Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to OSI Model and TCP/IP Model
The two most commonly used communication network models are TCP / IP and OSI. Many similarities and differences between them are here. The main differences are that the conceptual model is OSI which is not practical for communication, while TCP / IP is used for connection establishment and network communication. TCP / IP follows the horizontal approach, and the OSI model supports a vertical approach. For every network, including the Internet, TCP / IP is the standard protocol, whereas OSI is not a protocol but a benchmark model for understanding and design.
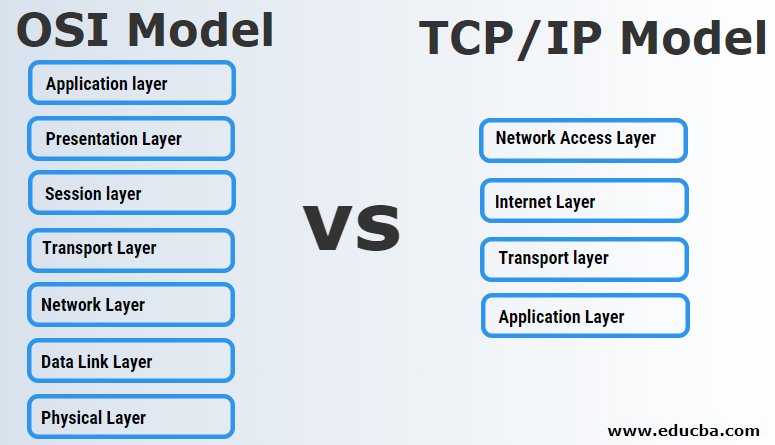
OSI Model
The OSI Model is a conceptual model developed by the International Organization for Standardization that allows various communication systems to communicate through standard protocols.
- Application layer: This is the only layer that interacts directly with user data. However, it should be noted that software applications are not components of the application layer; the application layer is accountable for protocols and information manipulation on which the software users are relying to obtain significant information.
- Presentation Layer: The primary task of this layer is to prepare the information so that the application layer can be used; that is to say, that layer 6 makes the information available for consumption apps. Two communicators may use different encryption methods to communicate so that the incoming data is converted to a syntax that the receiving device application layer can understand.
- Session layer: This is the layer used to open and close the communication between the two machines. The period between the opening and closing of the correspondence is known as the session.
- Transport Layer: Flow Control and error control is responsible for this layer. The transportation layer checks the receiving end for errors in ensuring the received data’s completeness and requests retransmission if not.
- Network Layer: The network layer allows the transfer of information between two distinct networks. The network layer also identifies the best physical route for the information to reach its destination.
- Data Link Layer: The data link layer collects packets from the layer and breaks them into smaller parts. Like the network layer, the flow control and error control in interconnected communication are responsible for the data link layer.
- Physical Layer: This layer contains physical devices, such as wires and switching, involved in information transfer. This is also the string of 1s and 0s, where the information becomes a bitstream.
TCP/IP Model
Internet Protocols are the rules set established for network communication. TCP/IP is considered a robust networking protocol model.
It is the condensed version of the OSI Model.
- Network Access Layer: Network Access Layer is the combination of Data Link Layer and Physical Layer available in the OSI model. Physical Addressing is done in this layer, i.e. MAC Address of source and destination is assigned to the data packets. Hence this layer is responsible for the physical transmission of data.
- Internet Layer: The Internet layer is used to send an independent packet to a network to the destination. All the machines, Web servers, nodes that are attached to the TCP/IP network are assigned in this layer.
- Transport layer: It allows the information to be delivered in an information chart format from the source to the destination host without defects.
- Application Layer: The application layer performs the OSI model’s tasks in three layers: Application, Presentation and Session Layer. It is required for the interaction between node and node and handles the requirements of the user interface. The application layer protocols are TFTP, HTTP, Telnet, SSH, NTP, DNS, NFS, FTP, SNMP, DHCP, SMTP.
Head to Head Comparison between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model(Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model.
Key Differences Between OSI Model and TCP/Ip Model
Let us discuss some of the major differences between the OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model.
- The horizontal approach is known to the OSI, and the vertical approach is called the TCP/IP approach.
- OSI is protocol-independent and generic, while TCP/IP has normal laws that support Internet development.
- As compare to OSI model TCP/IP model is more reliable.
- Packages are supplied to the OSI transport layer, whereas in the event of TCP/IP, this is not sure.
- In the OSI model, a presentation and session layer is available, while the TCP/IP model does not contain such a layer.
- TCP/IP implements the features that operate the system, OSI helps guide the network and serves as reference tools
- TCP/IP offers network-level connectivity facilities, whereas the OSI network layer offers both connection and connectionless services.
- No other model is TCP/IP, while OSI is attempting to match other model designs because it is a reference.
- Protocols can be easily terminated; while the original rules are in the TCP/IP model, new ones can be introduced in the OSI model.
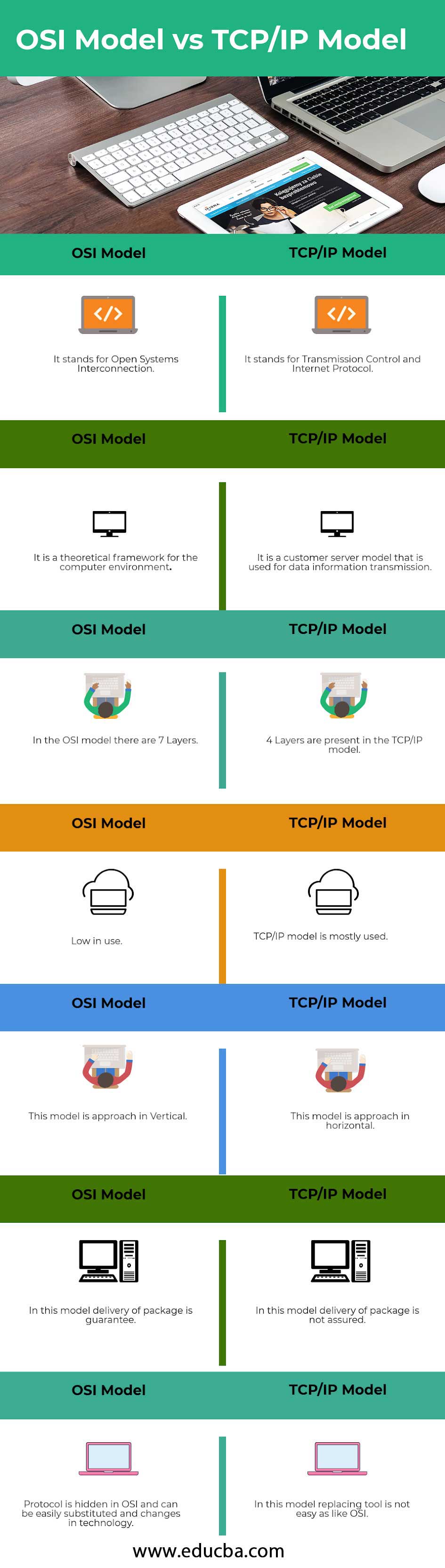
OSI Model and TCP/IP Comparison Table
Let us discuss the topmost differences between OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model.
| OSI Model | TCP/IP Model |
| It stands for Open Systems Interconnection. | It stands for Transmission Control and Internet Protocol. |
| It is a theoretical framework for the computer environment. | It is a customer service model that is used for data information transmission. |
| In the OSI model, there are 7 Layers | 4 Layers are present in the TCP/IP model |
| Low in use | TCP/IP model is mostly used |
| This model is an approach in Vertical | This model is an approach in horizontal |
| In this model, delivery of package is a guarantee | In this model, delivery of package is not assured |
| The protocol is hidden in OSI and can be easily substituted and changes in technology. | In this model, replacing tool is not easy as like OSI |
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen differences between both. TCP/IP is widely used to convey information via the internet from beginning to end. Hence, we can conclude that TCP/IP is more robust, flexible than the OSI model and indicates how information should be transmitted over the Internet.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –