Updated May 3, 2023
Difference Between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
Supervised learning and Unsupervised learning are machine learning tasks. Supervised learning is simply a process of learning algorithms from the training dataset. Supervised learning is where you have input variables and an output variable, and you use an algorithm to learn the mapping function from the input to the output. The aim is to approximate the mapping function to predict the output variables for that data when we have new input data.
Unsupervised learning involves modeling the data’s underlying or hidden structure or distribution to gain more insight and knowledge. Unsupervised learning is where you only have input data and no corresponding output variables.
Training dataset: A set of examples for learning where the target value is known.
Head-to-Head Comparisons Between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 comparisons between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning:
Key Differences Between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
Below are the lists of points that describe the key differences between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning:
- Machine learning algorithms discover patterns in big data. These different algorithms can be classified into two categories based on how they “learn” about data to make predictions. Those are supervised and unsupervised learning.
- In supervised learning, the scientist acts as a guide to teach the algorithm what conclusions or predictions it should come up with. Algorithms in unsupervised learning discover and present interesting hidden structures in the data on their own, as there is no correct answer or teacher to guide them.
- The supervised learning model will use the training data to learn a link between the input and the outputs.
- Unsupervised learning does not use output data. In unsupervised learning, there won’t be any labeled prior knowledge; in supervised learning, there will be access to the labels and prior knowledge about the datasets.
- Supervised learning: The idea is that training can be generalized, and the model can be used on new data with some accuracy.
- Supervised learning algorithms: Support vector machine, Linear and logistics regression, Neural network, Classification trees, random forest, etc.
- Unsupervised algorithms can be split into categories: Cluster algorithms, K-means, Hierarchical clustering, Dimensionally reduction algorithms, Anomaly detections, etc.
- One widely uses classification and regression algorithms in supervised learning. Support Vector Machines (SVM) are supervised machine learning models with associated learning algorithms that can be used for classification and regression purposes but are mainly used for classification problems.
- In the SVM model, we plot each data item as a point in n-dimensional space (where n is the features we have), with the values of each element being the value of a particular coordinate. One can classify by finding the hyperplane that differentiates the two classes.
- The main goal of regression algorithms is to predict the discrete or continuous value. Sometimes, one can use the expected value to identify the linear relationship between the attributes. Different regression algorithms can be used based on the problem at hand. Some basic regression algorithms are linear regression, polynomial regression, etc.
- Clustering is widely used in unsupervised learning. Clustering divides the data points into several groups so that the same trait points will be together as a cluster. There are many clustering algorithms; a few of them are Connectivity models, centroid models, Distribution models, and Density models.
- Hierarchical clustering comes under unsupervised learning. As the name suggests, hierarchical clustering is an algorithm that builds a hierarchy of clusters. This algorithm starts with all the data points assigned to a cluster of their own. The algorithm merges the nearest clusters into the same cluster and terminates when only one cluster is left.
- KMeans comes under the unsupervised clustering method. One can partition the data into k clusters based on their features, where each cluster is represented by its centroid, which is defined as the center of the points in the cluster. KMeans is simple and fast, but each run doesn’t yield the same result.
- Let’s take real-life examples to understand supervised and unsupervised learning better. Supervised learning: Let’s take one of Gmail’s functionality as an example: spam mail. Based on past information about spam emails, filtering a new incoming email into the Inbox or Junk folder. In this scenario, one model Gmail as a mapping function to segregate incoming mail based on prior knowledge about the mail, which is an example of supervised learning.
- Unsupervised learning: Let’s assume a friend invites you to her party, where you meet new people. Now you will classify them using no prior knowledge (Unsupervised learning), and this classification could be on any trait. It could be age group, gender, dress, educational qualification, or whatever way you would like. Since you didn’t use prior knowledge about people and classified them, it comes under unsupervised learning.
Supervised Learning vs Unsupervised Learning Comparison Table
Following are the lists of points that describe the comparisons Between Supervised Learning vs Unsupervised Learning:
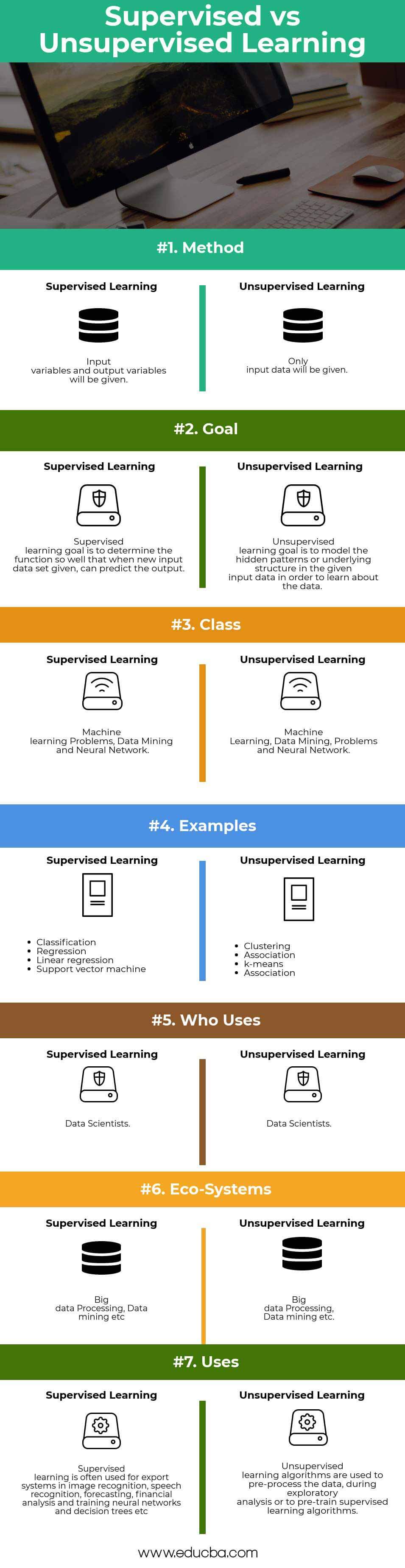
| Basis For Comparisons | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
| Method | Both input and output variables will be provided. | Only the input data will be provided. |
| Goal | Supervised learning aims to determine the function so well that it can predict the output when given a new input data set. | The unsupervised learning goal is to model the hidden patterns or underlying structures in the given input data to learn about the data. |
| Class | Machine learning Problems, Data Mining, and Neural Networks. | Machine Learning, Data Mining, Problems, and Neural Networks. |
| Examples |
|
|
| Who uses | Data scientists. | Data scientists. |
| Eco-systems | Big data Processing, Data mining, etc. | Big data Processing, Data mining, etc. |
| Uses | Various fields apply supervised learning, such as image recognition, speech recognition, forecasting, financial analysis, and training neural networks and decision trees. | Unsupervised learning algorithms can pre-process data during exploratory analysis or pre-train supervised learning algorithms. |
Conclusion
Using either a supervised or unsupervised machine learning algorithm typically depends on factors related to the structure and volume of your data and the use case. In reality, data scientists use both supervised and Unsupervised Learning approaches to solve the use case.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning. Here we have discussed Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –