Updated June 26, 2023
Introduction to Python Switch Case
Python Switch case is serious on conditional statements used in cases where we have too many if conditions. We have a switch function that accepts arguments and a series condition that fulfills the condition of the argument. If the condition does not match, it goes to the next condition. We use the break to come out of the condition and have a default condition. The default condition automatically executes if none of the conditions gets executed. The switch case also supports nesting, which means we can have another switch case inside a switch case condition.
Syntax:
This is the basic syntax of the switch case:
switch EXPR:
case EXPR:
SUITE
case EXPR:
SUITE
...
else:
SUITEExamples of Python Switch Case
Below are examples of a Python switch case:
Example #1
As we know, python doesn’t have a switch case, so that we will use a switcher here. It is similar to the switch case, we will take input from the user, and the condition mentioned in the switcher will be executed according to it. Let’s take an example:
Code:
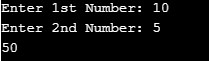
a = int(input("Enter 1st Number:"))
b = int(input("Enter 2nd Number:"))
def xyz(x):
switcher = {
'addition':a+b,
'multiplication':a*b,
'subtraction':a-b,
'division':a/b
}
return switcher.get(x,"Oops! Invalid Option")
result=xyz('multiplication')
print(result)Output:
We have written the above switch case program in Python using a switcher or also known as dictionary mapping. As we all know in the dictionary, we have key-value pairs. Similarly, here we have defined the case as a key, and the operation to that key is a value. In the above program, we defined a function XYZ accepting x as an input. We have defined, switched, and written multiple conditions in the curly bracket. We are performing operations on two variables, a and b.
In the dictionary, we have to get a method; the get method takes two parameters, the first parameter will be a matching condition, and the second parameter is a statement that will be returned to the user if none of the conditions is satisfied. Suppose the user passed ‘addition’ as an x to the XYZ function; the get method will execute the operation about the ‘addition’ key. If the user enters anything not found in the switcher, the second statement will be returned to the user, i.e., ‘Oops! Invalid Operation’. You can also pass the definition of another function in switcher keys.
Example #2
The below program takes input numbers and results into the corresponding month name. We created a month’s class and defined a function switch case with an instance of the class, i.e., self. Using instance, we can access the attributes and properties of the classes. We have passed month_number as the second parameter to accept user input. Then we have a dictionary getattr method with an instance, user input, and the default value.
Code:
class Months:
def switchCase(self, month_number):
default = "Oops! Wrong Input"
return getattr(self, 'month_' + str(month_number), lambda: default)()
def month_1(self):
return "January"
def month_2(self):
return "February"
def month_3(self):
return "March"
def month_4(self):
return "April"
def month_5(self):
return "May"
result = Months()
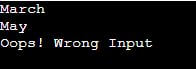
print(result.switchCase(3))
print(result.switchCase(5))
print(result.switchCase(10))Output:
We append month_ with the user input integer number, matching the switch case’s corresponding defined methods. The methods return the month name as a string. Then we created the result object of the class Months, and using this object, we can access all the attributes and properties of the class. Now we have to pass integer value from 1 to 5 to have the resulting month name, and if pass other than 1 to 5, then getattr() will return the default lambda function message ‘Oops! Wrong Input “.
Conclusion
As you have read till now, python doesn’t have a switch case of its own, but we have created switch case conditions using a switcher, and it works exactly like a switch case. Experts recommend using a switch case instead of having too many nested if-else conditions. Too many nested conditions make program execution slow.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Python Switch Case. Here we discuss the Introduction, its examples, and Code Implementation and Output. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –