Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to ORDER BY in Oracle
‘ORDER BY’ in Oracle is a keyword or clause used to sort the data being queried in ascending or descending orders, where ASC is added at the end of the ORDER BY clause for arranging in Ascending order and DESC for Descending order. If the order is not mentioned, that is an ORDER BY clause without ASC or DESC, the system returns the results in ascending order by keeping it as the default sort order. This conditional clause can be applied on a SELECT statement after the main query, with or without a WHERE condition.
Syntax:
SELECT columns/expressions FROM tables
[where conditions]
ORDER BY column/expression [DESC/ASC];
Parameters
Below are some of the important parameters of order by in oracle:
- columns/expression: The column names or any other calculations based on expressions(aggregate functions) we want to retrieve.
- tables: Name of the tables from where we want to retrieve the details.
- [where conditions]: It is an optional clause. If it is provided then the query will retrieve only those records which satisfy the condition mentioned in the WHERE clause.
- DESC: To order the result set in descending order.
- ASC: To order the result set in ascending order.
One important point to note that in case the modifier (ASC/DESC) is not mentioned than the default modifier will be ASC (ascending order).
How does ORDER BY Work in Oracle?
In the database, the data is not stored in order while inserting in the table so when we extract records from the database and we want the records to be displayed in any order numerically or alphabetically then we will have to specifically mention it to the oracle database. So, in order to do that, we will have to use the ORDER BY clause. The ORDER BY clause is used to rearrange the extracted data into a specific order as per the user’s wish. One more point to mention is that we can sort the records based on multiple columns where each column may also have different sort orders. The ORDER BY clause is always the last clause mentioned in the SELECT query.
In the above point, we discussed the working and need for the ORDER BY clause. Now we will look at some examples with screenshots to learn more about the ORDER BY clause in the oracle database.
Examples to Implement ORDER BY in Oracle
To have a more clear understanding of the topic we are going to look at a few examples.
Example #1
This is the example of sorting rows in ascending order by a column. For example in our oracle database, we have a table named employee which has six columns and we want to get the employee id and name of the employee but we also want the result set to be sorted in ascending order based on the name of the employee. In that case, we are going to write the below query using the ORDER BY clause.
Query:
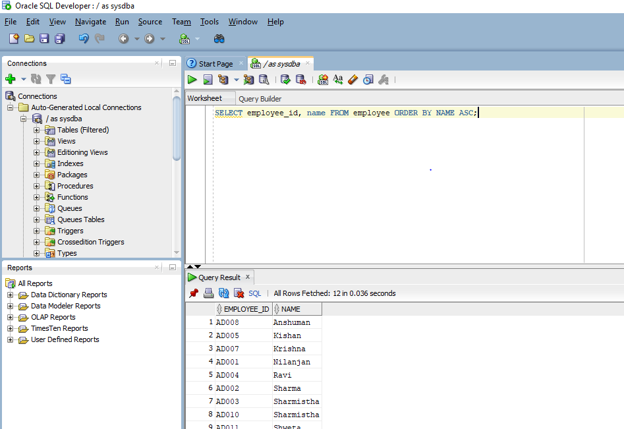
SELECT employee_id, name FROM employee ORDER BY NAME ASC;
To get the desired result we have given the column name as well as the sorting method at the end of the select query. ASC stands for ascending order. Let us now run the above query in SQL developer to see the output.
Output:
As we can see from the output the result set is sorted in ascending order based on the name column of the employee table.
Example #2
This is the example of sorting rows in descending order by column. Like the previous example, we are going to use the same table employee which has six columns but this time we want to get the employee id and name of the employee sorted in descending order based on the name of the employee. We are going to write the below query using the ORDER BY clause.
Query:
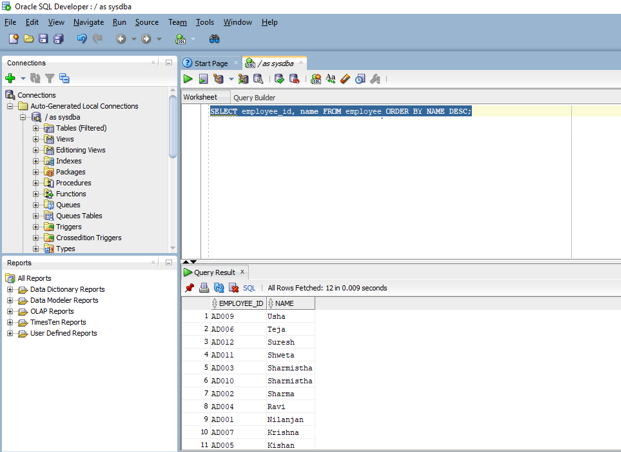
SELECT employee_id, name FROM employee ORDER BY NAME DESC;
To get the desired result we have given the column name as well as the sorting method at the end of the select query. DESC stands for descending order. Let us now run the above query in SQL developer to see the output.
Output:
We can see from the output that the result set is sorted in descending order based on the name.
Example #3
This is the example of sorting rows based on the column position in the table. In this case, we will do the previous operation with a little bit of change. In this example, we will not name the column on whose basis we want to do the sorting instead we will provide the position of the column present in the select list expression and then mention the type of sorting. For now, we will do an ascending order. Let us look at the query.
Query:
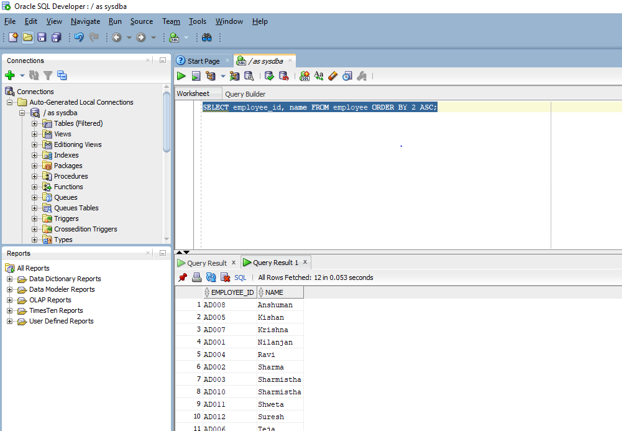
SELECT employee_id, name FROM employee ORDER BY 2 ASC;
As you can see the name is written second in the select list expression hence we have given the position as 2. Let us now run the above query in SQL developer.
Output:
As you can see the result set is sorted based on name in ascending order.
Example #4
This is the example of sorting based on function or expression. In the previous examples, we saw how to use the ORDER BY clause to sort using names or positions of columns. In this example we will see how we can use the ORDER BY clause with functions like UPPER(), LOWER() functions or even mathematical functions. For this example, we will use the UPPER() function to sort the names case-insensitively because we all know that it converts all letters into uppercase.
Query:
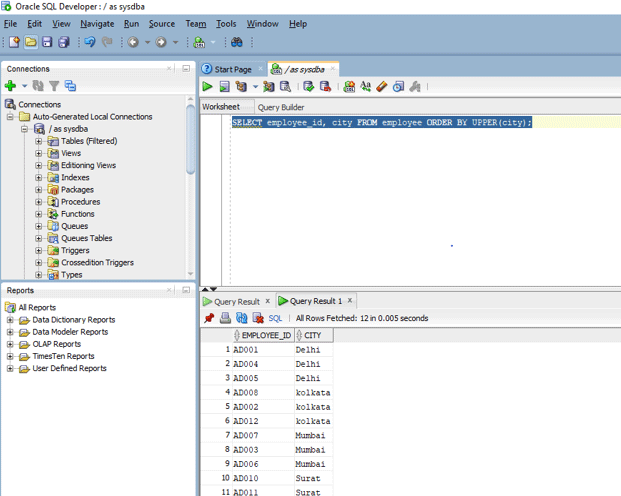
SELECT employee_id, city FROM employee ORDER BY UPPER(city);
As you can see we have put the UPPER() function after the ORDER BY clause instead of any column or expressions. Now let us run this query in oracle SQL developer.
Output:
As we can see the output is the case–insensitive as we have used the UPPER() function because it converts all cases into upper case.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about what is ORDER BY clause and its Syntax. We also learned about how it works and we went through various examples depicting various scenarios where we can use the ORDER BY clause.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ORDER BY in Oracle. Here we discuss syntax, parameters, and working of ORDER BY in Oracle along with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-