Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to Hashtable in PowerShell
PowerShell Hashtable is a compact data structure that stores key/value pairs in a hash table. In other words, a hashtable is an associative array or a dictionary with a key-value pair. A key/value pair is essentially a set of two elements that are related in some manner.
In a hashtable, the input is a unique key with an associated value and output is a table with two columns.
- Name
- Value
In PowerShell, each hashtable is a Hashtable object. This object is mostly a string or an integer, but it can be any object type.
Syntax:
Before using a hashtable, it must be created. Below is the syntax for doing so.
Creating an empty hashtable
$hash =@{}
You can also create a hashtable and add keys-values at the same time.
$hash = @{ key1 = item1; key2 = item2;... }
To an empty hashtable, data can be added in the following manner:
$hash.add( $key, $value )
An ordered dictionary can also be created using similar syntax.
Following is the syntax for creating an ordered dictionary. Here, we have only added [ordered] attribute before the “@” symbol.
$hash =[ordered] @{ key1 = item1; key2 = item2;... }
Note: The main difference between a hashtable and an ordered dictionary is that hashtable does not maintain the order in which entries are added but ordered dictionary does.
Accessing hashtable values: A hashtable value is accessed through the key.
$hash[“key1”]
Printing hashtable: To print /display a hashtable, just type the variable name in which hashtable is saved.
$hash
The above command displays a table with two columns, one for keys and the other one for the associated values for the keys.
How does Hashtable work in PowerShell?
- Hashtable transforms the key using a hash function into a hash.
- Hash is a number that the hash table uses to get the value.
- Hash then maps directly to a bucket in the array of key/value pairs.
Let’s understand the working of PowerShell through given examples:
- First, create an empty hashtable and then populate it with the key-value pairs or,
Code:
$hash = @{}
$hash.add( 'ID', 1 )
$hash.add( 'Subject', 'Maths')
$hash.add( 'Maths', 80 )
$hash
Output:
- You can also create a hashtable and initialize it at the same time.
Code:
$hash = @{ID=1; Subject='Maths'; Marks=80}
$hash
Output:
For an ordered hashtable
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths'; Marks=80}
$hash
Output:
Shown here are few examples to illustrate the actions which can be performed on a hashtable.
Editing items in a hashtable
.Set_Item() method is used to edit the items in a hashtable:
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths'; Marks=80}
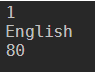
$hash.Set_Item("Subject", “English”)
$hash
Output:
- A new entry gets automatically added to the hashtable if it did not exist earlier.
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='English'; Marks=80}
$hash.Set_Item("NoOfStudents",30)
$hash
Output:
Removing items from a hashtable
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='English'; Marks=80}
$hash.Remove("NoOfStudents")
$hash
Output:
Printing the hashtable keys
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='English'; Marks=80}
$hash.keys
Output:
Printing the hashtable values
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='English'; Marks=80}
$hash.values
Output:
Searching for specific items
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths'; Marks=80}
If ($hash.Subject -eq ‘Maths’) {Echo ‘OK’}
Output:
Here, if the “Subject” key-value matches with ‘Maths’, the output is ‘OK’.
For partial matches, .ContainsKey or .ContainsValue methods are used.
$hash.ContainsKey(‘Subject’)
This will return True as output since Key matches with ‘Subject’.
$hash.ContainsKey('Date')
This will return False as output since Key does not match with ‘Date’.
$hash.ContainsValue(‘Maths’)
This will return True as output since Value matches with ‘Maths’.
$hash.ContainsValue('Physics')
This will return False as output since Value does not match with ‘Physics’.
You can also check if the particular key exists or not.
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths'; Marks=80}
If ($hash.Subject) {Echo ‘OK’}
Output:
Sorting Keys and Values
- Hashtable entries are unsorted by default.
- Each time you print the key/value, the order might appear different.
- Since it is always convenient to work with the sorted list of data, you can sort the hashtable key/value pairs in Powershell, though you can not sort the hashtable itself.
- GetEnumerator method is used to enumerate the keys and values
- Then, Sort-Object cmdlet is used to sort the enumerate values for printing.
Let us understand this through an example.
Code:
$hash.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object -Property key
Output:
In the above example first, the keys and values in the hashtable are enumerated In the $hash variable and then keys are sorted in alphabetical order.
- To sort the hashtable values in descending order, let us see the below example. It is done a similar way as above, only you need to add “Descending” in the cmdlet.
Code:
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths';Marks=80}
$hash.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object -Property key -Descending
Output:
Splatting Through a Hashtable
- Method of supplying parameters to a command as a unit using a dictionary or a list.
- It is helpful in cases when you need to specify a lot of parameters which makes your command lengthy and you end up scrolling off the screen or try wrapping it up to make it readable.
- With splatting, instead of providing all the parameters in one line stretching all across the screen, you can use an array or a hashtable which is much easier to read.
- Splatting makes code reading easier by providing a clean and concise format Let us understand this through a very simple example.
Code:
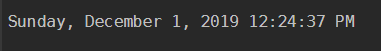
$splat= @{year = 2019; Month = 12; day=1}
get-date @splat
Output:
Note:$sign in variable name $splat becomes an @sign while executing the command
Use of @sign instead of $sign invokes the splat operation.
Looping through a Hashtable
Let us with the help of the below example:
1. Using ForEach
Code:
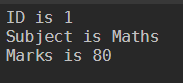
$hash=[ordered]@{ID=1; Subject='Maths';Marks=80}
foreach
($key in $hash.keys)
{
$message = '{0} is {1}' -f $key, $hash[$key]
Write-Output $message
}
Output:
Here, we are moving through each key in the hashtable and accessing the
value using it
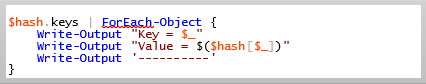
2. Using ForEach-Object
Code:
Output:
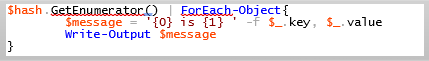
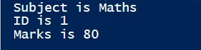
3. Unwrapping the hashtable object with GetEnumerator()
Code:
Output:
Here, each key-value pair passes through the pipeline. The main purpose of using the GetEnumerator() method is to unwrap the PowerShell object into its individual elements.
Conclusion – Hashtable in PowerShell
In this article, we touched upon some important aspects of a hashtable in Powershell.
To summarize:
- Hashtable is a lightweight data structure used as an associative array to map keys to values.
- It is a structured and effective way of finding and retrieving data.
- Can store lists.
- Can create calculated properties in PowerShell.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Hashtable in PowerShell. Here we discuss How does Hashtable work in PowerShell along with the Sorting Keys and Values. You may also look at the following article to learn more –