Updated June 29, 2023
Difference Between Predictive Analytics vs Data Mining
Predictive analytics is the process of refining that data resource, using business knowledge to extract hidden value from those newly discovered patterns. Data mining is the discovery of hidden data patterns through machine learning — and sophisticated algorithms are the mining tools.
Data mining + Domain knowledge => predictive analytics => Business Value
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Predictive Analytics and Data Mining
Below are the top 5 comparisons between Predictive Analytics and Data Mining:
Key Differences of Predictive Analytics vs Data Mining
Below is the difference between Predictive Analytics and Data Mining
Process – The process of Data Mining can be summarised into six phases-
- Business/Research Understanding Phase – Enunciate the project objectives and requirements in terms of the business or research unit as a whole
- Data Understanding Phase – Collect and use exploratory data analysis to familiarize yourself with the data and discover initial insights.
- Data Preparation Phase – Clean and apply a transformation to raw data so that it is ready for the modeling tools.
- Modeling Phase – Select and apply appropriate modeling techniques and calibrate model settings to optimize results.
- Evaluation Phase – Models must be evaluated for quality and effectiveness before we deploy. Also, determine whether the model achieves its objectives in phase 1.
- Deployment Phase – Using models in production might be a simple deployment, like generating a report, or a complex one, like Implementing a parallel data mining process in another department.
High-level steps in the Predictive Analytics process area:
- Define Business Goal – What business goal will be achieved, and how does data fit? For example, the business goal is more effective offers to new customers, and the data needed is the segmentation of customers with specific attributes.
- Collect Additional Data – Additional data needed might be user profile data from online systems or data from third-party tools to understand data better. This helps to find a reason behind the pattern. Sometimes Marketing surveys are conducted to collect data.
- Draft Predictive Model – Model created with newly collected data and business knowledge. A model can be a simple business rule like “There is a greater chance to get convert the users from age a to b from India if we give an offer like this” or a complex mathematical model.
Business Value – Data Ming itself adds value to business-like.
- Deeply understand customer segments across different dimensions.
- Get performance patterns specific to KPIs (Eg. Is subscription increasing with active users count?)
- Identify Fraudulent activity attempts and prevent them.
- System performance patterns (Eg -Page loading time across different devices – any pattern?)
Predictive analytics empowers organizations by providing three advantages:
- Vision – Helps to see what is invisible to others. Predictive analytics can go through a lot of past customer data, associate it with other pieces, and assemble them in the right order.
- Decision – A well-made predictive analytics model provides analytical results free of emotion and bias. It provides consistent and unbiased insights to support decisions.
- Precision – Helps to use automated tools to do the reporting job for you — saving time and resources, reducing human error, and improving precision.
Performance Measure – The performance of the Data Mining process is measured by how well the model finds patterns in data. It will usually be a regression, classification, or clustering model, and there is a well-defined performance measure for all these.
The performance of predictive analytics is measured on business impact. For example – How well the targeted ad campaign work compared to a general campaign? No matter how well data mining finds patterns, business insight is a must to work predictive models well.
Future – The data Mining field is evolving very fast. Trying to find patterns in data with lesser data points with a minimum number of features with the help of more sophisticated models like Deep Neural Networks. Many pioneers in this field, like Google, are also trying to make the process simple and accessible to everyone. One example is Cloud AutoML from Google.
Predictive analytics is expanding to various areas like Employee Retention prediction, Crime Prediction (predictive policing), etc. At the same time, organizations try to predict more accurately by collecting maximum information about users, like where they are going, what type of videos they watch, etc.
Predictive Analytics and Data Mining Comparison Table
Below are the lists of points that describe the comparisons between Predictive Analytics and Data Mining.
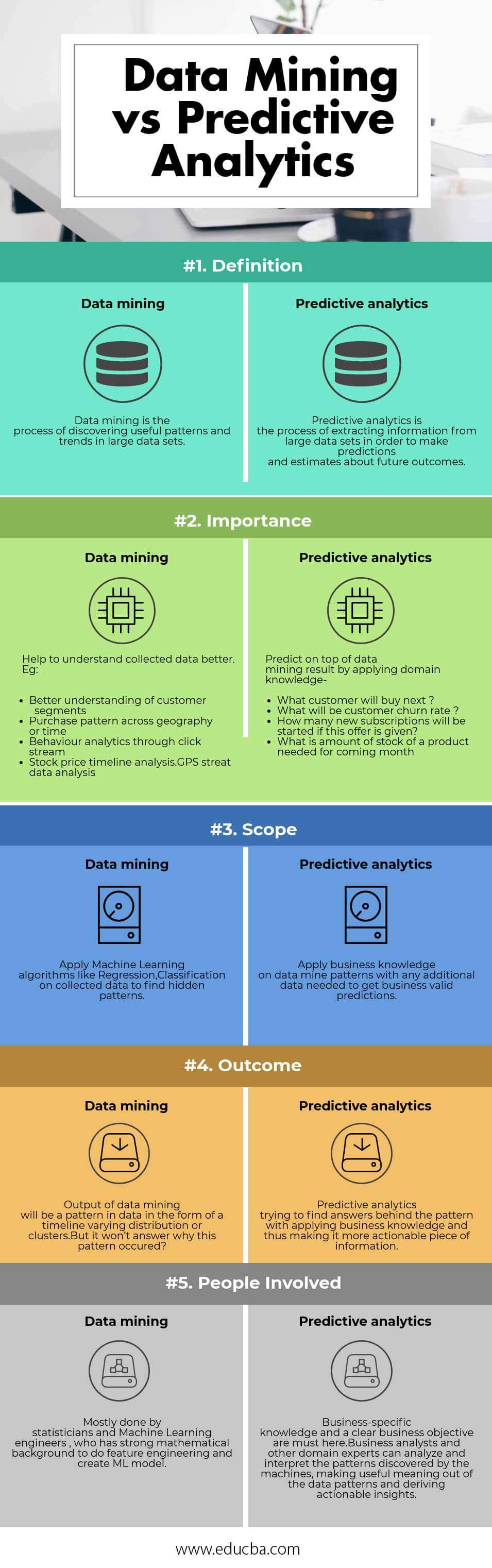
| Basis of Comparison | Data Mining | Predictive Analytics |
| Definition | Data mining is discovering useful patterns and trends in large data sets. | Predictive analytics is extracting information from large datasets to predict and estimate future outcomes. |
| Importance | Help to understand collected data better. E.g.:
|
Predict on top of data mining results by applying domain knowledge –
|
| Scope | Apply Machine Learning algorithms like Regression, Classification to collect data to find hidden patterns. | Apply business knowledge on data-mine patterns with any additional data needed to get business-valid predictions. |
| Outcome | The output of data mining will be a pattern in data in the form of a timeline with varying distributions or clusters. But it won’t answer why this pattern occurred. | Predictive analytics tries to find answers to the pattern by applying business knowledge and thus making it a more actionable piece of information. |
| People Involved | Done mainly by statisticians and Machine Learning engineers who have a strong mathematical background to do feature engineering and creating ML models. | Business-specific knowledge and a clear business objective are a must here. Business analysts and other domain experts can analyze and interpret the patterns discovered by the machines, making useful meaning out of the data patterns and deriving actionable insights. |
Conclusion
As Rick Whiting said in InformationWeek, What’s next is what’s next. Predictive analytics is where business intelligence is going. Data Mining helps organizations in many ways, and one of the most important is creating a good foundation for Predictive Analytics.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Predictive Analytics vs Data Mining” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.