Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Select in Oracle
Oracle is one of the most extensively used databases in the industry. The most commonly used query is a SELECT query. This query is used to retrieve data from one or more tables in the database. A SELECT query is not just used alone but with it, many conditions, clauses and inner queries are used to get data from databases in the industry. SELECT query does not manipulate any data in the table on which it is executed. Select keyword in oracle is applied for fetching a set of data, which can be used singly or by combining other conditional statements as filters. When a select statement is as ‘SELECT * from <Table_Name>’, the whole table is displayed as the result-set, whereas select statement as ‘SELECT Column_1, Column_2 from <Table_Name>’ displays the contents of only the column_1 & column_2 of ‘<Table_Name>’. ‘Where’, ‘Group By’, ‘Order By’ conditions can also be applied at the end of the Select statement.
Syntax:
SELECT expressions
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions];
The first two lines in the syntax is a compulsory part of syntax but [WHERE conditions] is optional as it is used if we want to extract data from one or more tables based on some conditions. The ‘expressions’ in the syntax represents columns of the table. If we want to extract all fields from the table we put ‘*’ in place of ‘expressions’ in the syntax otherwise we put the column names.
Examples to Implement Select in Oracle
Below are the different examples of select in oracle:
1. SELECT all fields without WHERE condition
To select all fields from tables: We will use ‘*’ character to signify that we want to extract all fields from a particular table.
Query:
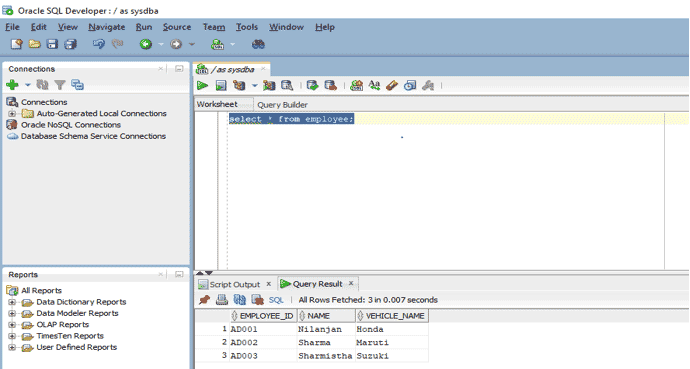
SELECT * from employee;
This query will fetch all the records from the table as there is no condition clause attached to it.
Output:
2. SELECT all fields with WHERE condition
We will now use where condition on the same earlier used query. In this query, we only want the details of a particular employee. To achieve this we will use the where condition. let us look at the query
Query:
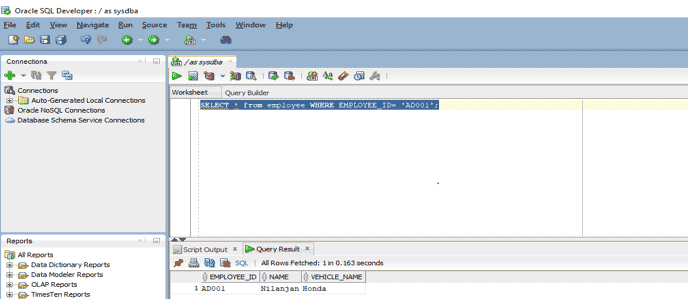
SELECT * from employee WHERE EMPLOYEE_ID= 'AD001';
We are using EMPLOYEE_ID in this query as it is the primary key in this table and so it is unique.
Output:
3. SELECT a single field from a table
In this example, we are going to use a SELECT statement to select a few fields but not all fields from a table. Let us look at the query.
Query:
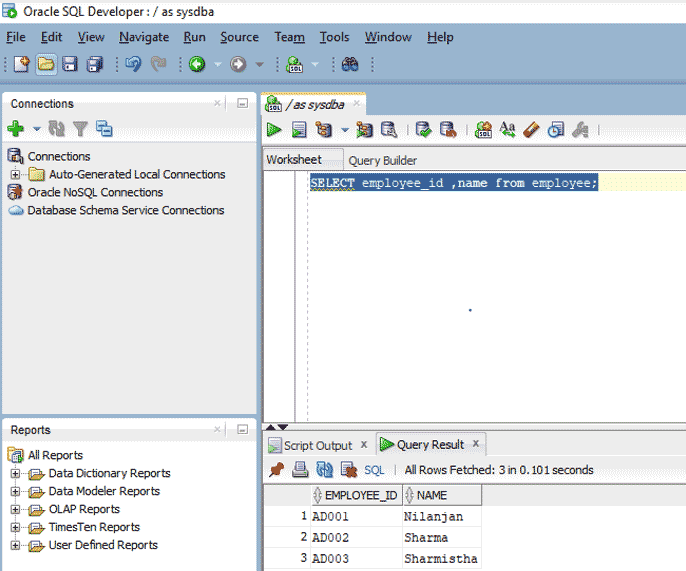
SELECT employee_id, name from employee;
This query will display only two columns because we have not used ‘*’ after SELECT in this query.
Output:
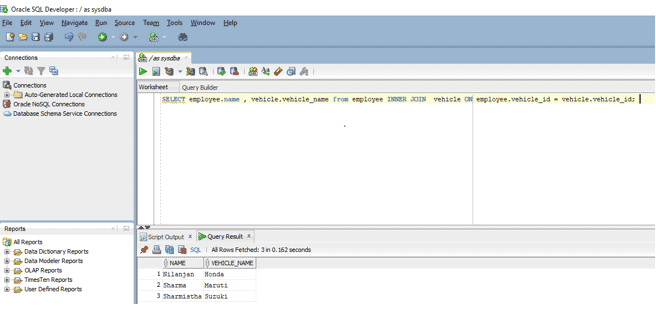
4. SELECT fields from multiple tables
In this example, we are going to use a SELECT statement to retrieve data from more than one table using JOIN. Let us look at the query.
Query:
SELECT employee.name, vehicle.vehicle_name from employee INNER JOIN vehicle ON employee.vehicle_id = vehicle.vehicle_id;
Here in this query, we are using the SELECT statement which joins two tables based on the condition that vehicle id from employees table should match vehicle id from the vehicle table. The query displays the employee name from the employee table and vehicle name from the vehicle table.
Output:
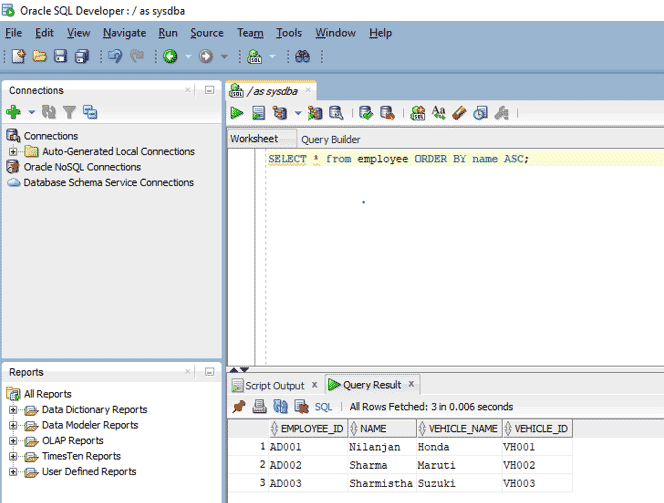
5. Display records in order using SELECT
We can also display particular records in ORDER which can be ascending or descending by using the ORDER BY clause with the query. We will look at both ascending and descending order queries.
a. Query for ascending order
SELECT * from employee ORDER BY name ASC;
In this query we are displaying all records and the result set is sorted by name in ascending order.
The below screenshot shows the output when query is executed in SQL Developer.
Output:
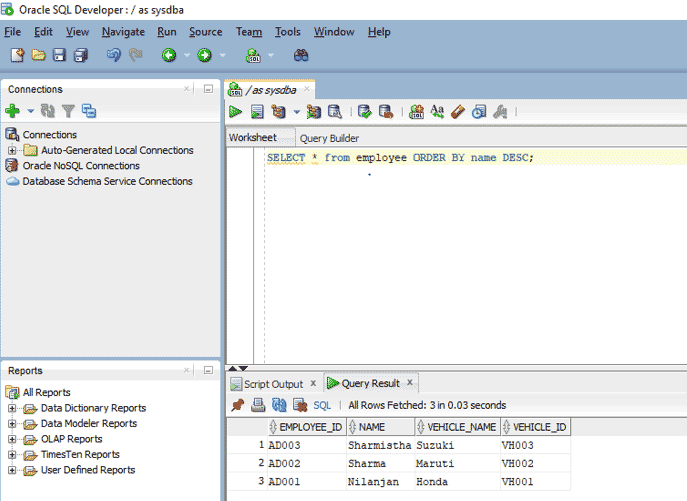
b. Query for descending order
SELECT * from employee ORDER BY name DESC;
In this query, we are displaying all records from the table and the result set is sorted by name in descending order
The below screenshot shows the output when query is executed in SQL Developer.
Output:
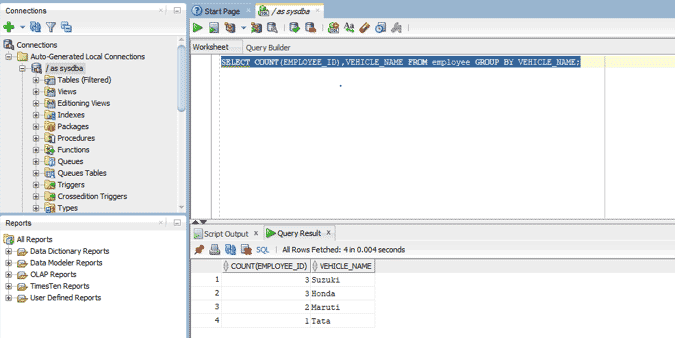
6. SELECT query with GROUP BY clause
We use the GROUP BY clause with SELECT statement when we want to get records based on groups. So basically it groups rows that have the same values. It is used generally in conjugation with aggregate functions. It is useful in producing summary reports.
We will now look at an example to see how we can use GROUP BY with SELECT statement in oracle database.
Query:
SELECT COUNT(EMPLOYEE_ID),VEHICLE_NAME FROM employee GROUP BY VEHICLE_NAME;
So in the above example basically we are finding the number of employees using a particular brand of car. GROUP BY groups the records based on the type of car and then we use aggregate function COUNT to calculate the number of employees in each group by using the column employee_id as it is the primary key of the table.
Output:
7. SELECT query with the HAVING clause
The having clause is used with a select statement where we want to have some conditions as where keyword cannot be used directly with aggregate functions. That is the reason the having clause was added in SQL. We are going to see an example of how we can use the having clause with a select statement.
Query:
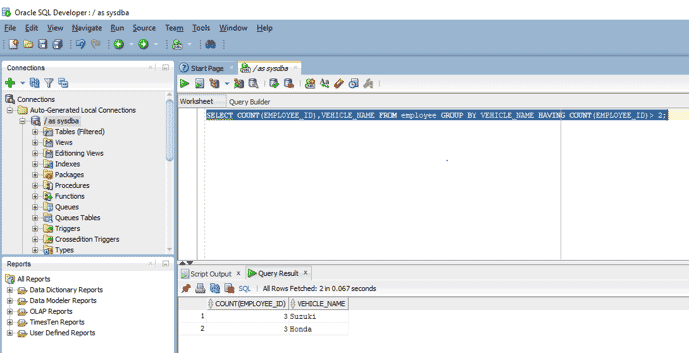
SELECT COUNT(EMPLOYEE_ID),VEHICLE_NAME FROM employee GROUP BY VEHICLE_NAME HAVING COUNT(EMPLOYEE_ID)> 2;
As we can see that we have added the HAVING clause with the GROUP BY due to which we are able to put a condition that only vehicles with employees more than two are to be displayed. This is where the HAVING clause becomes useful.
Output:
If we see the output we get only two records instead of five which we got when we used GROUP BY function.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned the syntax and the reason why we use SELECT and also the various ways in which we can write a SELECT query in SQL and also where and for what reason we should use them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Select in Oracle. Here we discuss the introduction and different examples of select query in SQL with syntax. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –