Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Joins in Oracle
Oracle join is used in queries to join two or more tables, columns or views based on the values of related columns of both the tables. For example, primary key of the first table and foreign keys of the second table are related columns to extract relevant data from database and again based on the requirements joins can be inner join, outer join, left outer join, right outer join, self join and all of these joins are supported in Oracle database.
Types of Joins in Oracle
In Oracle there are ten different types of joins are as given below:
- Inner Joins (also known as Simple Joins)
- Equi Joins
- Outer Joins
- Left Outer Joins (also called as Left Joins)
- Right Outer Joins (also called as Right Joins)
- Full Outer Joins (also called as Full Joins)
- Self Joins
- Cross Joins (also called as Cartesian Products)
- Anti Joins
- Semi Joins
Next, we understand each joins in detail with the syntax and examples.
1. INNER JOIN (also known as Simple Join)
Inner joins join the multiple tables and return those rows for which the join condition is true. The inner join is the most common join among the types of join.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1
INNER JOIN t2
ON t1.column = t2.column;
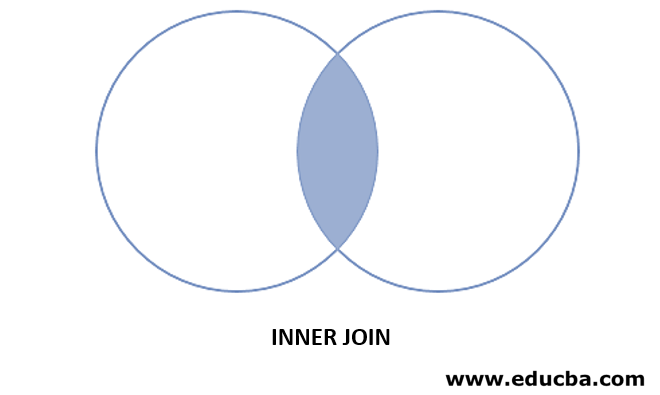
The below diagram represents the visual representation of the inner join, as in the diagram the shaded area return as the result of the Oracle INNER JOIN:
The Oracle INNER JOIN returns the intersect records of t1 and t2 as a result.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department. department_name
FROM employee
INNER JOIN department
ON employee.employee _id = department.employee _id;
This above Oracle INNER JOIN example will return all rows from the employee and department tables where the employee _id value in both the employee and department tables are matching.
2. Equi Joins
Oracle Equi Joins retrieves the matching column values of the multiple tables. The join condition or the comparison operator present in the WHERE clause of the select statement.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1 , t2
where t1.column = t2.column;
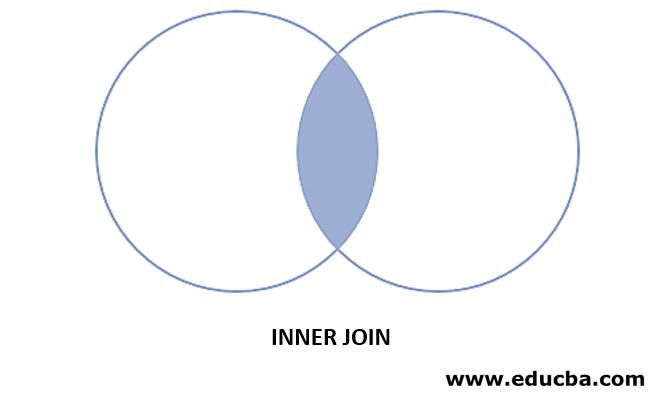
The below diagram represents the visual representation of the equijoin, as in the diagram the shaded area return as the result of the Oracle Equi Join.
The Oracle Equijoin returns the intersect records of t1 and t2 as a result.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department. department_name
FROM employee , department
where employee.employee _id = department.employee _id;
This above Oracle Equijoin example will return all rows from the employee and department tables where the employee _id value in both the employee and department tables are matching.
3. Outer Joins
Another type of joins is an outer join which returns a result of an inner join plus all the rows from one table for which the join condition is not true.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1
LEFT | RIGHT | FULL [OUTER] JOIN t2
ON t1.column = t2.column;
There are three types of outer join as given below:
- Left Outer Joins (also called as Left Joins)
- Right Outer Joins (also called as Right Joins)
- Full Outer Joins (also called as Full Joins)
4. Left Outer Join
The Left Outer Join returns contain all rows from the LEFT table ( according to the specified in ON condition) and from the other table only those rows where the joined condition is true.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1
LEFT [OUTER] JOIN t2
ON t1.column = t2.column;
The LEFT OUTER JOIN keyword, use a LEFT JOIN in some other databases.
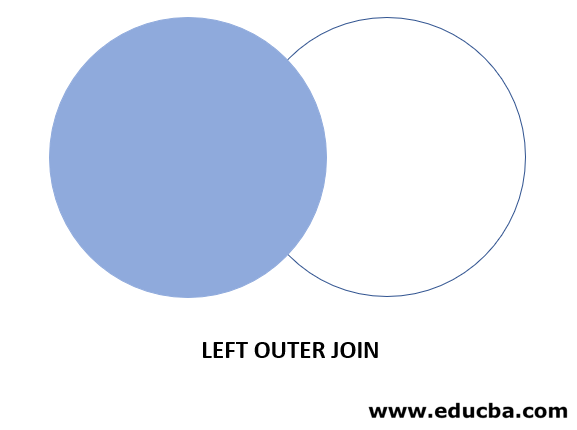
The below diagram represents the visual representation of the LEFT OUTER JOIN, as in the diagram the shaded area return as the result of the Oracle LEFT OUTER JOIN:
The Oracle LEFT OUTER JOIN returns all the records from t1 and the intersect records of t1 and t2 as a result.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department.department_name
FROM employee
LEFT OUTER JOIN department
ON employee.employee _id = department.employee _id;
This above Oracle LEFT OUTER JOIN example will return all rows from the employee table and from the department table only those rows where the joined condition is true. The department tables where the employee _id value in both the employee and department tables are matching.
If the employee _id value in the employee table does match in the department table, then the fields of the department table will be null in the result.
5. Right Outer Join
The RIGHT OUTER JOIN returns contain all rows from the RIGHT table (according to the specified in ON condition) and from the other table only those rows where the joined condition is true.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1
RIGHT [OUTER] JOIN t2
ON t1.column = t2.column;
The RIGHT OUTER JOIN keyword, use as RIGHT JOIN in some other databases.
The below diagram represents the visual representation of the RIGHT OUTER JOIN, as in the diagram the shaded area return as the result of the Oracle RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
The Oracle RIGHT OUTER JOIN returns all the records from t2 and the intersect records of t1 and t2 as a result.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department.department_name
FROM employee
RIGHT OUTER JOIN department
ON employee.employee _id = department.employee _id;
This above Oracle LEFT OUTER JOIN example will return all rows from the department table and from the employee table only those rows where the joined condition is true. The employee tables where the employee _id value in both the employee and department tables are matching.
If the employee _id value in the employee table does match in the department table, then the fields of the employee table will be null in the result.
6. Full Outer Join
The Full Outer Join returns contain all rows from the LEFT table and RIGHT table with null in fields where the join condition is not true.
Syntax:
SELECT column [ , column ]
FROM t1
FULL [OUTER] JOIN t2
ON t1.column = t2.column;
The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword, use as FULL JOIN in some other databases.
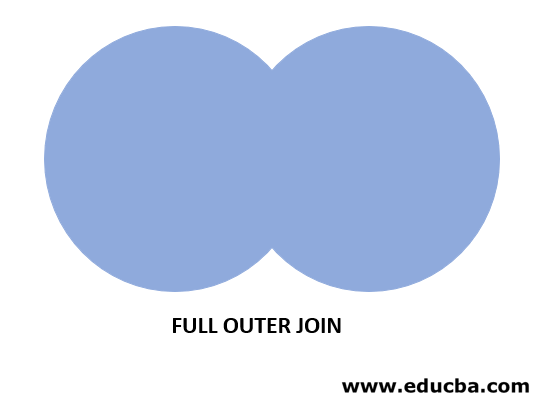
The below diagram represents the visual representation of the FULL OUTER JOIN, as in the diagram the shaded area return as the result of the Oracle FULL OUTER JOIN.
The Oracle FULL OUTER JOIN returns all the records from t1 and t2 tables as a result.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department.department_name
FROM employee
FULL OUTER JOIN department
ON employee.employee _id = department.employee _id;
This above Oracle FULL OUTER JOIN example will return all rows from the employee table and from the department table with null values where the joined condition is not true.
7. Oracle Self Joins
In self join the table uses twice in the FROM clause with the help of table aliases name. In other words, the self joins, join a table itself. The Oracle Self Join combines and returns rows of the table where the join condition is true.
Example:
SELECT emp1.employee_name || ‘works for’ || emp2.employee_name
FROM employees emp1, employees emp2
WHERE emp1.manager_id = emp2.employee_id
ORDER BY emp1.employee_name;
This above Oracle self JOIN example will return all rows from the employee table where the joined condition is true.
8. Oracle Cross Joins (also called as Cartesian Products)
Cross join applies where the two tables have no join condition.the cross join return the Cartesian product of the two tables, Cartesian product where each row of one table combines with each row of the other table. Suppose table1 contains 100 rows and table2 contains 10 rows then the join result would contain 1000 rows.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department.department_name
FROM employee
CROSS JOIN department
This above cross JOIN example will return all rows of employee table combine with all rows of the department table.
9. Oracle Anti Joins
The antijoin returns contain rows from the LEFT table ( according to the specified in ON condition) where the joined condition is true.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name, department.department_name
FROM employee
WHERE department_id NOT IN (SELECT department_id from department
WHERE department_name = ‘sales’;
This above Oracle ANTI JOIN example will return rows from the employee table and where the joined condition is true.
10. Oracle Semi Joins
The semijoin returns contain unique rows from the LEFT table ( according to the specified in ON condition) where the match an EXISTS subquery is true.
Example:
SELECT employee.employee _id, employee.employee_name
FROM employee
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT department_id FROM department
WHERE department_name = ‘sales’);
This above Oracle SEMI JOIN example will return rows from the employee table if the EXISTS returns true.
Conclusion
It is used to accessing the data from multiple tables. There are seven different types of joins in an Oracle.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Joins in Oracle. Here we discuss an introduction and its 10 different types in Joins in Oracle respectively. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –