Updated July 24, 2023
Difference Between Sell Side vs Buy Side
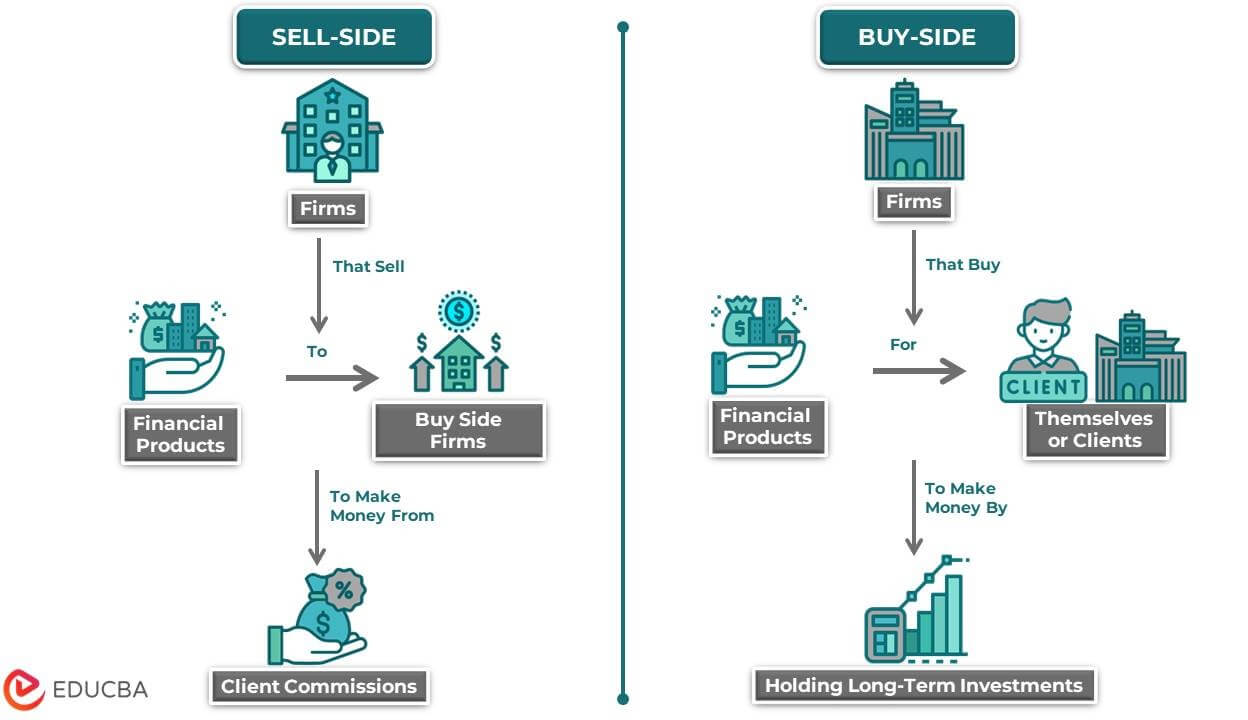
In the sell side vs. buy side, the sell side sells investments to others, while the buy side buys and holds those investments for themselves or their clients.
Basically, the “sell side” is made up of people who work for companies that sell investments. It might be an investment bank, commercial bank, or brokerage firm. Their job is to convince others to buy the investments that their company is selling.
On the other hand, the “buy side” is made up of people who work for companies that choose which investments to buy and hold for themselves or their clients. These companies might be mutual funds, hedge funds, or pension funds.
Suppose a farmer, George, grows crops and sells them for a living. Here, the “sell side” is like the farmer who tries to convince buyers to purchase his crops. On the other hand, the “buy side” is like a grocery store that purchases crops from the farmer to sell to his customers.
What is the Sell Side?
Sell Side firms, like investment banks and brokerages, sell financial products and services to clients. The clients they sell to are called Buy Side firms, which can include institutional and retail investors.
To sell these financial products, the sell side firms do a lot of research and analysis. Based on their findings, they try to convince investors to buy or sell through their trading desk. Their ultimate goal is to generate profits for their own firm.
Example:
A company hires an investment bank to value shares for its upcoming IPO. Here, the investment bank is the Sell Side firm that helps the company (its client) to sell the shares to the public through the stock exchange.
What is the Buy Side?
The buy side comprises big investors like hedge, mutual, and pension funds. They buy and hold financial assets for their clients or beneficiaries.
They make money by getting good returns on their investments, and their main goal is to ensure their clients’ investments are doing well.
Example:
A pension fund (buy-side firm) invests in a diversified asset portfolio after conducting proper due diligence to generate long-term returns for its client. In return, the pension fund will charge a fee to manage the asset portfolio.
Head To Head Comparison Between Sell Side vs Buy Side (Infographics)
Below are the Top 7 Differences Sell Side vs. Buy Side:
Sell Side vs. Buy Side Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Sell Side vs. Buy Side:
| Basis of comparison | Sell Side | Buy Side |
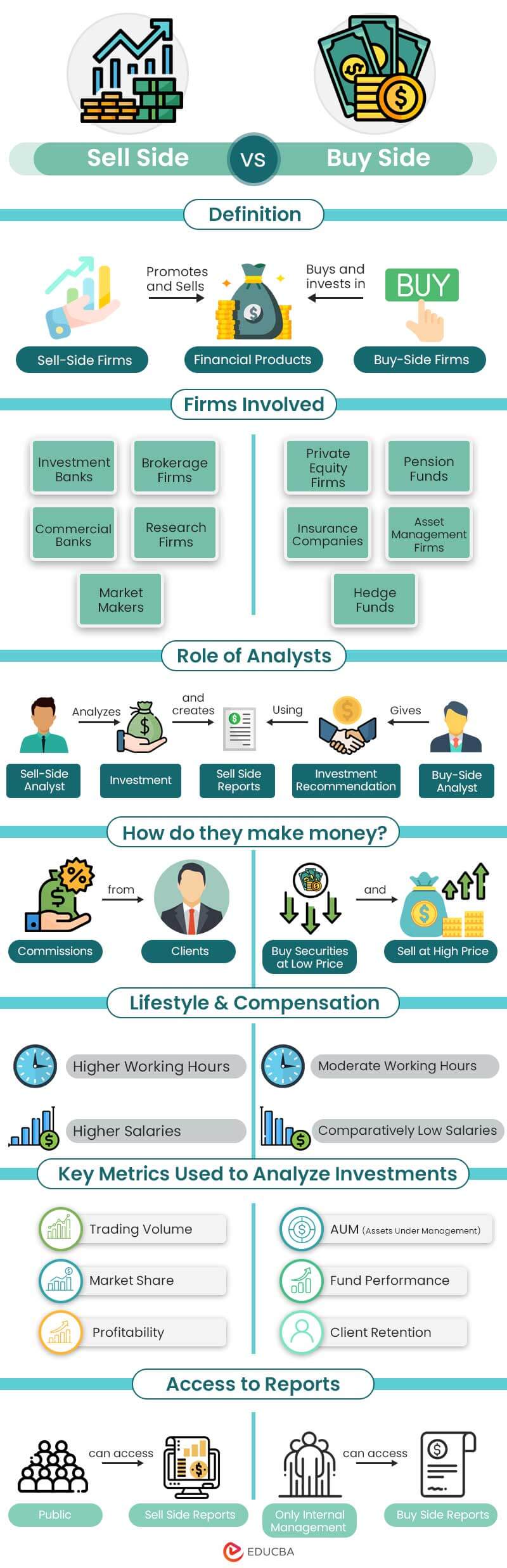
| Definition | These individuals or firms pitch and facilitate the sale and trading of financial products or opportunities. | These are firms that purchase financial products, assets, or opportunities on behalf of clients. |
| Goals | Maximize revenue and profits for the firm. | Maximize returns for clients while minimizing risk. |
| How do they Make Money? | They charge commissions or fees for creating, promoting, and selling financial products. | They buy financial securities at low prices and sell the same at high prices. |
| Type of Structure | These are large complex firms with a hierarchical structure. The employees’ designations are in a hierarchical order. | These firms have a focused and streamlined structure. It is leaner with only three positions. |
| Hierarchy |
|
|
| Lifestyle | The lifestyle is more erratic. The analysts have extensive working hours because they act as investment banks and are always at clients’ service. | The lifestyle is comparatively not that erratic. The analysts have lesser working hours too. |
| Number of Analysts | They employ a higher number of Analysts. | They employ a decent number of Analysts. |
| Compensation | Often high, with bonuses tied to individual and firm performance. | Typically lower than the sell side, with a focus on long-term incentives tied to AUM growth and performance. |
| Role of Analysts | The analysts Provide research and analysis to support trading and investment decisions and recommend selling or buying. | The Analysts use reports the sell-side analysts provide to carry out further analysis to identify opportunities. |
| Firms Involved |
|
|
| Clientele/ Investors | Mostly institutional investors such as banks, hedge funds, etc. | Mostly retail investors such as individual investors and pension funds, etc. |
| Trading | Often engages in proprietary trading and takes on market risk. | Typically follows a long-term investment approach and seeks to minimize risk. |
| Risk Appetite | High-risk appetite as they engage in proprietary trading. | Low-risk appetite as they aim to preserve and grow clients’ assets. |
| Key Metrics | Trading volume, market share, profitability, etc. | AUM (Assets Under Management), fund performance, client retention, etc. |
| Reports | They provide publicly available equity research reports with investment recommendations for buying, selling, or neutral. | They create internal reports that are not publicly available that emphasize portfolio performance, investment outlooks, and market trends. |
Sell Side vs. Buy Side Skills
Some common skills that both sell side vs. buy side employees must have are:
- Risk management: Understanding risk management principles and managing and mitigating risk.
- Client relationship management: Ability to build and maintain relationships with clients and understand their needs.
- Ethics: Commitment to ethical and professional standards in all dealings with clients and colleagues.
- Negotiation: Ability to negotiate deals and contracts with clients.
- Product knowledge: In-depth knowledge of financial products and services offered by the firm.
- Teamwork: Ability to work effectively as part of a team and collaborate with colleagues across departments.
- Communication: Strong verbal and written communication skills to effectively convey complex financial information to clients
- Technology: Familiarity with financial technology and tools such as trading platforms, data analytics, and research databases
- Microsoft Tools: Expertise in MS Excel, MS PowerPoint, and MS Word.
Other skills that are specific for the sell side vs. buy side are as follows:
Sell-Side Analyst Skills:
- Multitasking efficiently
- Staying up to date with the latest trends in the economy and global markets
- Developing and implementing effective sales and marketing strategies
- Providing insights and recommendations to clients
- Analyzing companies and their financial information.
Buy-Side Analyst Skills:
- Analyzing financial data and market trends
- Managing a portfolio of assets to achieve the fund’s investment objectives
- Working long hours and prioritizing tasks effectively
- Regularly monitoring clients’ portfolios to ensure they meet investment objectives.
Careers and Salary
Here is a list of Investment banking related jobs with their respective responsibilities and salary ranges for the sell side:
|
Jobs in Investment Banking |
||
|
Job Title |
Responsibilities |
Salary Range |
| Investment Banker |
|
$56,000 – $250,000 |
| Equity Research Associate |
|
$52,000 – $134,000 |
| Quantitative Analyst |
|
$62,000 – $136,000 |
| Risk Manager |
|
$60,000 – $135,000 |
| Compliance Officer |
|
$48,000 – $117,000 |
| Sales Operations Specialist |
|
$43,000 – $83,000 |
(Source: Payscale)
Here is a list of private equity and venture capital-related jobs with their respective responsibilities and salary ranges for the buy side:
|
Jobs in Private Equity and Venture Capital |
||
|
Job Title |
Responsibilities |
Salary Range |
| Portfolio Manager |
|
$59,000 – $152,000 |
| Research Analyst |
|
$44,000 – $85,000 |
| Risk Manager |
|
$60,000 – $135,000 |
| Trader |
|
$60,000 – $153,000 |
| Investment Analyst |
|
$50,000 – $100,000 |
(Source: Payscale)
Sell Side vs. Buy Side Top Firms
The table below lists the top 10 sell-side firms in the world, along with their respective location and assets under management (AUM):
|
Sell-Side Firms |
|||
|
Rank |
Name | Location |
AUM (Assets Under Management) |
| 1 | JPMorgan Chase & Co. | New York, USA | $2.5 trillion (2022) |
| 2 | Goldman Sachs Group Inc. | New York, USA | $2.54 trillion (2022) |
| 3 | Morgan Stanley | New York, USA | $1.3 trillion (2022) |
| 4 | Bank of America Merrill Lynch | Charlotte, USA | $1.46 trillion (2022) |
| 5 | Citigroup Inc. | New York, USA | $250 billion (2022) |
| 6 | Credit Suisse Group AG | Zurich, Switzerland | $1.29 trillion (2022) |
| 7 | Deutsche Bank AG | Frankfurt, Germany | $902.52 billion (2022) |
| 8 | UBS Group AG | Zurich, Switzerland | $3.1 trillion (2022) |
| 9 | Barclays | London, UK | $9.8 trillion (2021) |
| 10 | Lazard | New York City, United States. | $216 billion (2022) |
The table below lists the top 10 buy-side firms in the world, along with their respective location and assets under management (AUM):
|
Buy-Side Firms |
|||
|
Rank |
Name | Location |
AUM (Assets Under Management) |
| 1 | BlackRock | New York, USA | $8.59 trillion (2022) |
| 2 | Vanguard Group | Pennsylvania, USA | $8.1 trillion (2022) |
| 3 | State Street Global Advisors | Massachusetts, USA | $3.5 trillion (2022) |
| 4 | Fidelity Investments | Massachusetts, USA | $3.9 trillion (2022) |
| 5 | Capital Group Companies | California, USA | $1.7 trillion (2022) |
| 6 | PIMCO (Pacific Investment Management) | California, USA | $2.24 trillion (2022) |
| 7 | Legal & General Investment Management | London, UK | $1.4 trillion (2021) |
| 8 | Amundi | Paris, France | $2.09 trillion (2022) |
| 9 | Wellington Management Company | Massachusetts, USA | $1.48 trillion (2022) |
| 10 | Invesco Ltd. | Georgia, USA | $1.409 trillion (2022) |
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Sell Side vs. Buy Side. Here we discuss their key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more: