Updated May 3, 2023
Introduction to Aggregate Function in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL aggregate functions are used to compute the set of input values in one result. It produced a single result for an entire group of tables. PostgreSQL aggregate functions are used to create a summarized set of results. They return results based on a group of rows set. Aggregate functions will treat all table rows as a group by default. Like the group by clause of the select statement, the statement divides all rows into smaller groups or chunks. Aggregate functions support aggregating multiple rows in a single dataset. We can see a list of aggregate functions using the \df command.
Various Aggregate Functions in PostgreSQL
Below is the list of aggregate functions in PostgreSQL as follows.
- COUNT
- SUM
- MIN
- MAX
- AVG
Below is a detailed description of aggregate functions. Also, below is the syntax of aggregate functions. We have used the customer table as an example.
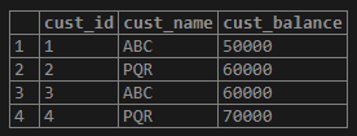
Customer table:
select * from Customer;select version();Syntax:
- Aggregate function using the expression:
aggregate_name (expression [... , ] [order_by_clause] )- Using ALL as an aggregate function:
aggregate_name (ALL expression [,...] [ order_by_clause] )- Aggregate function using DISTINCT clause:
aggregate_name (DISTINCT expression [,...] [ order_by_clause] )- Using the asterisk (*), perform an aggregate function:
aggregate_name (*)Below is the parameter description are as follows.
- Aggregate name: Name of the aggregate function.
- Expression: This is the value or value of a column in an aggregate function, which does not contain any aggregate expression.
- Order by the clause: It is optional used to set to arrange results in a set of orders.
1. Count Aggregate Function
- The count aggregate function in PostgreSQL returns the count of rows from a selected number of columns.
Syntax:
COUNT (* | DISTINCT ALL | Column_name)Below is the parameter description of syntax are as follows.
- Column name: Name of the column that we have used in the query to count the records’ values.
- Asterisk (*): The Asterisk (*) indicates all the rows, it will return the count of rows of the column which have been used in a query.
- DISTINCT: This clause is used to find unique values from the table; also, this parameter is optional.
- ALL: This is the default clause of the count aggregate function also; this is optional.
Example:
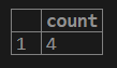
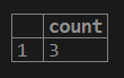
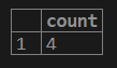
1. If we want to get a total count of rows from the customer table.
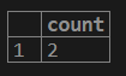
testing=# select COUNT (cust_balance) from customer;2. If we want to get a count of distinct rows for the customer balance column from the customer table.
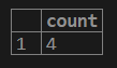
testing=# select COUNT (distinct(cust_balance)) from customer;3. If we want to get the count of rows for the cust_id column from the customer table.
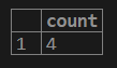
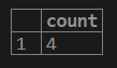
testing=# select count(cust_id) from customer;select count (*) from a customer;select count (1) from a customer;select count (cust_name) from customer;select count (distinct(cust_name)) from customer;2. SUM Aggregate Function
The sum aggregate function in PostgreSQL returns the sum of values from a selected number of columns. It will select a total of no numeric function and return a sum of all records.
Syntax:
SUM (* | DISTINCT ALL | Column_name)Below is the parameter description of syntax are as follows.
- Column name: Name of the column that we have used in the query to sum the records’ values.
- Asterisk (*): The Asterisk (*) indicates all the rows, it will return the sum of columns that have been used in a query.
- DISTINCT: This clause is used to find unique values from the table; also, this parameter is optional.
- ALL: This is a default clause of the SUM aggregate function; also, this is optional.
Example:
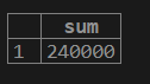
1. If we want to calculate the total sum of customer balance from the customer table.
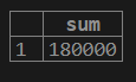
testing=# select SUM (cust_balance) from customer;2. If we want to calculate the distinct sum of customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select SUM(distinct(cust_balance)) from customer;3. MIN Aggregate Function
The Min function returns the result of the smallest value of all selected values of the column. It will select the lowest value from a selected column.
Syntax:
MIN (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | Column_name)Below is the parameter description of syntax are as follows.
- Column name: Name of the column that we have used in the query.
- Asterisk (*): The Asterisk (*) indicates all the rows, it will return all rows MIN value of tables.
- DISTINCT: This clause is used to find the unique smallest value from the table.
- ALL: This is the default clause of the MIN aggregate function also; this is optional.
Example:
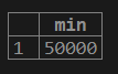
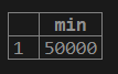
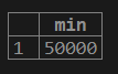
1. If we want to calculate the minimum value of customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select MIN (cust_balance) from customer;2. If we want to calculate the distinct minimum value of customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select MIN(distinct(cust_balance)) from customer;select MIN(ALL(cust_balance)) from customer;4. MAX Aggregate Function
MAX function returns the result of the largest value of all selected values of the column. It will select the largest value from the selected column.
Syntax:
MAX (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | Column_name)Below is the parameter description of syntax are as follows.
- Column name: Name of column.
- Asterisk (*): The Asterisk (*) indicates all the rows
- DISTINCT: This clause is used to find the unique largest value from the table.
- ALL: This is a default clause of the MAX aggregate function also; this is optional.
Example:
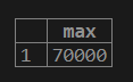
1. If we want to calculate the maximum customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select MAX (cust_balance) from customer;2. If we want to calculate a distinct maximum customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select MAX(distinct(cust_balance)) from customer;select MAX(ALL(cust_balance)) from customer;5. AVG Aggregate Function
AVG function returns the average of all selected values of the column.
Syntax:
AVG (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | Column_name)Below is the parameter description of syntax are as follows.
- Column name: Name of the column that we have used to calculate the average.
- Asterisk (*): The Asterisk (*) indicates all the rows
- DISTINCT: This clause is used to find a unique average value from the table.
- ALL: This is a default clause of the AVERAGE aggregate function also; this is optional.
Example:
1. If we want to calculate the maximum customer balance from the customer table.
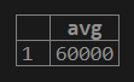
testing=# select AVG (cust_balance) from customer;2. If we want to calculate a distinct maximum customer balance from the customer table.
testing=# select AVG(distinct(cust_balance)) from customer;select AVG(ALL(cust_balance)) from customer;Conclusion
PostgreSQL aggregate function is handy for finding the result of tables. Mainly COUNT, MAX, MIN, AVG, and SUM functions are used in PostgreSQL. The aggregate function will support the aggregate no of columns in a table. The aggregate function will produce a single result for the entire group of tables.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Aggregate Functions in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.