Updated July 1, 2023
Differences Between Python Tuple and List
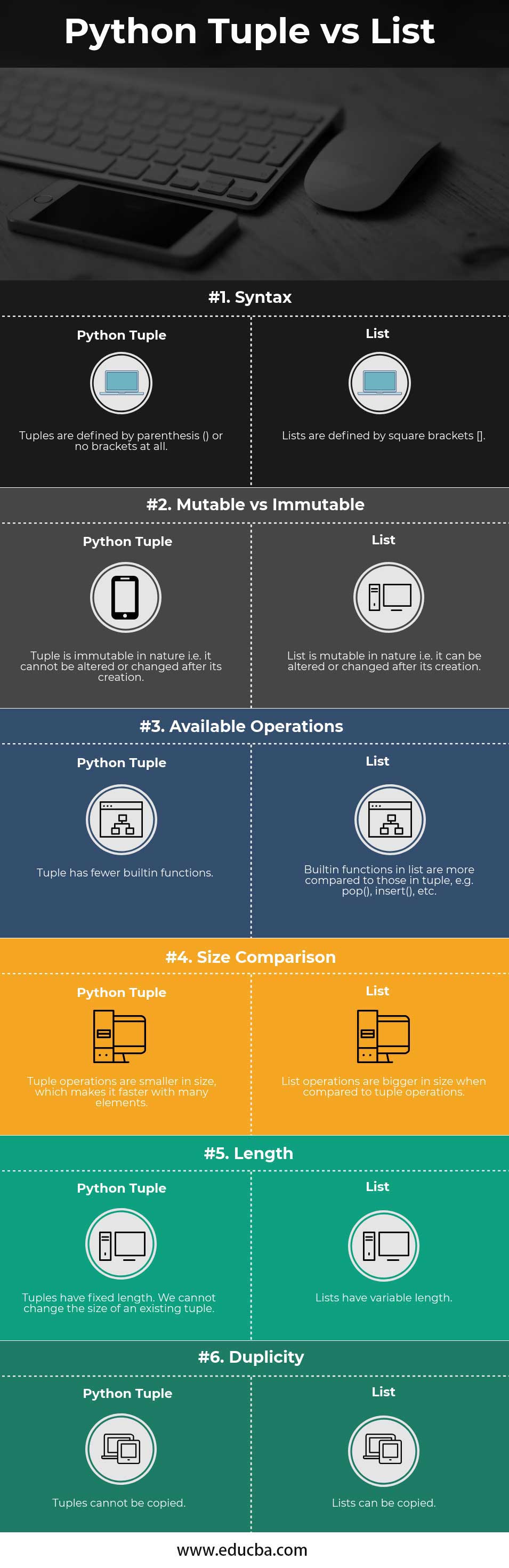
Python Tuple defines and stores a set of values using (), the curly parenthesis. On the other hand, a list is used for defining and storing values using the square brackets represented as []. When comparing the built-in functions for Python Tuple and the list, Python Tuple has lesser pre-defined built-in functions than the lists. A few advantages of lists against the Python Tuple are that the list can be defined for variable lengths and copied from one destination to another, but Python Tuple can have only fixed lengths and cannot be copied.
Let us look at this example for a tuple:
def test()
return 1,2
a,b = test()
print(a,b)
Here, we have used a tuple to return the value from the function; hence, we cannot modify it while printing the value.
A Python Tuple can either have no brackets around it or parenthesis like “()” This helps Python understand a list from a tuple. Square brackets define the Python list. Its functionality is similar to how an array works in other languages. Example:
x = [1,3,5,6,2,1,6]
print(x): Prints the complete list
print(x[0],x[1]): Prints the list starting at Index 0
Often confused due to their resemblances, these two structures are significantly different.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Python Tuple and List (Infographics)
Below is the Top 6 Comparison Python Tuple vs List
Key Differences Between Python Tuple and List
Below are the lists of points; describe the key differences between Python Tuple vs List:
Functionality of Operations
Lists have a supplementary built-in function when compared to tuples. Lists and tuples have in common the index() and count() methods, but other than these, lists have many functions that apply only specifically to lists like append(), remove(), clear(), sort(), reverse(), etc.
We can use the inbuilt function dir([object]) to find out all the functions associated with lists and tuples. The output for such a command would be as follows:
List Object:
[‘__add__’,‘__class__’,
‘__contains__’,
‘__delattr__’,
‘__delitem__’,
‘__dir__’,
‘__doc__’,
‘__eq__’,
‘__format__’,
‘__ge__’,
‘__getattribute__’,
‘__getitem__’,
‘__gt__’,
‘__hash__’,
‘__iadd__’,
‘__imul__’,
‘__init__’,
‘__init_subclass__’,
‘__iter__’,
‘__le__’,
‘__len__’,
‘__lt__’,
‘__mul__’,
‘__ne__’,
‘__new__’,
‘__reduce__’,
‘__reduce_ex__’,
‘__repr__’,
‘__reversed__’,
‘__rmul__’,
‘__setattr__’,
‘__setitem__’,
‘__sizeof__’,
‘__str__’,
‘__subclasshook__’,
‘append’,
‘clear’,
‘copy’,
‘count’,
‘extend’,
‘index’,
‘insert’,
‘pop’,
‘remove’,
‘reverse’,
‘sort’]
Tuple Object:
[‘__add__’,‘__class__’,
‘__contains__’,
‘__delattr__’,
‘__dir__’,
‘__doc__’,
‘__eq__’,
‘__format__’,
‘__ge__’,
‘__getattribute__’,
‘__getitem__’,
‘__getnewargs__’,
‘__gt__’,
‘__hash__’,
‘__init__’,
‘__init_subclass__’,
‘__iter__’,
‘__le__’,
‘__len__’,
‘__lt__’,
‘__mul__’,
‘__ne__’,
‘__new__’,
‘__reduce__’,
‘__reduce_ex__’,
‘__repr__’,
‘__rmul__’,
‘__setattr__’,
‘__sizeof__’,
‘__str__’,
‘__subclasshook__’,
‘count’,
‘index’]
We can see additional functionalities linked with a list than for a tuple.
Size Evaluation
Tuple operations have a smaller size than list operations. This makes the operations faster when there is an enormous number of elements. Let us see an example to calculate the size of the list and tuple elements.
x= (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0)
y= [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0]
print(‘x=’,x.__sizeof__())
print(‘y=’,y.__sizeof__())
Output:
x= 104
y= 120
In this example, we have a tuple x and a list y holding the same number of items, but the size of the tuple is less than that of the list.
Diverse Use Cases
Initially, it may seem like lists will always be able to replace tuples, but this is not the case. We can understand this due to the following reasons:
- When a tuple is used instead of a list, it gives the viewer an idea that the present data can and should not be changed.
- Tuples are frequently used to store data as the equal of a dictionary without keys.
Example:
[(‘Employee1’, 1000), (‘Employee2’, 1001), (‘Employee3’, 1002)]Tuples can also be used as keys in dictionaries because of their hashtable and immutable nature. Lists are inappropriate for this as they cannot handle the function __hash__() and are mutable.
key_value = {(‘a’,’b’):1} #Valid
key_value = {[‘a’,’b’]:1} #Invalid
- Readability is increased, i.e., reading information is easier when tuples are stored in a list instead of when lists are stored in a list. Example:
Usage of Tuples and Lists
We use a tuple when we know what information is to be given, and we need to save the values from being modified, like when we need to store credentials for a website. Tuples are also used as keys for a dictionary because only immutable values can be hashed. Hence, we cannot use a list in such cases. If we still want to use a list as a key, we need first to convert the list into a tuple.
On the other hand, we can use a list when we want to modify the values given within the collection and when we do not know whether our collection size is fixed.
Python Tuples vs Lists Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Python tuples vs Lists
| Features | Lists |
Tuples |
| Syntax | Lists are defined by square brackets []. | Tuples are defined by parenthesis () or no brackets at all. |
| Mutable vs Immutable | The list is mutable in nature, i.e., it can be altered or changed after its creation. | A tuple is immutable in nature, i.e., it cannot be altered or changed after its creation. |
| Available Operations | Built-in functions in the list are more compared to those in a tuple, e.g., pop(), insert(), etc. | Tuple has fewer built-in functions. |
| Size Comparison | List operations are bigger in size when compared to tuple operations. | Tuple operations are smaller, making them faster with many elements. |
| Length | Lists have a variable length. | Tuples have fixed lengths. We cannot change the size of an existing tuple. |
| Duplicity | Lists can be copied | Tuples cannot be copied. |
Conclusion
This is all about Python Tuples vs Lists. Now that we have understood the differences between Python tuples and lists, it will be easier for us to decide which of the two should be used. Therefore, we can conclude that although both lists and tuples are important data structures in Python, there are notable differences between them, with the major difference being that lists are mutable, whereas tuples are not.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to the Difference between Python Tuple vs List. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-