2,3,4,5
The above is an integer array and it can hold only integer values.
Accessing an Array
Let us define an array,
Example:
$test=@(‘test1’,’test2’,’test3’,’test4’)
$test [0] will return test1, $test [3] will return test4. Many languages allow only a single index to be specified, whereas in PowerShell multiple indexes can be used simultaneously.
In the above $test [1, 3] will return,
test2
test4
Operations on an Array
Adding items to an array. Let’s see an example of how to add an element to an existing array.
Example:
$test=@(‘welcome’,’home’)
To add to the above array, the ‘+=’ operator is used.
$test+=’Raj’
Running $test will return,
welcome
home
Raj
Getting the Count of an Array
Here we explain, how to use the following input to get the count of an array.
Input:
$test=@(‘test1’,’ertr’,’fgdfgfd’,’dfgfdg’,’dfdfsd’,’dfgfdgdfg’)
$test.Count will return 6 which is the count/length of the array.
1. Sorting the Elements in an Array
The sort operator can be used to sort the elements of an array if the elements are of the same datatype.
Input:
$test=@(‘oneee’,’zddsdsad’,'thraewawe')
$test |sort
The above command will sort the elements in the ascending order
Output:
Input:
$test |sort -Descending will sort the elements in the descending order
Output:
2. Updating Item in an Array
The index can be used to update an element in the array
Input:
$test=@(‘oneee’,’zddsdsad’,'thraewawe')
$test[0]=’changed’
The above command will change the ‘one’ to ‘changed’. Executing $test will return
Output:
3. Finding an Element in an Array
To check an array for value, the like operator can be used
Input:
$test=@(‘viki’,ramu,'aravind','vikram')
$test -like "*vik*"
Output:
Multidimensional Array in PowerShell
We can create a multidimensional array as follows,
$testMultidimensionalArrays = @(1,2,3), @(4,5,6), @(7,8,9)
Each array has one row and three columns.
Looping an Array
Like in any other languages the for loop can be used to loop items in an array.
Input:
$test=@(‘viki’,’ramu’,'aravind','vikram')
for($i=0;$i -lt $test.Length; $i++)
{
Write-Host $test[$i]
}
Output:
For-each can be used to perform an action against each item in the array.
Input:
$test=@(1,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)
foreach($i in $test)
{
$i=$i+5
Write-Host $i
}
Output:
Array List in PowerShell
One of the drawbacks with Array is adding items to it, to overcome that we have an array list.
The following is the syntax to create an Array List,
$myarray = [System.Collections.ArrayList]::new()
$myarray.Add(1)
$myarray.Add(2)
$myarray.Add(3)
$myarray
The first line is the way to initialize an Array List and the subsequent lines are to add items to the ArrayList
Array vs Array List Performance
The following examples show the difference in performance while performing an operation on an array and array list
Input:
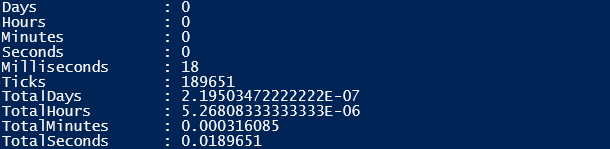
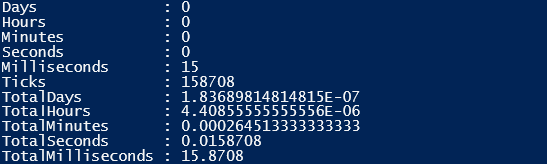
Measure-Command -Expression { 0..250 | ForEach-Object { $arr += $_+1 }}
$arrlit = [System.Collections.ArrayList]@()
$f arrlit _performance = Measure-Command -Expression { 0..250 | ForEach-Object { $ arrlit += $_+1 }}
$ arrlit _performance
The first command performs an operation on the array and the third line does that same on an array list.
Output:
- Performance of Array
- Performance of Array List
The performance of the array list is faster and better than that of the array.
Example of Array in PowerShell
Following is an example to find the length of an array using for loop, foreach loop and while loop.
Input:
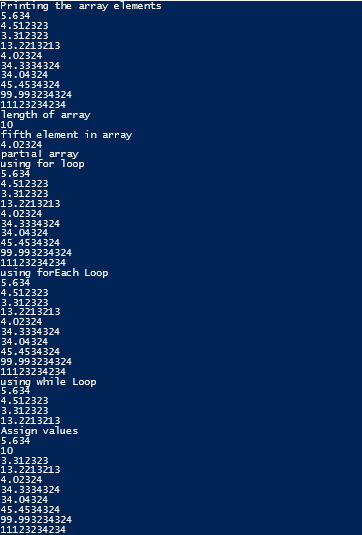
$testlist = 5.634, 4.512323, 3.312323, 13.2213213, 4.02324, 34.3334324, 34.04324, 45.4534324, 99.993234324, 11123234234 write-host("Printing the array elements")
$testlist
write-host("length of array")
$testlist.Length
write-host("fifth element in array")
$testlist[4]
write-host("partial array")
$subList = $testlist[1..3]
write-host("using for loop")
for ($i = 0; $i -le ($testlist.length - 1); $i += 1) {
$testlist[$i]
}
write-host("using forEach Loop")
foreach ($e in $testlist) {
$e
}
write-host("using while Loop")
$i = 0
while($i -lt 4) {
$testlist[$i];
$i++
}
write-host("Assign values")
$testlist[1] = 10
$testlist
Output:
Hash Table
Hash table is used to implement a structured array. In the hash table, the values are stored in a key-value format. They are also known as Dictionary or Associative array.
Syntax:
$testhashtable=@{}
Or
$testhashtable=@{ key1=”test1”;key2=”test2”;key3=”test3”}
Where key1, key2, and key3 are the keys and test1, test2 and test3 are the values.
Input:
$testhashtable
Output:
The key or the values can be accessed as follows using the .dot operator
Input:
$testhashtable.keys
Output:
Input:
$testhashtable.Values
Output:
Example
Following is an example to find all the hashtable keys and hashtable values.
Input:
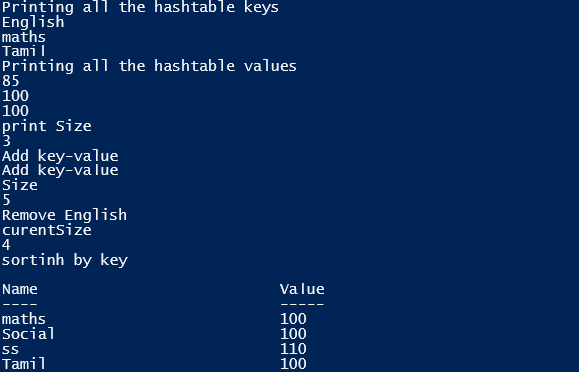
$testht = @{ English = "85"; Tamil = "100"; maths = "100"}
write-host("Printing all the hashtable keys")
$testht.keys
write-host("Printing all the hashtable values")
$testht.values
write-host("print Size")
$testht.Count
write-host("Add key-value")
$testht["Social"] = "100"
write-host("Add key-value")
$testht.Add("ss","110")
write-host("Size")
$testht.Count
write-host("Remove English")
$testht.Remove("English")
write-host("curentSize")
$testht.Count
write-host("sortinh by key")
$testht.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object -Property key
Output:
Conclusion – Array in PowerShell
The main advantage of an array is memory management. They can be accessed directly from the cache which helps in faster retrieval. They are reusable, once it’s declared they can be reused multiple times.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Array in PowerShell. Here we discuss the introduction and the implementation of an array, array list and hash table in PowerShell. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –